Chemical embryotoxicity prediction model and establishing method thereof
A technology of embryotoxicity and predictive models, applied in the field of prediction of embryotoxicity of new chemicals, can solve problems such as research, difficult metabolism and mechanism, and many influencing factors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
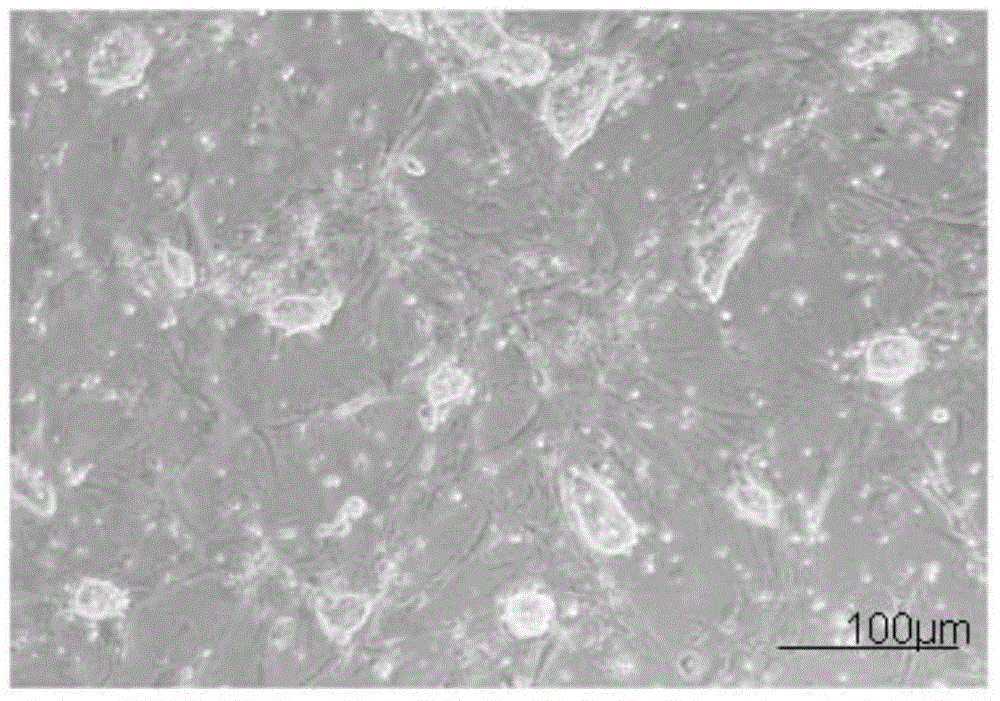
[0098] Example 1: Isolation and culture of mouse embryonic fibroblasts
[0099] In the present invention, mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) are used as trophoblast cells for culturing ES.
[0100] 1.1 Isolation method of MEF primary cells:
[0101] (1) Take a beaker filled with 50ml of 75% ethanol, soak scissors, tweezers and other surgical instruments, the soaked instruments are roasted and sterilized by an alcohol lamp, then cooled and set aside.
[0102] (2) Prepare several bacterial culture dishes with a diameter of 60 mm, which are respectively numbered as No. 1 dish, No. 2 dish, and No. 3 dish, and put in appropriate amount of PBS sterilized by high temperature and high pressure, and add appropriate amount of penicillin-streptomycin solution into it. Among them, dish No. 1 contained the uterus taken out during the dissection of pregnant mice, dish No. 2 contained embryos with torn membranes, and dish No. 3 contained embryo trunks after treatment.
[0103] (3) After ane...
Embodiment 2
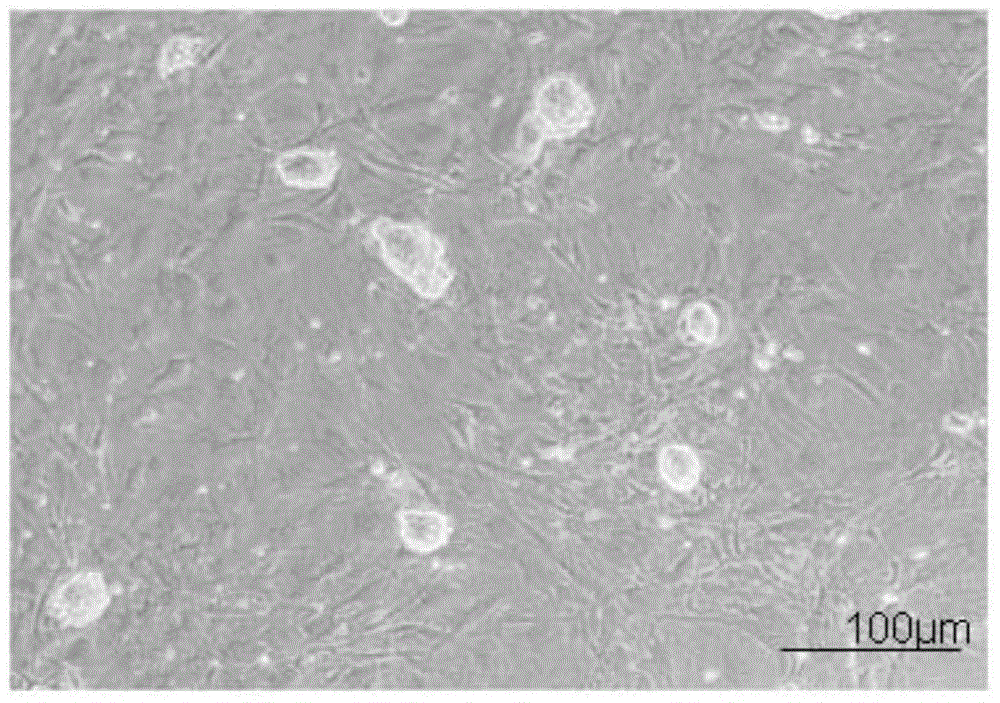
[0115] Example 2: In vitro expansion and culture of mouse ES
[0116] 2.1 Preparation of trophoblast cells
[0117] (1) Select MEF cells with appropriate algebra and density, add mitomycin C to the cell culture medium at a working concentration of 10 μg / ml, mix well and place in an incubator to continue culturing.
