Method for extracting lithium from solution containing lithium
A lithium solution and lithium extraction technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, extraction water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in recovering lithium carbonate and extracting lithium, and achieve a high recovery rate , the effect of efficient extraction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0165] Example 1: Concentrating the brine containing carbonate ions and separating the precipitate from solid-liquid
[0166] According to the following table 1, the preparation containing Li, Na, K, SO 4 , Cl, CO 3 etc. solution.
[0167] [Table 1]
[0168]
[0169] For the prepared as above containing Li, Na, K, SO 4 , Cl, CO 3 etc., using an evaporating concentrator, and evaporated under reduced pressure at a temperature of 40°C.
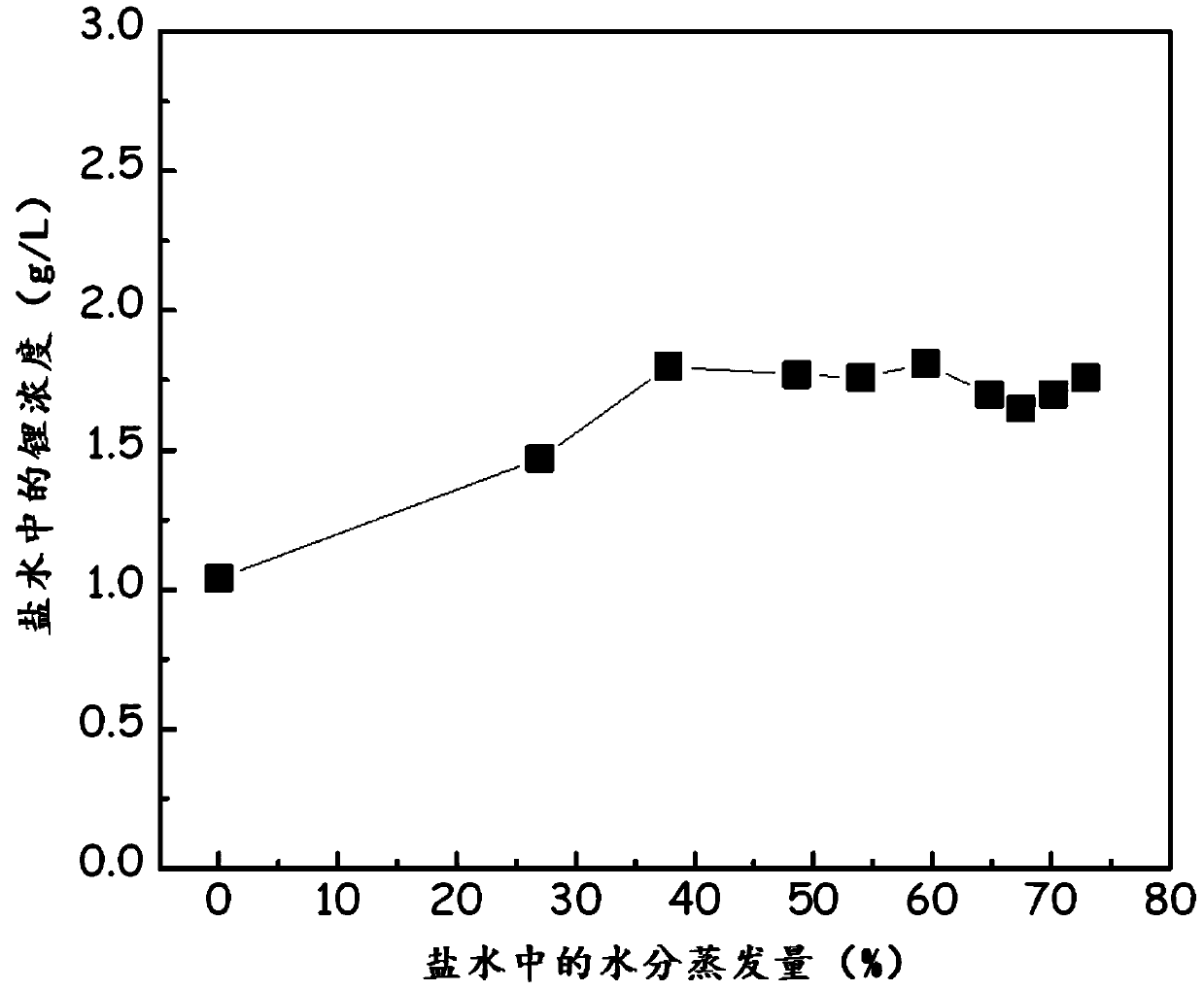
[0170] figure 1 Data showing changes in the concentration of lithium ions in the filtrate according to the amount of water evaporation when brine is concentrated.
[0171] When the brine is concentrated, as the water evaporates, the lithium concentration in the brine starts to rise from the initial 1.04g / L, and increases to 1.80g / L when the water evaporation is 37.8%.
