Method of photoresist strip
A photoresist and photoresist layer technology, which is applied in the manufacture of electrical components, electrical solid-state devices, semiconductor/solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problem of long soaking time in photoresist stripping solution, increased environmental production costs, and scattered bumps. And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
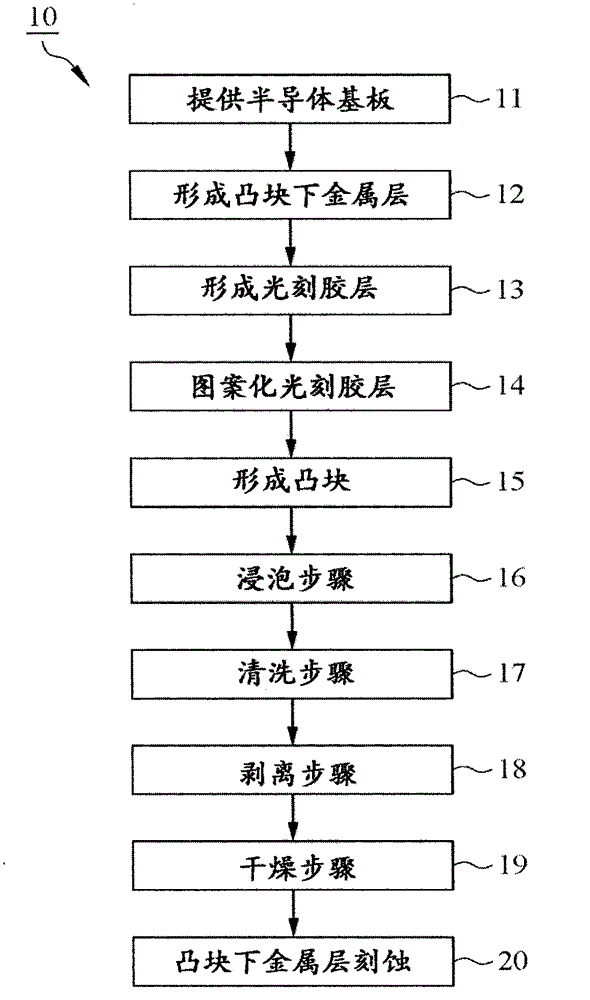
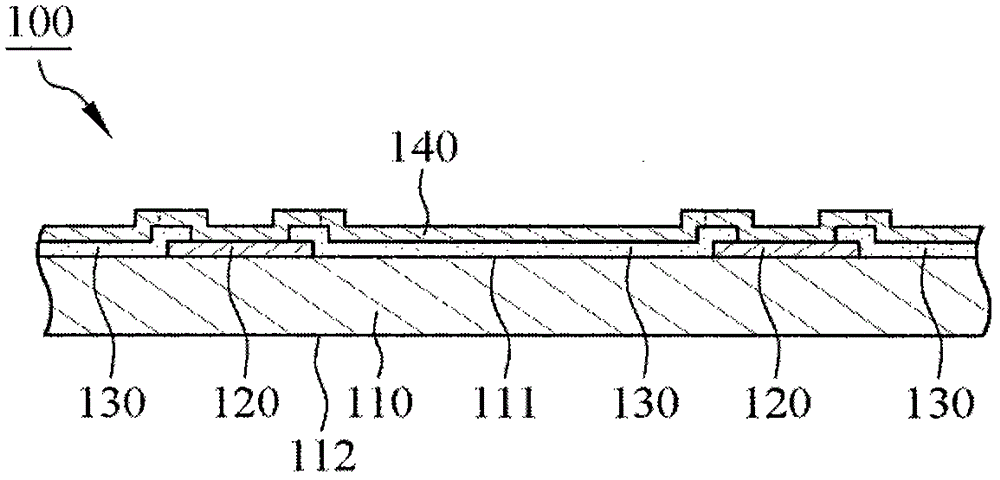
[0044] see figure 1 , is the first embodiment of the present invention, a flow chart of a photoresist stripping method 10, please refer to figure 1 and figure 2, provide a semiconductor substrate 100 in "providing a semiconductor substrate 11", wherein the semiconductor substrate 100 has a substrate 110, a bonding pad 120 and a protective layer 130, the bonding pad 120 is located on the surface 111 of the substrate 110, and the protective layer 130 covers the substrate 110 and the pad 120 , and the protective layer 130 has an opening 131 , the opening 131 exposes the pad 120 , and the pad 120 can be selected from copper, aluminum, copper alloy or other conductive materials.
[0045] see figure 1 and image 3 In "forming the UBM layer 12", the UBM layer 140 is plated on the protective layer 130 by evaporation, sputtering, electroplating or electroless plating, and the UBM layer 140 covers the protection layer 130, and the UBM layer 140 is connected to the pad 120, wherein ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com