Method for preparing ceramic substrate containing conductive copper cylinder
A technology of ceramic substrates and ceramic substrates, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as difficult interconnection, usage restrictions, and serious pollution of three wastes, so as to improve yield and reliability, The effect of excellent performance and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The processing steps of this embodiment are:
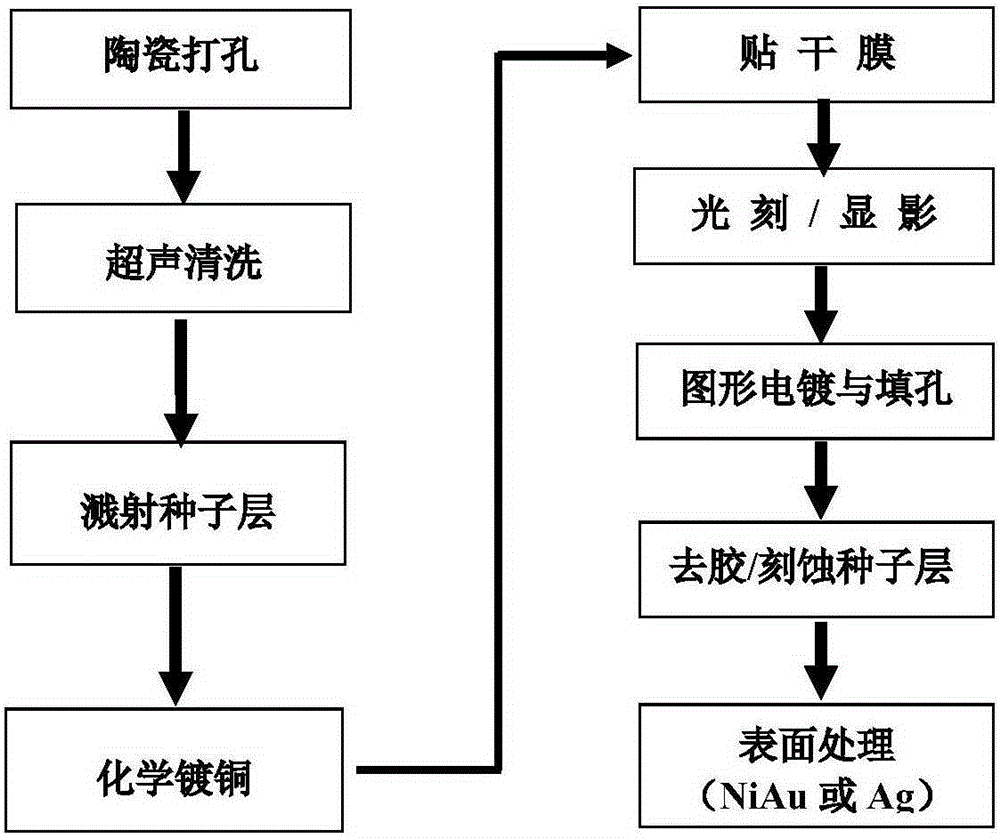
[0024] 1) Drilling: using a laser to prepare an array of through-holes with a diameter of 100um on the alumina ceramic substrate (thickness: 0.5mm);
[0025] 2) Pretreatment: ultrasonically clean the ceramic substrate in deionized water, acetone, and ethanol solution for 5 minutes, and then dry it (100°C, 30 minutes);
[0026] 3) Sputtering coating: the ceramic substrate is placed in a coating machine, and 200nm titanium (Ti) and 200nm copper (Cu) are sequentially deposited on the surface of the substrate by a sputtering process as a seed layer;
[0027] 4) Thickening of electroplating: the whole board electroplating copper technology is adopted to increase the thickness of the seed layer to 3 μm;
[0028] 5) Prepare wall-solidifying solution: Stir and mix 1 gram of graphene, 100 grams of deionized water, and 1 ml of sodium hexametaphosphate, and adjust the pH value of the solution to 10.0 with potassium hydroxide;
[002...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The processing steps of this embodiment are:
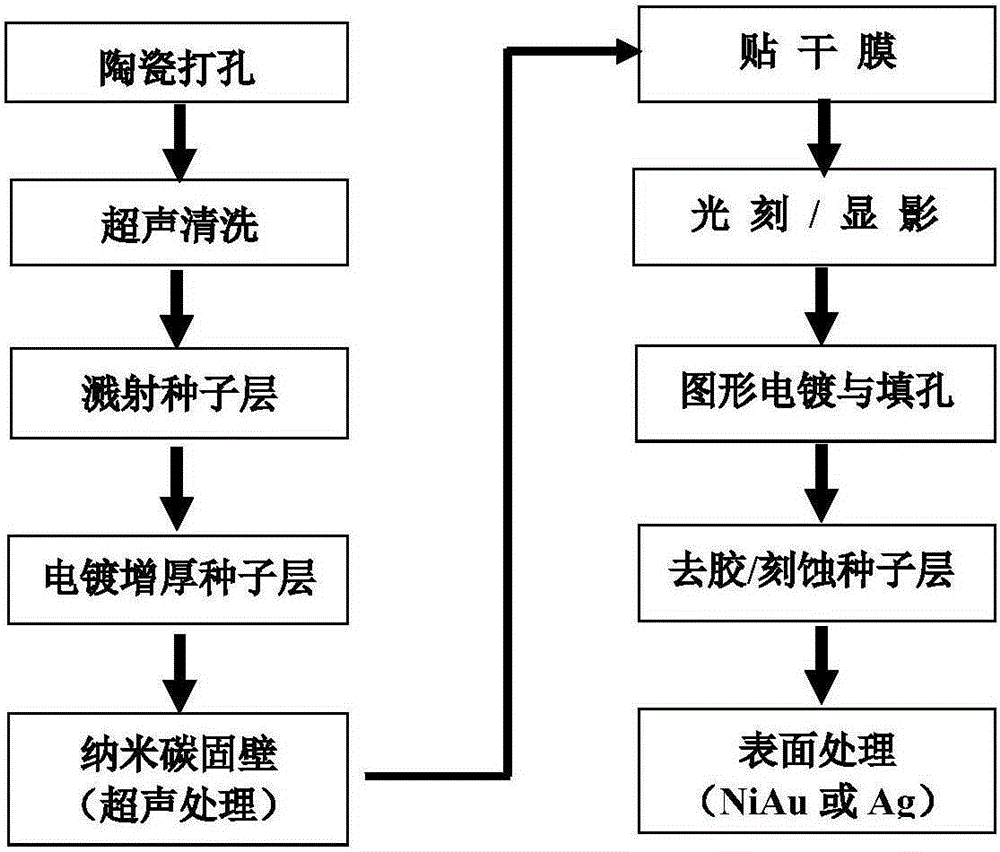
[0036] 1) Drilling: using a laser to prepare an array of through holes with a diameter of 200um on the aluminum nitride ceramic substrate (thickness: 1.0mm);
