Method for noninvasive antenatal diagnosis through separating fetal nucleated red blood cells from peripheral circulating blood of pregnant woman
A technology for pregnant women's peripheral blood and nuclear red blood cells, which is applied in the field of non-invasive prenatal diagnosis to achieve efficient and high-specificity capture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
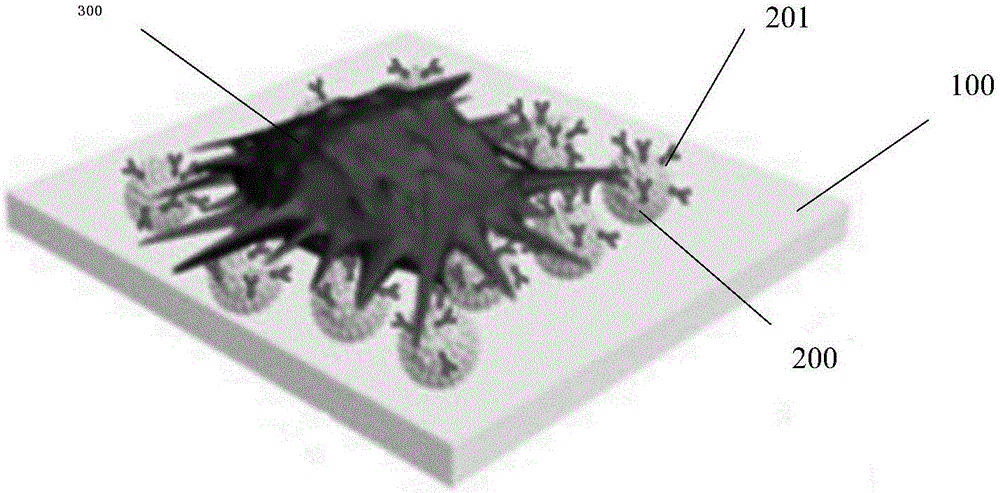
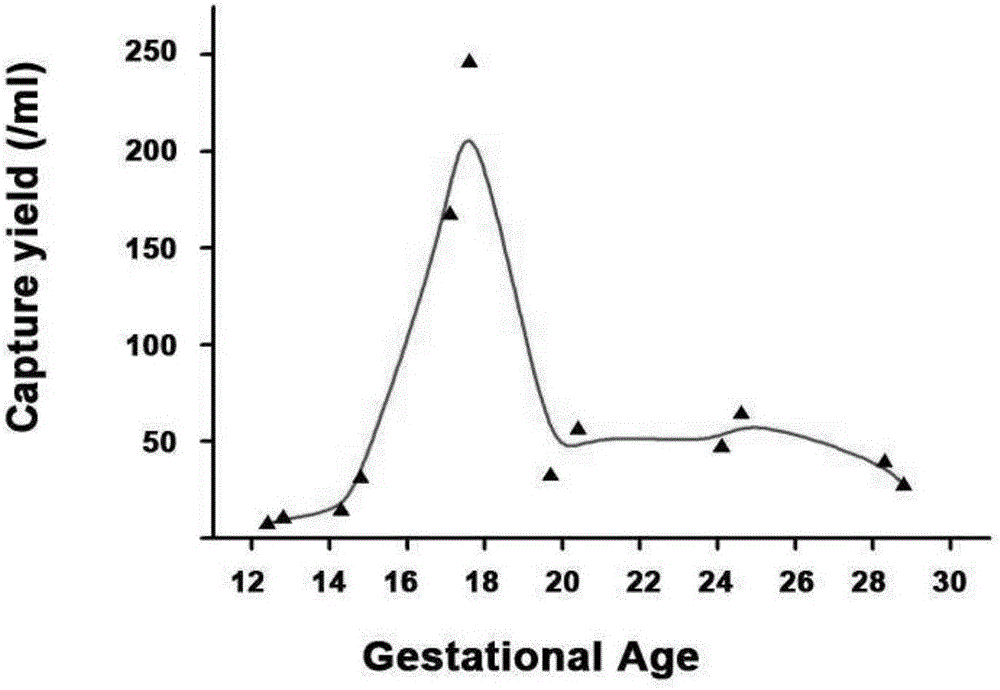
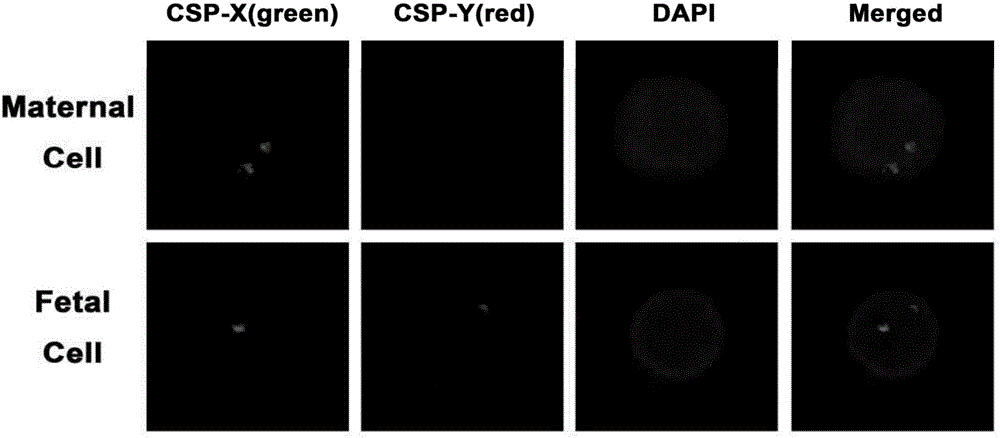
[0034] according to figure 1 The illustrated embodiment of the present invention uses nanomaterials to separate fetal nucleated red blood cells from the peripheral blood of pregnant women for non-invasive prenatal diagnosis. First, chemical modification methods (MPTMS, GMBS and Streptavidin are used to process the nano-substrates in sequence for 1 hour, 45 Minutes and 6 hours), and then drop the antibody with biotin group onto the substrate, and the nanoparticle 200 is combined with the antibody 201 to prepare a nanoparticle substrate modified with specific antibodies. The method of separating fetal nucleated red blood cells from the peripheral blood of pregnant women for non-invasive prenatal diagnosis firstly enters the step of capturing fetal nucleated red blood cells in the peripheral blood of pregnant women S1100: the venous blood of the pregnant women whose gestational age is 12 weeks and 3 days is collected from the hospital and stored in In the blood collection tube wit...
Embodiment 2