[0172] However, when the water evaporation was greater than or equal to 37.8%, the lithium concentration did not increase even though the brine was concentrated, becau...
Embodiment 2
[0175] Example 2: Extraction of lithium phosphate from concentrated brine
[0176] Table 2 below shows the dissolved ion concentration in the filtered solution after evaporating 37.8% of the water in the brine containing a large amount of carbonate ions.
[0177] [Table 2]
[0178]
[0179] The lithium concentration of the concentrated filtered solution was 1.8 g / L, and after adding phosphoric acid equivalent to the lithium concentration equivalent, the lithium concentration was measured at room temperature at different times.
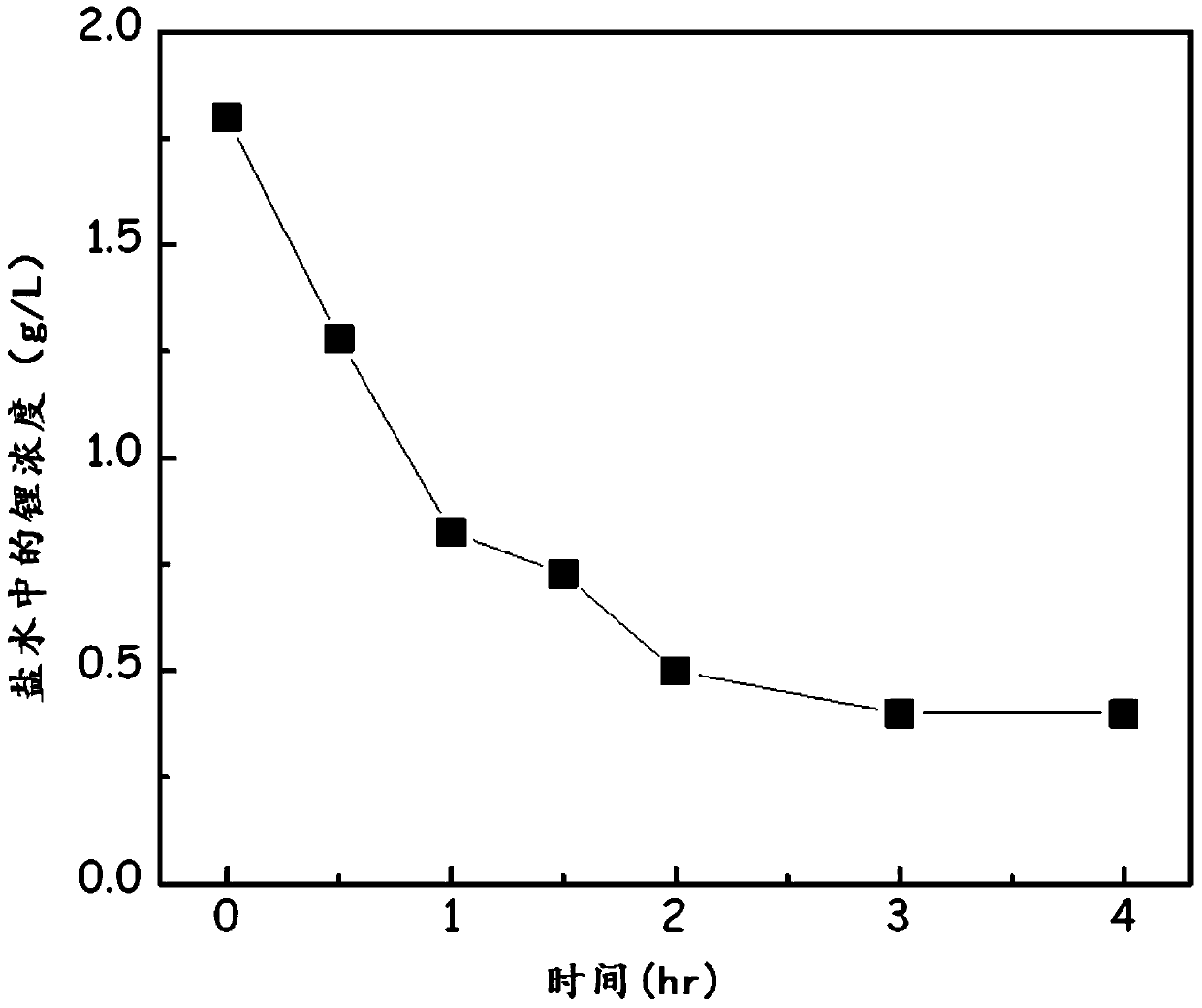
[0180] figure 2 Data showing the lithium concentration in the brine as a function of time after the addition of phosphoric acid.
[0181] Such as figure 2 As shown, the lithium concentration was initially 1.8g / L, and gradually decreased over time, and when the reaction time was 3 hours, the lithium concentration was 0.4g / L, and the lithium recovery rate was 77.7%.
