A method for detecting biological activity of marine polysaccharides
A marine polysaccharide and biologically active technology, applied in the direction of analysis by electron paramagnetic resonance, can solve the problems of heavy workload, individual animal differences, and high capital consumption, and achieve improved stability, simple detection process, and wide detection range Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
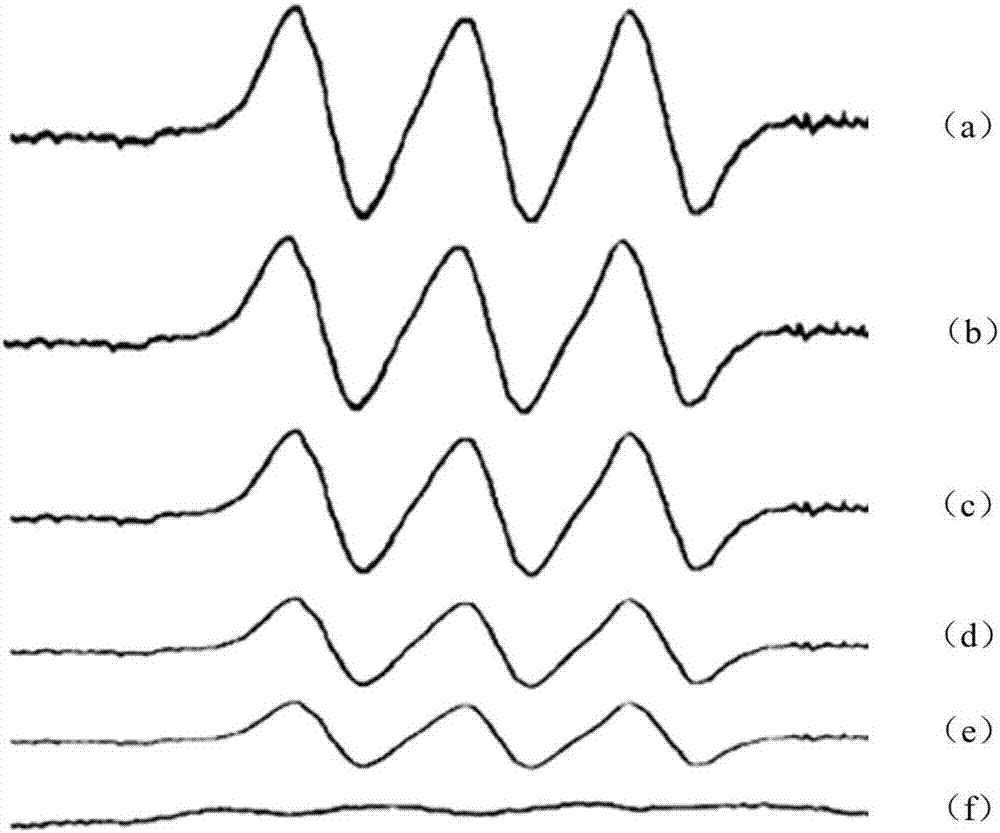
[0039] Example 1 Detection of Scallop Polysaccharides Regulating NO Production in Macrophages
[0040] Get the scallop polysaccharide sample, prepare 200 μg / mL scallop polysaccharide solution with DMEM medium or distilled water;
[0041] Adjust the RAW264.7 cell density to 10 with DMEM medium 5 ~10 6 a / mL;
[0042] The cells with adjusted density were placed in a 96-well cell culture plate and cultured at 37°C for 24 hours;
[0043] Add appropriate amount of scallop polysaccharide to the 96-well culture plate, so that the concentration of scallop polysaccharide is 0 μg / mL, 12.5 μg / mL, 25 μg / mL, 50 μg / mL, 100 μg / mL, 200 μg / mL;
[0044] 37°C, CO 2 Cultivate in a carbon dioxide incubator with a concentration of 5% for 48 hours;
[0045] Collect the cell supernatant;
[0046] Use the ESR method to detect the concentration of NO free radicals;
[0047] Add cell supernatant and NO radical scavenger (MGD) to the tube 2 -Fe 2+ (contains 10mmol·L -1 MGD and 2mmol·L -1 FeSO ...
