Tin-tungsten ore selection method
A beneficiation method and tin ore technology, applied in the field of tungsten-tin ore beneficiation, can solve problems such as low recovery rate, difficulty in obtaining beneficiation indicators, over-grinding and over-powdering of metals, etc., to achieve low production costs, ensure tungsten-tin recovery rate, and equipment The effect of fewer units
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
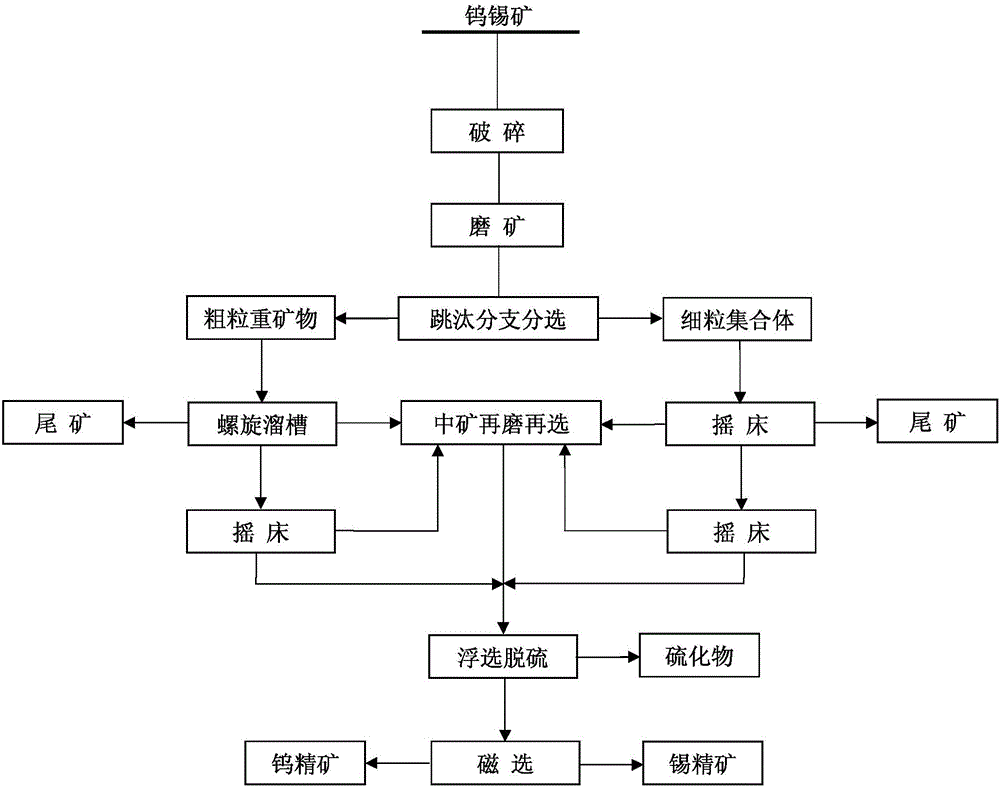
[0020] An example of the beneficiation method of tungsten-tin ore of the present invention, comprises the steps:
[0021] 1. Mineral raw materials:
[0022] Raw ore main metal grade: Sn0.32%, WO 3 0.035%. Phase analysis shows that tin exists in the form of cassiterite, and tungsten is mainly wolframite with a small amount of scheelite.
[0023] 2. Operation steps and control technical conditions:
[0024] (1) Grind the ore to -0.35mm, and use jigging to separate the minerals into two branches: coarse-grained heavy minerals and fine-grained aggregates. The coarse-grained heavy minerals refer to monomer tin and tungsten with relatively coarse particle size Minerals and rich contiguous bodies with large specific gravity and fine-grained aggregates refer to single tin-tungsten minerals with finer particle size and poor contiguous bodies with small specific gravity, which are hereinafter referred to as coarse-grained heavy minerals and fine-grained aggregates, and then The two ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Another example of the beneficiation method of tungsten-tin ore of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0035] 1. Mineral raw materials:
[0036] Raw ore main metal grade: Sn0.24%, WO 3 0.22%. Phase analysis shows that tin exists in the form of cassiterite, and tungsten is mainly wolframite.
[0037] 2. Operation steps and control technical conditions:
[0038] (1) The ore is ground to a particle size of -0.30mm, and the minerals are divided into two branches by jigging separation: coarse-grained heavy minerals and fine-grained aggregates, and then the two minerals are separated separately.
[0039] (2) Coarse-grained heavy minerals are roughed through the spiral chute to obtain the spiral chute rough concentrate and spiral chute tailings, and the spiral chute coarse concentrate shaker is re-selected to obtain tungsten-tin coarse concentrate 1, shaker medium ore 1 and shaker tailings 1;
[0040] (3) The fine-grained aggregate minerals are recovere...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Another example of the beneficiation method of tungsten-tin ore of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0049] 1. Mineral raw materials:
[0050] Raw ore main metal grade: Sn0.083%, WO 3 0.46%. Phase analysis shows that tin exists in the form of cassiterite, and tungsten is mainly wolframite.
[0051] 2. Operation steps and control technical conditions:
[0052] The ore is ground to a particle size of -0.36mm, and the coarse-grained heavy minerals and fine-grained aggregates are obtained by jigging separation, and then the coarse-grained heavy minerals and fine-grained aggregates are separated separately.
[0053] (2) Coarse-grained heavy minerals are roughed through the spiral chute to obtain the spiral chute rough concentrate and spiral chute tailings, and the spiral chute coarse concentrate shaker is re-selected to obtain tungsten-tin coarse concentrate 1, shaker medium ore 1 and shaker tailings 1;
[0054] (3) The fine-grained aggregate minerals...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com