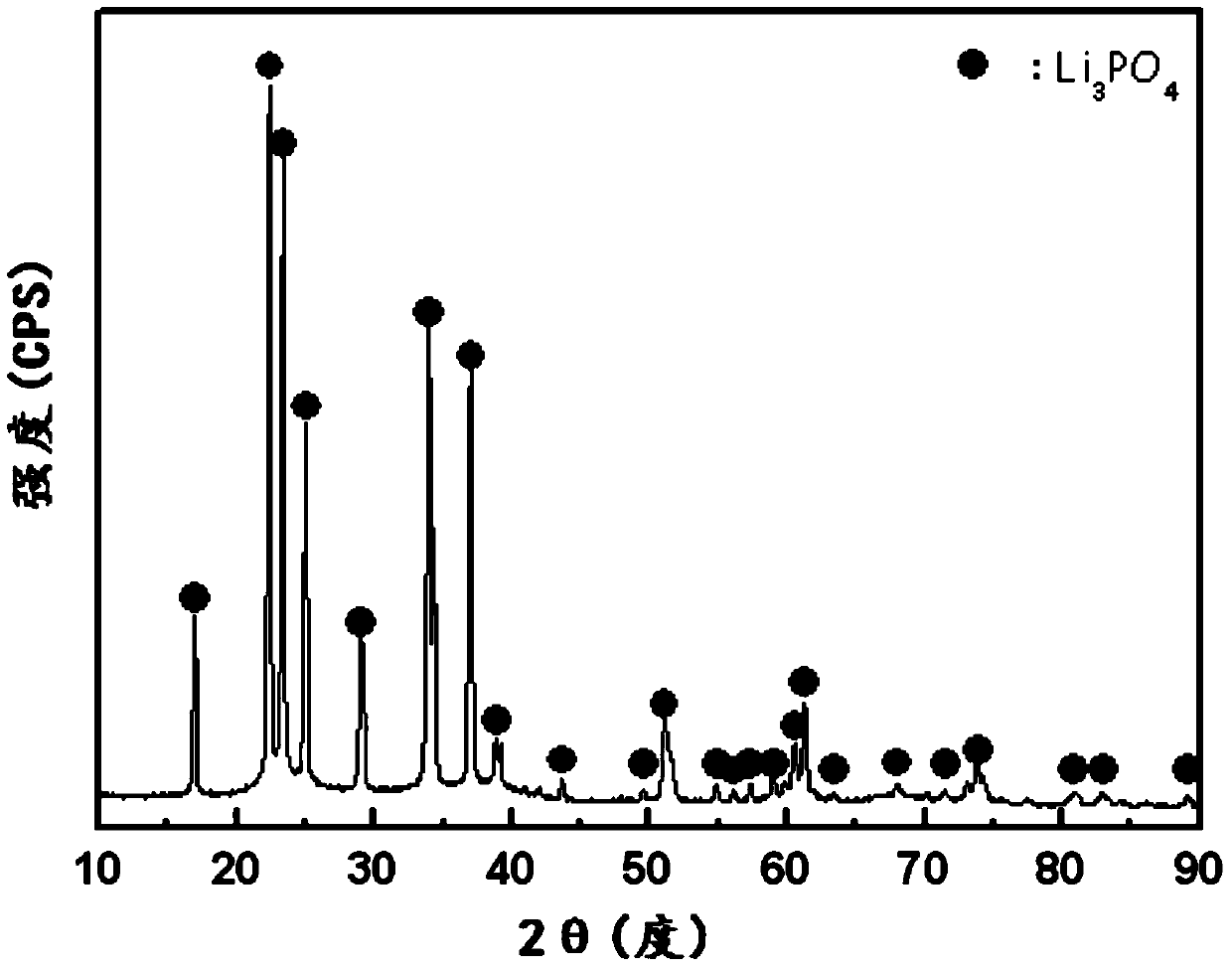
[0182] image 3 shows the mineral phase analysis results of the precipitate...
Embodiment 3
[0183] Example 3: Reconcentration of Filtration Solution and Extraction of Lithium Phosphate Using Nuclear Particles
[0184] The brine from which the lithium has been extracted is concentrated again to a range in which lithium is not precipitated. The main mineral phases of the precipitate are NaCl, KCl and NaK 3 (SO 4 ) 2 .
[0185] Table 3 below shows the composition of the filtered solution when the moisture evaporation rate is 60%.
[0186] [table 3]
[0187] project
Li
Na
K
SO 4
CO 3
Cl
Concentration(g / L)
0.877
143.1
74.6
21.0
67.9
156.5
[0188] To extract lithium from the solution, lithium phosphate was added as a seed to 1 equivalent of dissolved lithium, at which point no water-soluble phosphoric acid was added, and the lithium concentration at different times was subsequently measured.
[0189] Figure 4 The data showing the lithium concentration in the brine as a function of time a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com