[0118] (2) After 2 hours, the culture medium containing mitomycin C was aspirated, and washed with PBS sterilized by high temperature and high pressure for 5 times, 5 minutes each time.
[0119] (3) After washing, replace with fresh culture medium to recover ES cells or continue culturing. The treated trophoblast cells supported the growth and maintenance of the undifferentiated state of mouse ES cells for up to 5 days.
[0120] 2.2 Recovery of ES cells
[0121] (1) Take out the ES cell cryopreservation tube from the liquid nitrogen, put it in a 37°C water bath to dissolve, take it out when it dissolves to the state of small ice crystals, and put it into the ult...
Embodiment 3
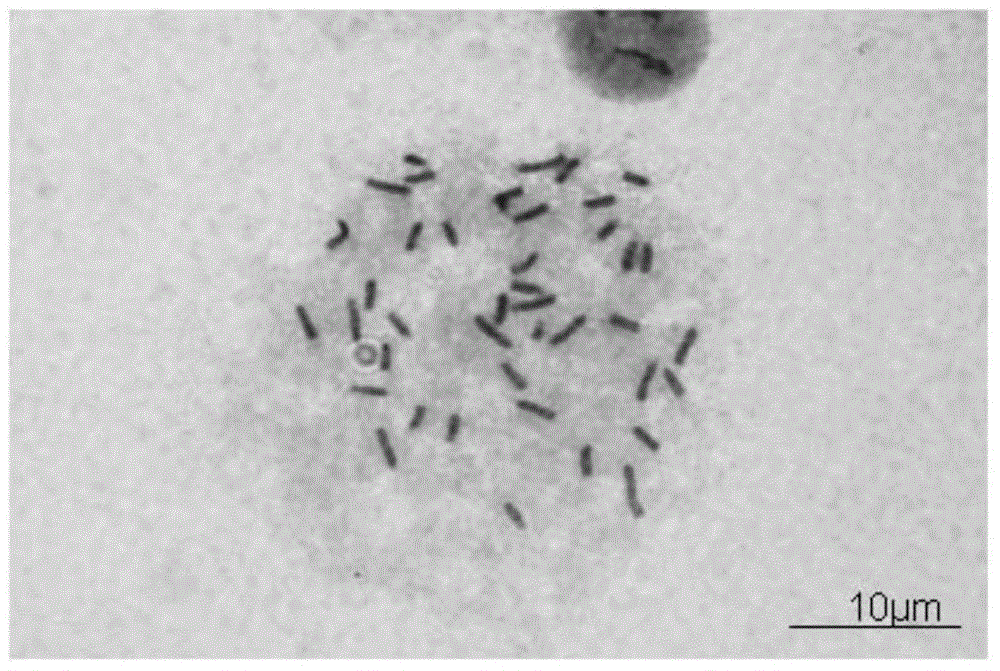
[0132] Example 3: Karyotype analysis and gender identification of mouse ES
[0133] 3.1 Karyotype analysis
[0134] (1) ES cells are cultured on a gelatin-coated petri dish, and the follow-up operations are carried out after the cells cover more than 80% of the petri dish;
[0135] (2) According to the results of the growth curve described in 2.4, add 50 ng / ml colchicine in the logarithmic growth phase, and continue culturing for 2 hours.
[0136] (3) Add EDTA-trypsin digestion solution after sucking up the culture solution, place it in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for 5 minutes, blow gently with a pipette, then collect the cell suspension into a graduated centrifuge tube, and store at room temperature Centrifuge at 800 rpm for 5 minutes.
[0137] (4) Use a pipette to remove the supernatant, leaving about 0.1ml, then add hypotonic solution 0.56% w / v KCl to make up to 1ml, and put it in a water bath for 5 minutes.
[0138] (5) Add methanol: glacial acetic acid = ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com