Embodiment 2
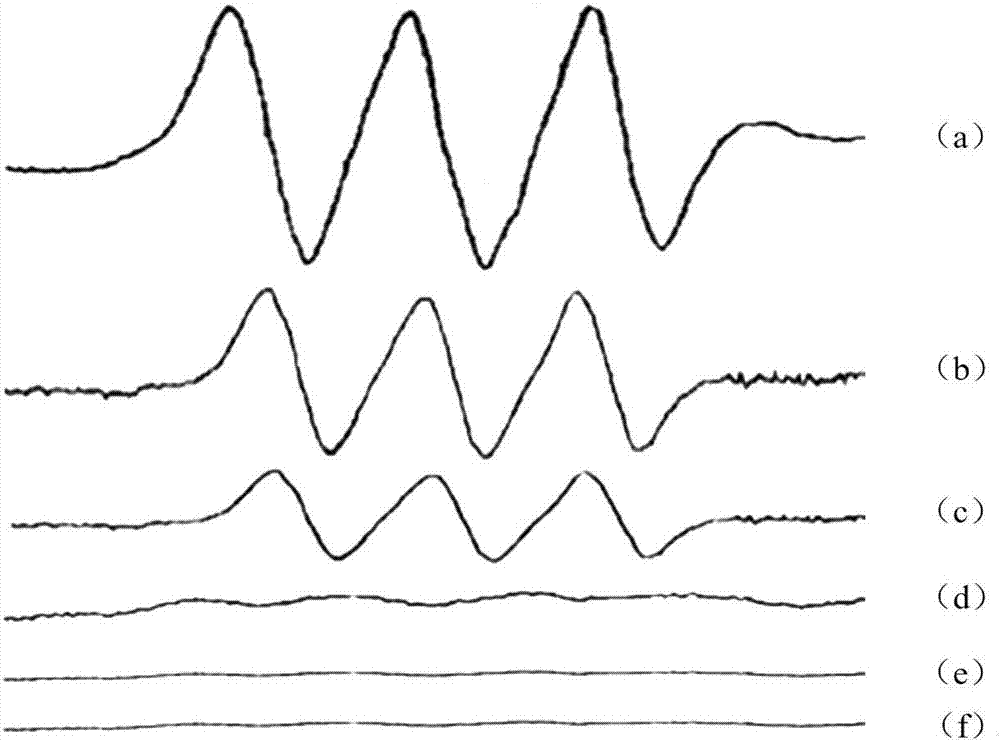
[0051] Example 2: detection of wakame sporophyll polysaccharides regulating NO production in macrophages
[0052] Get the wakame sporophyll polysaccharide sample, prepare 200 μg / mL wakame sporophyll polysaccharide solution with DMEM medium or distilled water;
[0053] Adjust the RAW264.7 cell density to 10 with DMEM medium 5 ~10 6 a / mL;
[0054] The cells with adjusted density were placed in a 96-well cell culture plate and cultured at 37°C for 24 hours;
[0055] Add appropriate amount of wakame sporophyll polysaccharides to the 96-well culture plate, so that the polysaccharide concentrations are 0 μg / mL, 12.5 μg / mL, 25 μg / mL, 50 μg / mL, 100 μg / mL, 200 μg / mL;
[0056] 37°C, CO 2 Cultivate in a carbon dioxide incubator with a concentration of 5% for 48 hours;
[0057] Collect the cell supernatant;
[0058] Use the ESR method to detect the concentration of NO free radicals;
[0059] Add cell supernatant and NO radical scavenger (MGD) to the tube 2 -Fe 2+ (contains 10mmol...
Embodiment 3
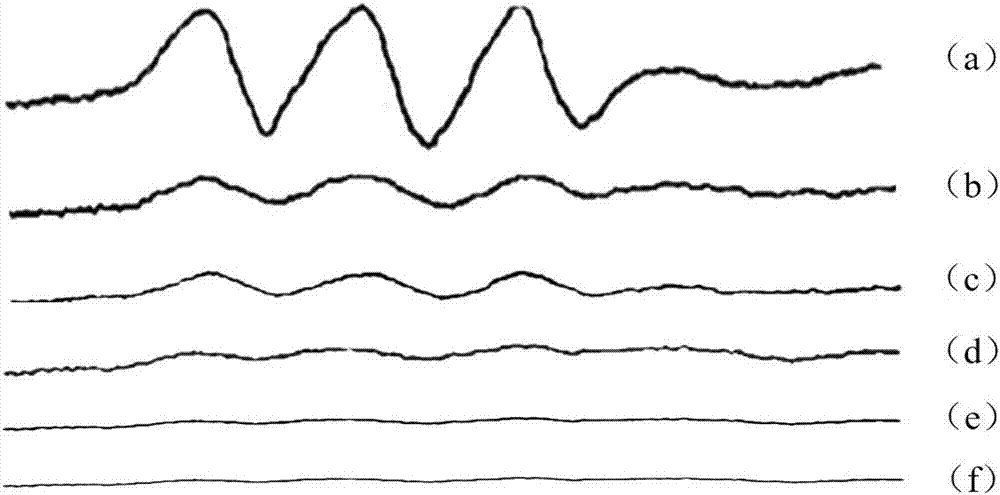
[0063] Example 3: Detection of the regulation of NO production in macrophages by polysaccharides in sea cucumber boiled liquid
[0064] Take the polysaccharide sample of sea cucumber boiled liquid, and prepare 200 μg / mL sea cucumber boiled liquid polysaccharide solution with DMEM medium or distilled water;
[0065] Adjust the RAW264.7 cell density to 10 with DMEM medium 5 ~10 6 a / mL;
[0066] The cells with adjusted density were placed in a 96-well cell culture plate and cultured at 37°C for 24 hours;
[0067] Add an appropriate amount of sea cucumber boiled liquid polysaccharides to the 96-well culture plate, so that the polysaccharide concentrations are 0 μg / mL, 12.5 μg / mL, 25 μg / mL, 50 μg / mL, 100 μg / mL, and 200 μg / mL;
[0068] 37°C, CO 2 Cultivate in a carbon dioxide incubator with a concentration of 5% for 48 hours;
[0069] Collect the cell supernatant;
[0070] Use the ESR method to detect the concentration of NO free radicals;
[0071] Add cell supernatant and NO...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Resonant frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com