Degradable substrate for flexible optoelectronic device and manufacture method thereof
A technology of optoelectronic devices and substrates, which is applied in the fields of electrical solid-state devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, photovoltaic power generation, etc. Light transmittance, crystallinity reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0106] Such as figure 1 In the substrate structure shown, the flexible substrate 2 is shellac doped with UV-sensitive glue, and the conductive layer 1 is graphene. The preparation method is as follows:
[0107] ① Clean the rigid substrate with surface roughness less than 1nm, and dry it with dry nitrogen after cleaning;
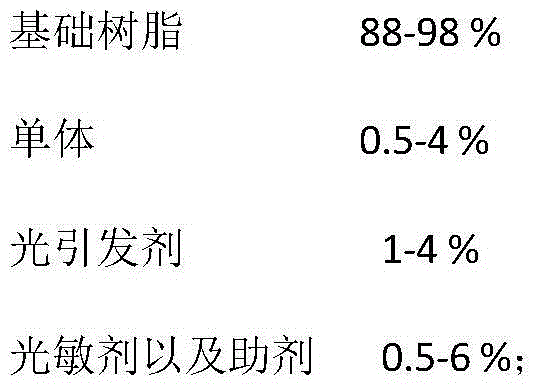
[0108] ② Prepare a flexible substrate by spin coating on a rigid substrate, the flexible substrate is shellac, and the shellac is mixed with a UV-sensitive glue with a mass ratio of 0.3%, and the film thickness is 100 μm. The UV-sensitive glue is A mixed system of free-radical UV-sensitive adhesive and cationic UV-sensitive adhesive, the mass ratio of free-radical UV-sensitive adhesive to cationic UV-sensitive adhesive is 1:10, and the raw material of the free-radical UV-sensitive adhesive includes 88% base Resin, 4% monomers, 4% photoinitiators and 4% photosensitizers and auxiliary agents; the cationic UV-sensitive adhesive raw materials include 98% cation...
Embodiment 2
[0114] Such as figure 1 In the substrate structure shown, the flexible substrate 2 is shellac doped with UV-sensitive glue, and the conductive layer 1 is carbon nanotubes. The preparation method is as follows:
[0115] ① Clean the rigid substrate with surface roughness less than 1nm, and dry it with dry nitrogen after cleaning;
[0116] ② Prepare a flexible substrate by spin coating on a rigid substrate, the flexible substrate is shellac, and the shellac is mixed with a UV-sensitive glue with a mass ratio of 0.5%, and the film thickness is 150 μm. The UV-sensitive glue is A mixed system of free-radical UV-sensitive adhesive and cationic UV-sensitive adhesive, the mass ratio of free-radical UV-sensitive adhesive and cationic UV-sensitive adhesive is 1:8, and the raw material of the free-radical UV-sensitive adhesive includes 90% base Resin, 3.5% monomer, 1% photoinitiator and 5.5% photosensitizer and auxiliary agent; the cationic UV-sensitive adhesive raw material includes 95...
Embodiment 3
[0122] Such as figure 1 In the substrate structure shown, the flexible substrate 2 is shellac doped with UV-sensitive glue, and the conductive layer 1 is silver nanowires. The preparation method is as follows:
[0123] ① Clean the rigid substrate with surface roughness less than 1nm, and dry it with dry nitrogen after cleaning;
[0124] ② Prepare a flexible substrate by spin coating on a rigid substrate, the flexible substrate is shellac, and the shellac is mixed with a UV-sensitive glue with a mass ratio of 0.9%, and the film thickness is 200 μm. The UV-sensitive glue is A mixed system of free-radical UV-sensitive adhesive and cationic UV-sensitive adhesive, the mass ratio of free-radical UV-sensitive adhesive and cationic UV-sensitive adhesive is 1:5, and the raw material of the free-radical UV-sensitive adhesive includes 92% base Resin, 3% monomers, 2% photoinitiators and 3% photosensitizers and auxiliary agents; the cationic UV-sensitive rubber raw material includes 93% ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com