Construction method and application of dcf1-knocked-out mouse model
A dcf1, mouse model technology, applied in the use of vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, cells modified by introducing foreign genetic material, recombinant DNA technology, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
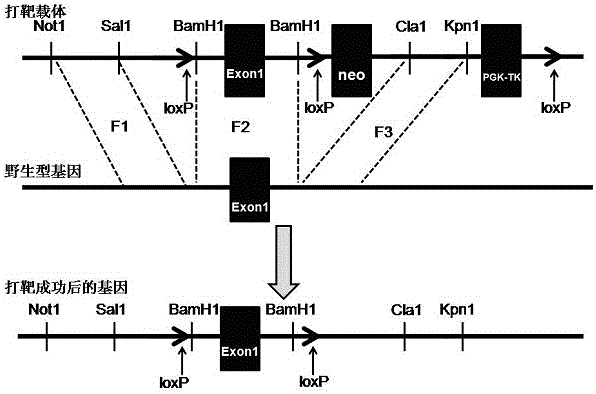
[0032] dcf1 knockout mouse construction method, see figure 1 .
[0033] 1. The mouse dcf1 gene is located on chromosome 4, and the mouse dcf1 gene is cloned from the mouse BAC library (ID: RP23-423N6). The construction of the targeting vector pLNT-dcf1 is based on the reconstruction of the pLNT plasmid as the parent plasmid, such as figure 1 As shown, three genes are inserted in the middle, and the DNA fragment of the first exon (Exon1) of the dcf1 gene is inserted between BamHI and BamHI, and two 1oxP sites arranged in the same direction are installed on both sides, and the neo gene is positive Screening marker gene, PGK-TK gene is a negative screening marker gene, also has 1oxP sites on both sides. The length of the upstream homologous recombination arm (F1) is 1.2kb (NotI—SalI), the length of the downstream homologous recombination arm (F3) is 4.8kb (ClaI—KpnI), and the length of the intermediate condition deletion part (F2) is 1.4kb, which is dcf1 Part of the first exon...
Embodiment 2
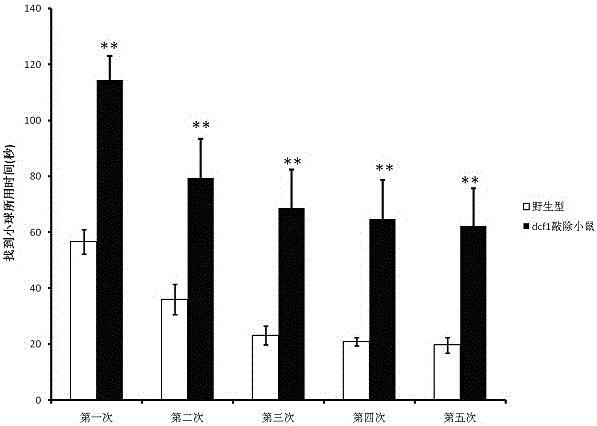
[0042] Example 2: Detection of olfactory sensitivity of dcf1 knockout mice by food burial bead test
[0043]On the day before the experiment, the mice were forbidden to eat, and drinking water was provided normally. Rat food was not provided and the rats were left in a state of extreme hunger. Each cage was covered with 3 cm thick corncob litter, and a grain of 0.5 g rat food was randomly buried in each cage, with a depth of about 0.5 cm. Experimenter 1 puts the mouse into the test cage and covers the cage cover (to prevent the mouse from climbing out of the cage). Experimenter 2 starts timing at the same time. After the mouse finds the mouse food and digs it out, grabs it with its forelimbs. The experiment is over and stops. Time and record the time. If the mouse is not found within 5 minutes, the experiment will also end. The control group included 10 wild-type mice and 10 dcf1 knockout mice each. Each mouse corresponds to a cage, and it is guaranteed that there will be n...
Embodiment 3
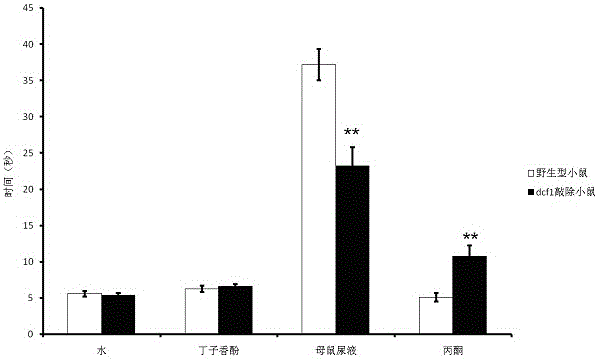
[0046] The olfactory preference assay detects olfactory preference in dcf1 knockout mice
[0047] The experimental mice were individually placed in each cage for 1 hour to acclimate to the environment. Aim the camera at one side of the cage from the side, put a 3cm×3cm filter paper in the cage, and soak the filter paper with the specified solution. The experiment time was 3 minutes, the experiment was ended, the filter paper was taken out, and the mice were put back into the original cage. The control group included 10 wild-type mice and 10 dcf1 knockout mice each. A stopwatch was used to count the total time the mice sniffed the filter paper. If the mouse licked the filter paper with its tongue or grasped the filter paper with its forelimbs, these times could not be counted.
[0048] Mice can distinguish between different odors, which can be roughly divided into three categories: preferred odors, neutral odors (neither like nor dislike) and aversive odors. In the olfactory...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com