Method for producing bio-organic fertilizers by quick fermentation of kitchen wastes
A bio-organic fertilizer and kitchen waste technology is applied in the preparation of organic fertilizers, the treatment of bio-organic parts, and organic fertilizers. Speed, time-reducing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
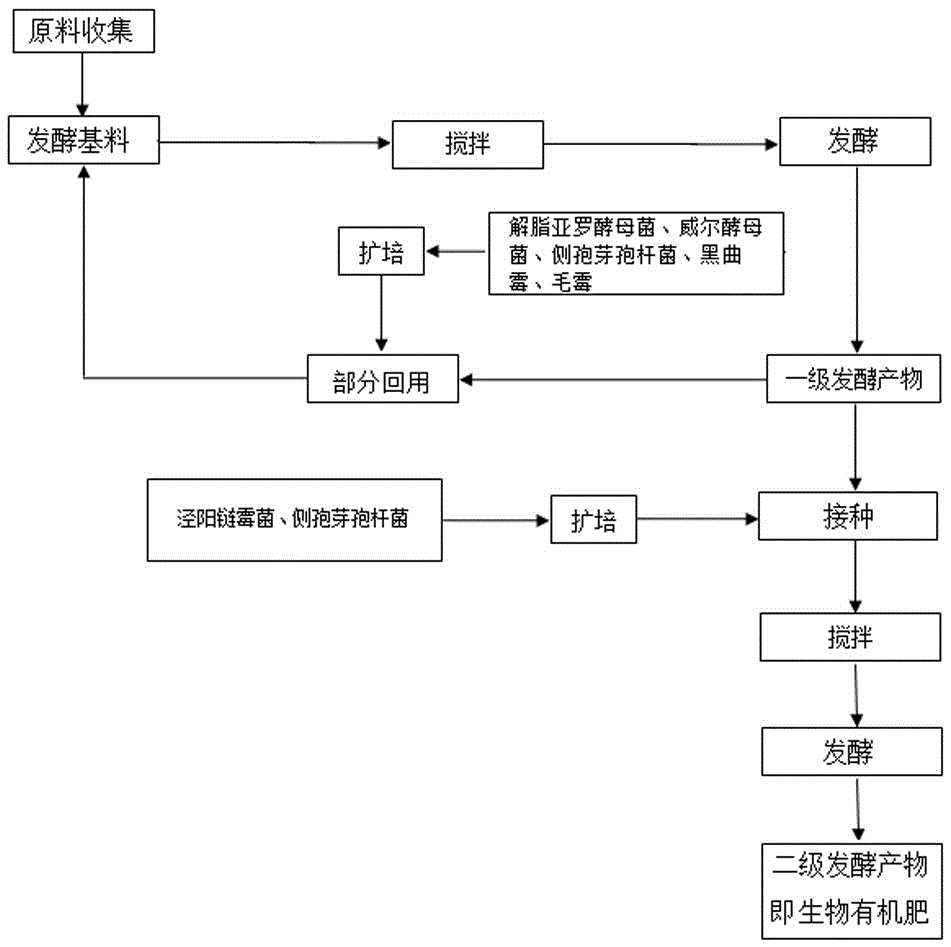
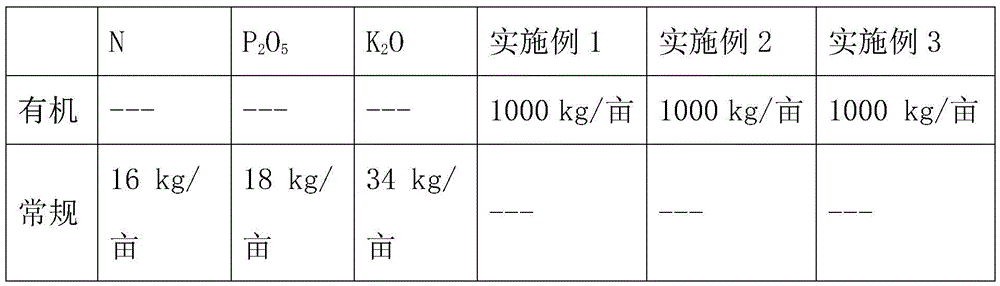
[0029] A method for rapidly fermenting food waste to produce bio-organic fertilizer, which is characterized in that it comprises the following steps: collecting fresh food waste, separating solid oil to obtain solid residue, and removing plastic and metal from the solid residue , bowls and cup fragments and other sundries were picked out to obtain solid food residue; in parts by weight, 45 parts of solid food residue, 5 parts of straw, 5 parts of bacteria bag, and 5 parts of discarded grains were mixed to obtain fermentation base material; inoculate 0.2×10 per kilogram of fermentation base 9 CFU Yarrowia lipolytica, 0.5×10 9 CFU Will yeast, 0.5×10 9 CFU Bacillus paraspora, 1×10 9 CFU Aspergillus niger and 0.5 x 10 9 CFU mucormyces, add water, turn over and stir evenly and adjust the pH value to 6.5, the weight ratio of the fermentation base material and water is 1:1, then ferment, the fermentation time is 5 days, and obtain the primary fermentation product; 15% of the firs...
Embodiment 2
[0038] A method for rapidly fermenting food waste to produce bio-organic fertilizer, which is characterized in that it comprises the following steps: collecting fresh food waste, separating solid oil to obtain solid residue, and removing plastic and metal from the solid residue , bowls and cup fragments and other sundries are picked out to obtain solid food residue; in parts by weight, 70 parts of solid food residue, 10 parts of straw, 10 parts of bacteria bag, and 10 parts of discarded grains are stirred and mixed to obtain fermented food residue. Base material; inoculate 2×10 per kilogram of fermentation base material 9 CFU Yarrowia lipolytica, 1×10 9 CFU Will yeast, 2×10 9 CFU Bacillus paraspora, 2×10 9 CFU Aspergillus niger and 1 x 10 9 CFU Mucor, add water, turn over and stir evenly and adjust the pH value to 7.5, the weight ratio of the fermentation base material to water is 1:1.2, then ferment, the fermentation time is 8 days, and obtain the primary fermentation prod...
Embodiment 3
[0047] A method for rapidly fermenting food waste to produce bio-organic fertilizer, which is characterized in that it comprises the following steps: collecting fresh food waste, separating solid oil to obtain solid residue, and removing plastic and metal from the solid residue , bowls and cup fragments and other sundries were picked out to obtain solid food residue; in parts by weight, 57.5 parts of solid food residue, 7.5 parts of straw, 7.5 parts of bacteria bag, and 7.5 parts of waste were stirred and mixed to obtain fermented base material; inoculate 1.1×10 per kilogram of fermentation base material 9 CFU Yarrowia lipolytica, 0.75×10 9 CFU Will yeast, 0.75×10 9 CFU Bacillus lateralis, 1.5×10 9 CFU Aspergillus niger and 0.75 x 10 9 CFU Mucor, add water, turn over and stir evenly, and adjust the pH value to 7. The weight ratio of the fermentation base material to water is 1:1.1, and then ferment, and the fermentation time is 7 days to obtain a primary fermentation produc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com