Preparation method for rare ginsenoside C-K and F1 and four kinds of isomer ginsengenin
A technology for rare ginseng saponins and isomers, which is applied to the preparation of F1 and four isomers of ginsenosides, and the field of rare ginseng saponins C-K, can solve the problems of many by-products, low conversion rate, great difficulty, etc. High yield and purity, simple operation and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] a. Using ginseng as a raw material, extracting a ginseng diol saponin mixture and a panaxatriol saponin mixture:
[0050] Ginseng (with fibrous root) 1 kg, cut into slices (2-4mm thick), soak in 8 liters of methanol, stir and extract at 35-40°C for 6-12 hours, separate the extract, repeat three times; filter, combine the extract, reduce Concentrate under pressure (recover methanol) to a specific gravity of Baumé 20, add 500 ml of petroleum ether, stir and degrease for 1 hour, separate the grease layer, and repeat 2 times. Dilute the degreased ginseng extract with 3 to 5 times the volume of water, repeatedly absorb saponin in a 1.5 liter volume macroporous resin (AB-8 resin or HP-20 resin) column, and use 7.5 to 10 liters of deionized The water elution column removes sugar and other impurities; the macroporous resin column that absorbs saponin is eluted with ethanol-water gradient: the ethanol concentration gradient is 30% to 84%, the total volume of eluent is 11 liters,...
Embodiment 2
[0063] a. Taking ginseng as a raw material, extracting a mixture of panaxatriol saponins is the same as in Example 1;
[0064] b. Use ginseng triol saponin mixture as raw material, prepare substrate solution with organic solvent and buffer solution, and then react substrate solution with crude enzyme solution obtained from Aspergillus microbial fermentation:
[0065] The crude enzyme solution is prepared according to the following conventional methods:
[0066]Aspergillus oryzae sp.39g (isolated from Daqu; literature, Wang Dongming, Yu Hongshan, etc. Process Biochemistry 2012, 47, 133-138. Dalian University of Technology Culture Collection, preservation number: Aspergillusoryzaesp.39g) was inoculated in a sterilized 1 kg of wheat bran with a water content of 50% (containing 50 g of ginseng powder), cultured at 28-32°C for 4-7 days (stirred 4-6 times a day), and then mixed with 5 liters of 0.02 mole, pH 5. 0 acetic acid buffer to leach the enzyme; the enzyme liquid is centrifu...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Preparation of ginseng self-saponin enzyme complex: take 1 kg of ginseng extract saponin slag described in Example 1, add 6 liters of deionized water, stir at 55-65°C for 2-3 hours, centrifuge to collect supernatant, concentrate in high vacuum (product temperature below 65°C) to Baume degree 25 (about 500 ml), it is the saponinase complex of ginseng itself.
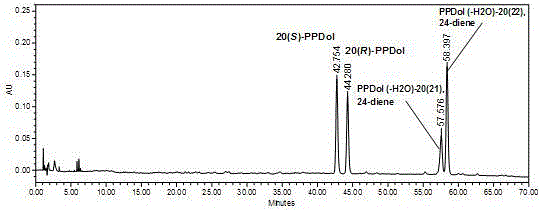
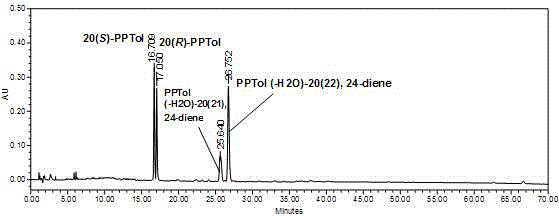
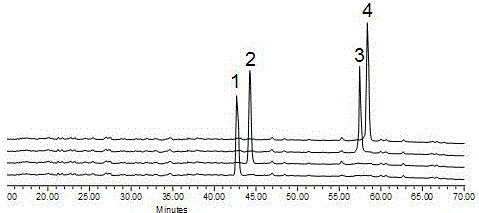
[0075] React the obtained ginseng self-saponinase complex with C-K obtained in Example 1, add formic acid, acetic acid or citric acid with a reaction volume of 0.1 to 50% in the reaction system to reduce the pH reaction, and prepare four isomers of ginseng Diol saponin.
[0076] The details are as follows: Take 20 grams of the product C-K saponins of Example 1, 50 grams of ginseng autosaponinase complex, 350 milliliters of deionized water, and 25 grams of citric acid, mix them, and react at 70-75° C. for 2 hours. Use TLC method to detect, after the reaction is complete, add 400 ml of water-saturated n-butanol to e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com