A high-throughput screening method for an L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase producing strain
A technology of aspartic acid and decarboxylase, which is applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and the determination/inspection of microorganisms, which can solve the problems of decreased cell enzyme activity and increased pH value.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1 Screening of L-aspartic acid β-decarboxylase producing bacteria
[0023] 1. Enrichment and separation of microorganisms in samples
[0024] Enrichment medium: beef extract 0.5%, peptone 1%, yeast powder 0.2%, KH 2 PO 4 0.05%, K 2 HPO 4 ·H 2 O0.14%, NaCl1.5%, pH7.0-7.2, sterilized at 121°C for 20min, cooled for later use;
[0025] Separation medium plate: 0.5% beef extract, 1% peptone, 1.5% NaCl, 2% agar, pH8.5-9.0, sterilized at 121°C for 20min, then pour the plate to make a separation plate, 20mL / dish, cool and solidify use;
[0026] 1. Sampling
[0027] It has been reported in the literature that marine microorganisms have an ecological community structure diversity and species diversity unmatched by terrestrial microorganisms. Therefore, the Yellow Sea area of Yantai was selected as the sampling site, and a total of 10 samples of sponges, corals, and seabed mud were collected.
[0028] 2. Enrichment
[0029] After the sample was taken back to the...
Embodiment 2 Embodiment 1
[0059] Example 2 Identification of the bacterial species of the L-aspartic acid β-decarboxylase producing bacteria obtained in Example 1
[0060] 1. Identification of strain morphology and physiological and biochemical characteristics
[0061] Refer to the method of "Common Bacteria System Identification Manual" to identify strains with strain morphology and physiological and biochemical characteristics
[0062] 1. Morphological characteristics of the thalline The L-aspartic acid β-decarboxylase producing bacteria obtained in Example 1 is a Gram-negative bacterium, and the cells are short rod-shaped, with extreme flagella and no spores; they can form a flat plate on the broth agar plate The round colonies are yellowish in color, with a rough surface, and the old culture has a foul smell.
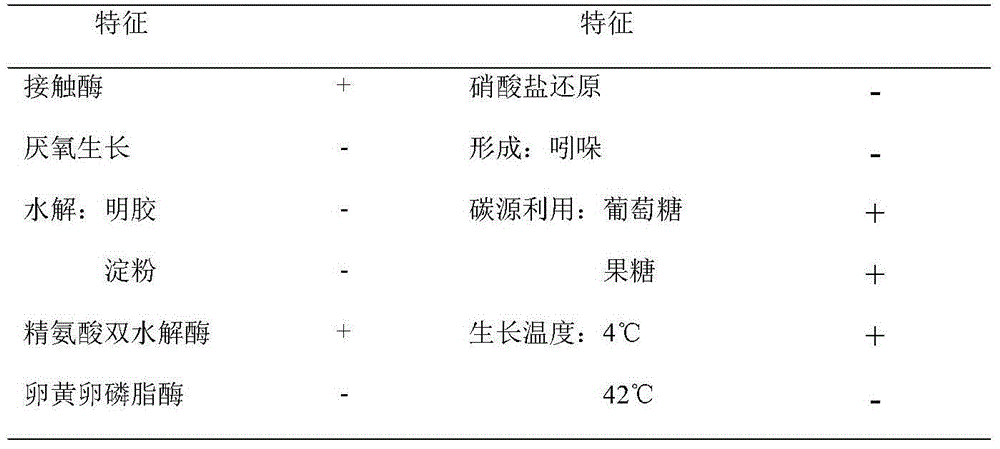
[0063] 2. The identification results of physiological and biochemical characteristics are shown in Table 1.
[0064] Table 1 Physiological and biochemical characteristics of L-aspartate β-...
Embodiment 3
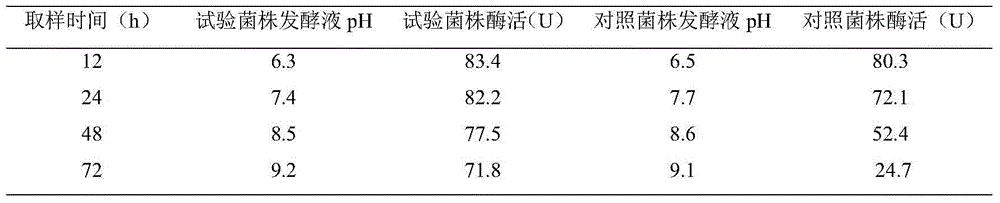
[0068] Example 3 Comparative example: performance investigation of biotransformation production of L-alanine
[0069] This comparative example investigated the performance difference between the test strain and the control strain for transforming and producing L-alanine. Wherein the test strain is the high-yield bacterial strain control bacterial strain Pseudomonas putida (Pseudomonasputida) screened in embodiment 1, and the control bacterial strain Pseudomonas dacunhae is purchased from China Industrial Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center, numbering 1511C0005000003137, and this bacterial strain is the production of L-alanine strain.
[0070] 1. Shake flask fermentation culture
[0071] Shake flask fermentation medium formula: glucose 3%, peptone 1%, yeast powder 0.2%, NaCl 1.5%, KH 2 PO 4 0.05%, K 2 HPO 4 ·H 2 O0.14%, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.03%, CaCl 2 0.05%, pH6.5-7.0. The shake flask fermentation medium was sterilized at 121°C for 20 minutes, after cooling...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com