Method for phase transition of hydrophobic nanoparticles by using DNA nanostructure
A technology of nanoparticles and nanostructures, applied in the field of DNA nanostructures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Synthesis of functionalized DNA tetrahedra
[0021] Dilute DNA strands A, B, C and D in TM buffer (10mM Tris-HCl, 50mM MgCl 2 , pH 8.0) in a medium molar mix to a final concentration of 10 μM. After mixing the DNA, heat it to 95°C and then rapidly cool it to 4°C to obtain a DNA tetrahedral solution containing aptamers. Formation of DNA tetrahedral nanostructures can be verified by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (see figure 1 ).
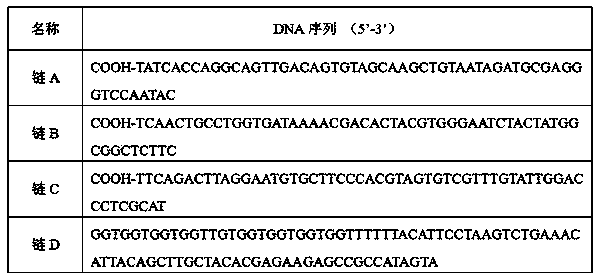
[0022] Table 1 Detailed information on the DNA sequence used in the present invention
[0023]
Embodiment 2
[0025] Phase transition of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles dispersed in chloroform
[0026] Slowly add 0.2mL chloroform solution containing 100μg / mL iron oxide nanoparticles (purchased from American Ocean Nanotechnology Company (Springdale, AR, USA)) to 0.2mL solution containing 10μM DNA tetrahedron. The iron nanoparticles are transferred from the chloroform layer to the water layer. Then move the aqueous solution into a microtube, centrifuge and wash with TM buffer, and redisperse in TM buffer to obtain water-soluble iron oxide nanoparticles.
[0027] attached figure 2 a, 2b are transmission electron microscope images of iron oxide nanoparticles before and after phase transition. attached figure 2 c is the dispersion diagram of iron oxide nanoparticles in chloroform and in water before and after phase transition, attached figure 2 d is a diagram of the magnetic separation phenomenon of iron oxide nanoparticles in aqueous solution after phase transition.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Phase transition of rare earth upconverting luminescent nanoparticles dispersed in cyclohexane
[0030] Slowly add 0.2 mL cyclohexane solution containing 100 μg / mL rare earth up-conversion luminescent nanoparticles to 0.2 mL aqueous solution containing 10 μM DNA tetrahedron. When the aqueous layer is reached, transfer the aqueous layer solution to a microtube. After the excess DNA tetrahedron is separated and washed by centrifugation, it is removed from the aqueous solution of the hydrophilic rare earth up-conversion luminescent nanoparticles. Finally, the hydrophilic rare earth up-conversion luminescent nanoparticles are redispersed in TM buffer solution to obtain the rare earth up-conversion luminescent nanoparticles dispersed in the aqueous solution.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com