Method for effectively increasing yield of tetraene macrolide antibiotics
A technology of macrolides and antibiotics, applied in the field of microorganisms, to achieve the effect of increasing production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1: Obtaining rifampicin-resistant mutant strains (the first round of screening of drug-resistant mutant strains)
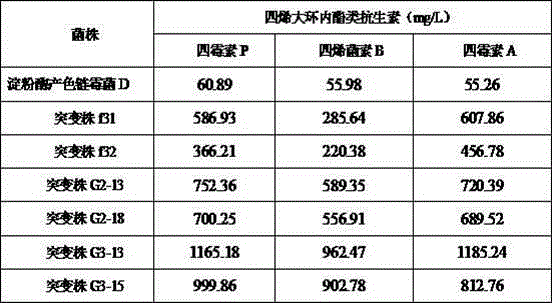
[0024] A GYM solid plate with a final rifampicin concentration of 20 μg / mL was prepared, that is, the rifampicin concentration in the GYM solid plate was 20 μg / mL. Use a pipette to draw 100μL of amylase-producing Streptomyces chromogenes D spore suspension (1×10 6 Pieces / mL) on the GYM solid plate, spread evenly with a sterile coating rod, and place it in a 28°C incubator for 7 days. Pick a single colony to a new GYM solid plate containing 20μg / mL rifampicin (one A single colony is divided into a plate), placed in an incubator at 28°C for 5 days, and the strain that can grow again on the new GYM solid plate is the rifampicin-resistant mutant. A total of 2 rifampicin-resistant mutant strains were obtained, numbered f31 and f32, respectively. The two mutant strains were cultured in liquid fermentation according to step (4) in the technical scheme. The fe...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2: Obtaining of low-concentration streptomycin resistant mutant strains (the second round of screening of resistant mutant strains)
[0026] A GYM solid plate with a final concentration of streptomycin of 30 μg / mL was prepared, that is, the concentration of streptomycin in the GYM solid plate was 30 μg / mL. Use a pipette to pipette 100μL of rifampicin-resistant mutant f31 spore suspension (1×10 6 Pieces / mL) on the GYM solid plate, spread evenly with a sterile coating rod, place it in an incubator at 28°C for 7 days, pick out single colonies to a new GYM solid plate containing 30μg / mL streptomycin (one A single colony is drawn on a plate), placed in an incubator at 28°C for 5 days, and the strain that can grow again on the new GYM solid plate is a low-concentration streptomycin resistant mutant. A total of 2 low-concentration streptomycin resistant mutant strains were obtained, numbered G2-13 and G2-18 respectively. The two mutant strains were cultured in liquid ferm...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3: Obtaining high-concentration streptomycin-resistant mutant strains (the third round of screening of drug-resistant mutant strains)
[0028] Prepare a GYM solid plate with a final concentration of 300 μg / mL of streptomycin, that is, the concentration of streptomycin in the GYM solid plate is 300 μg / mL. Use a pipette to pipette 1000μL of low-concentration streptomycin resistant mutant strain G2-13 spore suspension (1×10 12 Pcs / mL) on the GYM solid plate, spread evenly with a sterile coating rod, and place it in a 28℃ incubator for 10-15 days. Pick a single colony to a new GYM solid plate containing 300μg / mL streptomycin (One single colony draws one plate), place it in a 28°C incubator for 7-10 days, and the strain that can grow again on the new GYM solid plate is a high-concentration streptomycin resistant mutant. A total of 2 high-concentration streptomycin resistant mutant strains were obtained, numbered G3-13 and G3-15 respectively;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com