[0037] 2) Pretreatment: ultrasonically clean the ceramic substrate in deionized water, acetone, and ethanol solution for 5 minutes, and then dry it (100°C, 30 minutes);
[0038] 3) Sputtering coating: the ceramic substrate is placed in a coating machine, and 100nm titanium (Ti) and 200nm copper (Cu) are sequentially deposited on the surface of the substrate by a sputtering process as a seed layer;
[0039] 4) Thickening of electroplating: the whole board electroplating copper technology is adopted to increase the thickness of the seed layer to 5 μm;
[0040] 5) Prepare wall-solidifying solution: Stir and mix 3 grams of nano-graphite flakes, 100 grams of deionized water, and 2 ml of sodium alkylphosphocarboxylate, and adjust the pH value of the solution to 10.5 with ...
Embodiment 3
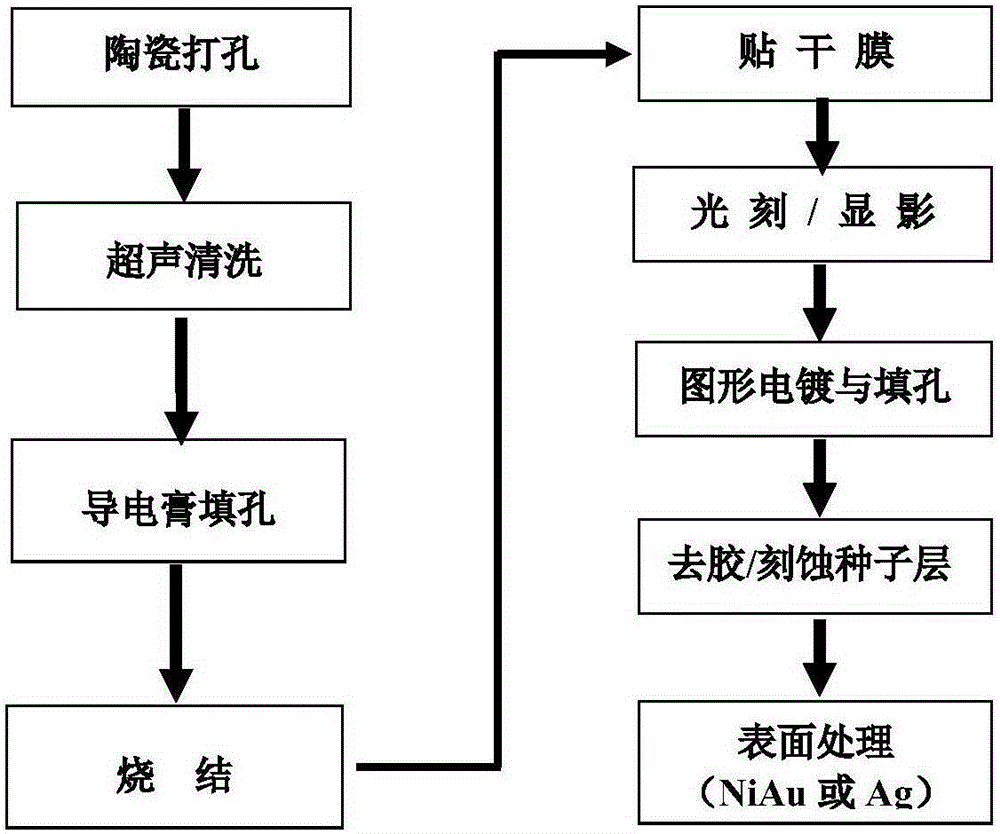
[0047] The processing steps of this embodiment are:
[0048] 1) Drilling: using a laser to prepare an array of through holes with a diameter of 50um on the beryllium oxide ceramic substrate (thickness: 0.38mm);
[0049] 2) Pretreatment: ultrasonically clean the ceramic substrate in deionized water, acetone, and ethanol solution for 5 minutes, and then dry it (100°C, 30 minutes);
[0050] 3) Sputtering coating: the ceramic substrate is placed in a coating machine, and 100nm titanium (Ti) and 200nm copper (Cu) are sequentially deposited on the surface of the substrate by a sputtering process as a seed layer;
[0051] 4) Thickening of electroplating: the whole board electroplating copper technology is adopted to increase the thickness of the seed layer to 2 μm;
[0052] 5) Prepare wall-solidifying solution: Stir and mix 5 grams of nano-carbon powder, 100 grams of deionized water, and 3 ml of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, and adjust the pH value of the solution to 9.5 with pota...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com