[0036] according to figure 1 The illustrated embodiment of the present invention uses nanomaterials to separate fetal nucleated red blood cells from the peripheral blood of pregnant women for non-invasive prenatal diagnosis. First, chemical modification methods (MPTMS, GMBS and Streptavidin are used to process the nano-substrates in sequence for 1 hour, 45 Minutes and 6 hours), and then drop the antibody with biotin group onto the substrate, and the nanoparticle 200 is combined with the antibody 201 to prepare a nanoparticle substrate modified with specific antibodies. The method for separating fetal nucleated red blood cells from the peripheral blood of pregnant women for non-invasive prenatal diagnosis firstly enters the step of capturing fetal nucleated red blood cells in the peripheral blood of the pregnant women. S1100: The venous blood of the pregnant women whose gestational age is 17 weeks and 4 days is collected from the hospital and stored in In the blood collection tu...
Embodiment 3
[0038] according to figure 1 The illustrated embodiment of the present invention uses nanomaterials to separate fetal nucleated red blood cells from the peripheral blood of pregnant women for non-invasive prenatal diagnosis. First, chemical modification methods (MPTMS, GMBS and Streptavidin are used to process the nano-substrates in sequence for 1 hour, 45 Minutes and 6 hours), and then drop the antibody with biotin group onto the substrate, and the nanoparticle 200 is combined with the antibody 201 to prepare a nanoparticle substrate modified with specific antibodies. The method of separating fetal nucleated red blood cells from the peripheral blood of pregnant women for non-invasive prenatal diagnosis first enters the step of capturing fetal nucleated red blood cells in the peripheral blood of pregnant women S1100: the venous blood of the pregnant women whose gestational age is 28 weeks and 2 days is collected from the hospital and stored in In the blood collection tube with ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com