Bacterial engineering
一种细菌、突变体的技术,应用在生物技术应用领域,能够解决方式不完全理解、不能等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
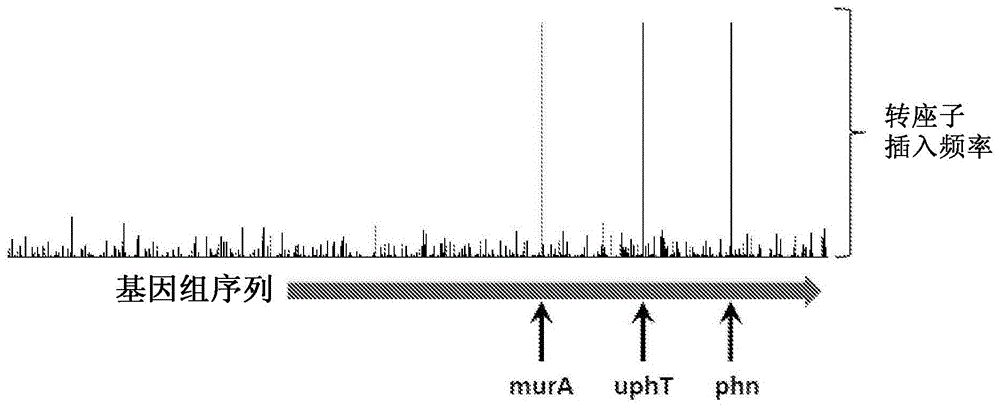
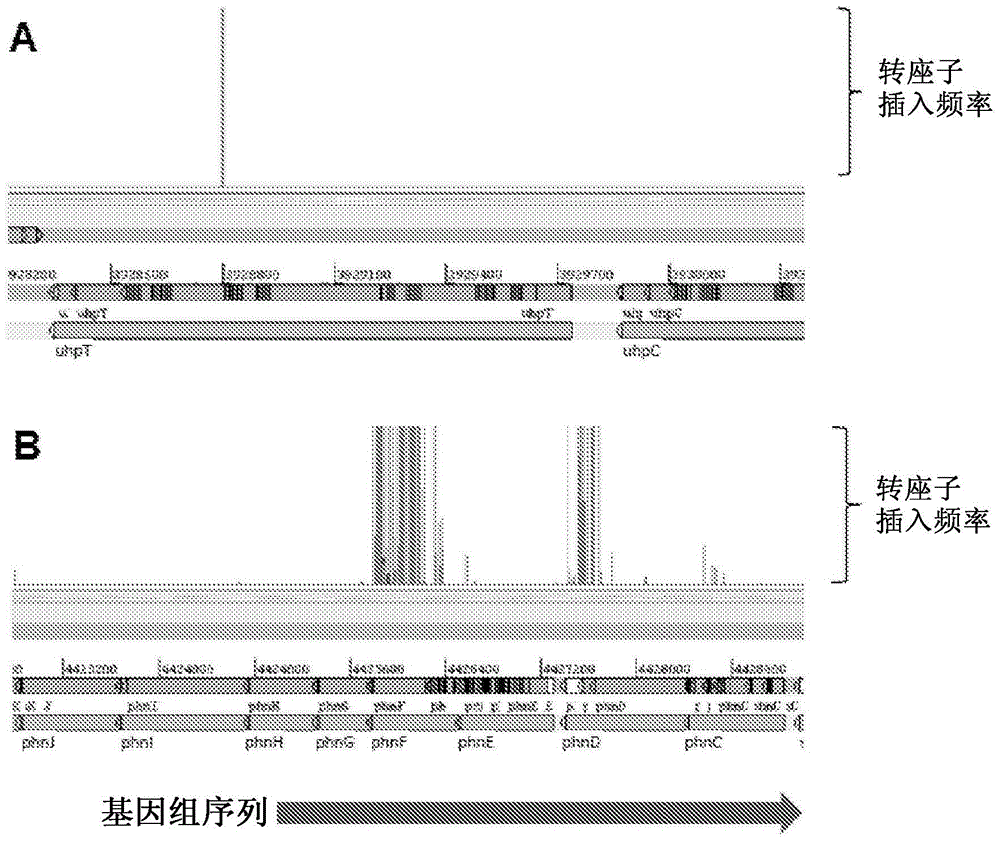
[0118] Example 1: Production of mutant bacteria exhibiting improved survival and / or growth in the presence of fosfomycin
[0119] (i) Activated transposon (Tn A ) construction
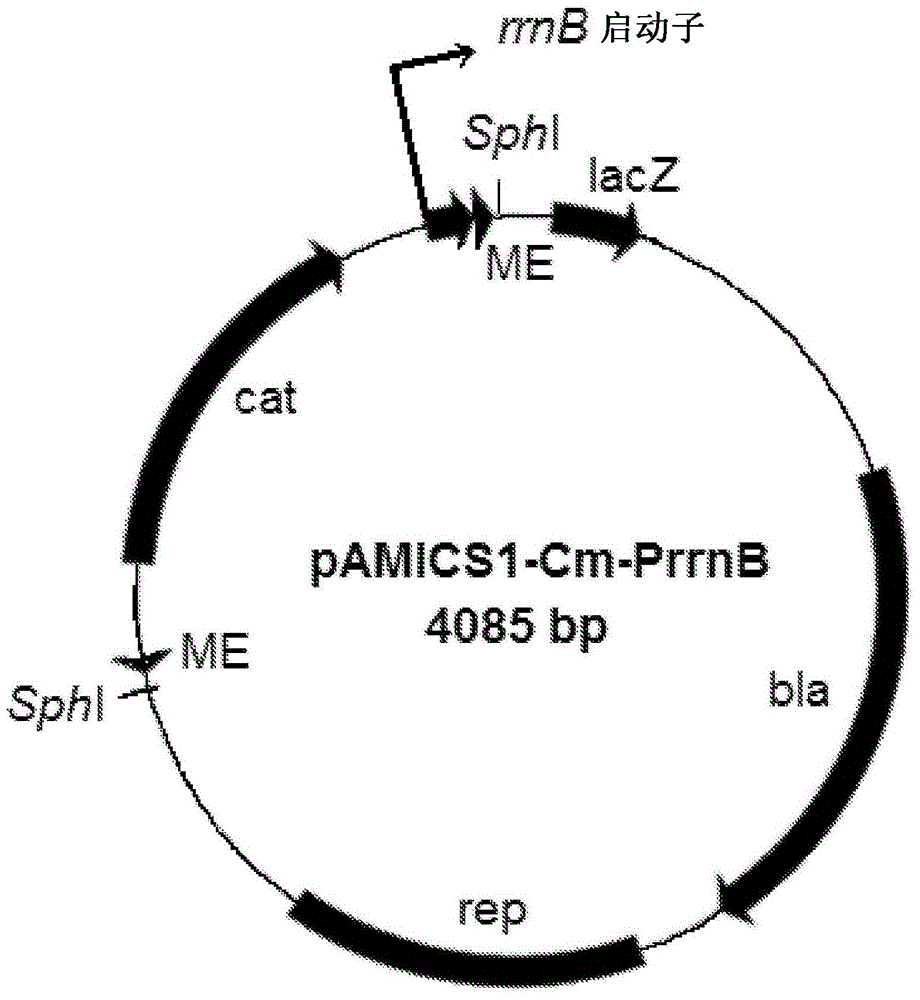
[0120] The constructed plasmid incorporates an amplifiable nucleotide sequence that acts as a transposon. Elements of the transposon include a 19 bp mosaic end recognized by a specific transposase and define a transposon (an antibiotic for selection of transformants produced by transposition- resistance gene), and an outward oriented promoter at one end of the transposon to activate the expression of a target gene adjacent to the transposon insertion site.
[0121] Alternative plasmids were constructed from different genes from E. coli, Acinetobacter, Pseudomonas or Rhodopseudomonas using different outwardly directed promoters. Table 1 provides details of the different promoters used. In addition, different host species bacteria require different antibiotic resistance genes to select transformants,...
Embodiment 2
[0157] Example 2: Mutant Rhodopseudomonas palustris exhibiting improved growth in industrial waste production
[0158] Rhodopseudomonas palustris is a purple photosynthetic bacterium that belongs to the α-proteobacteria. It has extraordinary metabolic versatility, growing by any of four life-supporting metabolic modes: photoautotrophy and photosynthesis (energy from light and carbon from carbon dioxide), photoheterotrophy (energy from light and carbon from organic compounds), chemoheterotrophy (carbon and energy from organic compounds) and chemoautotrophy (energy from inorganic compounds and carbon from carbon dioxide). This metabolic flexibility facilitates the use of this bacterium in biotechnological applications, including bioremediation of industrial waste.
[0159] Preparation of Electrocompetent Rhodopseudomonas palustris
[0160] Electrocompetent cells for transposon mutagenesis were prepared by inoculating 500 mL of Yeast Peptone Dextrose (YPD) broth with Rhod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com