Method for using lignocellulose as raw material to co-produce ethyl alcohol and electric energy
A technology for lignocellulose and raw materials, applied in the field of co-production of ethanol and electric energy, can solve the problems of low conversion efficiency of biomass to electric energy, complicated process, poor contact, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Optimization of lignocellulose pretreatment conditions with heteropolyacids.
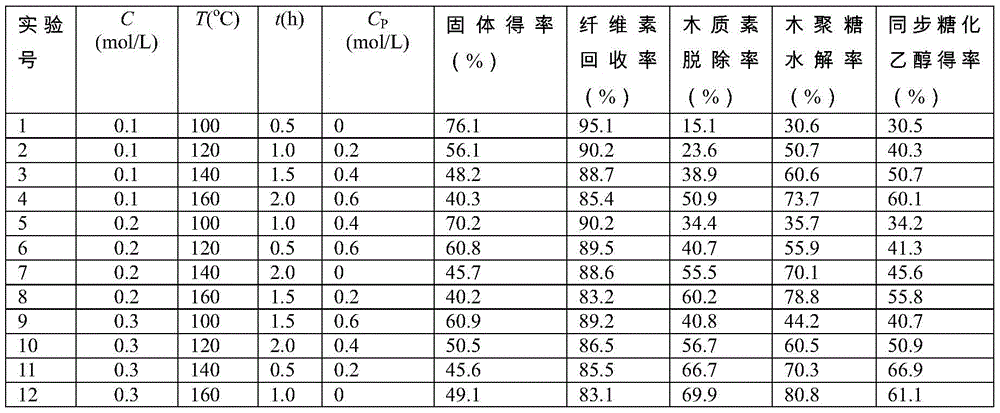
[0039] The lignocellulosic raw material used is wheat straw, and its main component content is determined to be 35.1% dextran, 23.4% xylan and 21.1% lignin. Adopt phosphomolybdic acid to carry out pretreatment, carry out pretreatment under the solid-liquid ratio of 1:10 (w / v), analyze phosphomolybdic acid concentration C (mol / L), pretreatment temperature T ( ℃ ), time t(h) and phosphoric acid concentration C P (mol / L) on the composition of pretreated cellulose solids and the impact of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation on the production of ethanol, the results are shown in the table below. It can be seen that phosphomolybdic acid can pretreat wheat straw raw materials under the conditions of concentration of 0.1-0.4, temperature of 100-160° C., time of 0.5-2.0 hours and phosphoric acid concentration of 0-0.6 mol / L. The optimal conditions for pretreatment of wheat straw with phos...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Comparison of pretreatment of wood fiber with different heteropolyacids or their salts.
[0045] The lignocellulosic raw material used is the same as in Example 1, and the concentration of heteropoly acid or its salt is 0.3mol / L, the concentration of phosphoric acid is 0.2mol / L, the solid-liquid ratio (w / v) is 1:10, and the temperature is 140°C. After 0.5 hour, the results of pretreatment with different heteropolyacids or their salts are shown in the table below. It can be seen that different oxidation states of heteropolyacids or their salts can obtain better pretreatment effects on wood fibers, and the pretreatment effects of phosphomolybdic acid, phosphotungstic acid, phosphomolybdovanadic acid, and phosphotungstovanadic acid most.
[0046] Table 2 Comparison of different oxidation states of heteropolyacids or their salts pretreated wood fiber
[0047]
Embodiment 3
[0049] Performance comparison of different reduced heteropolyacids or their salts in the oxidative regeneration of liquid flow fuel cells.
[0050] The reduced heteropolyacid or its salt obtained after pretreatment of wheat straw at 140°C was used as the anode electron donor, and oxygen was used as the cathode electron acceptor. figure 2 discharge in a liquid flow fuel cell. The liquid flow fuel cell is composed of a graphite bipolar plate, a carbon cloth electrode, a Nafion 115 proton exchange membrane produced by DuPont, and a plexiglass splint. Among them, there are grooves inside the graphite bipolar plate, which are used as the anode or cathode liquid or gas flow path and reaction chamber, and the active electrode area of the battery is 40cm 2 , load 5mg / cm on the cathode carbon cloth -1 Pt(60%)-C as catalyst. The discharge temperature is room temperature (25°C). The comparison of the maximum power density generated by the discharge of different reduced heteropolya...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com