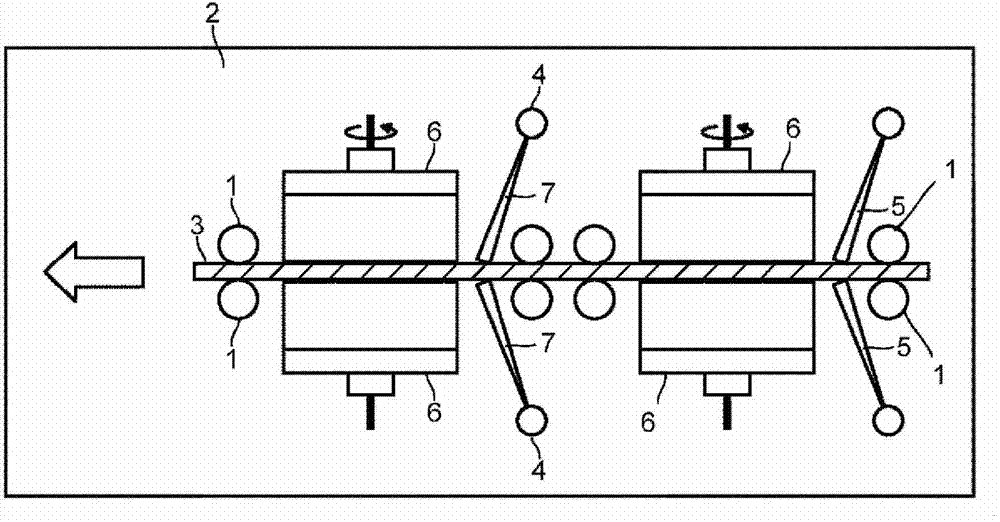
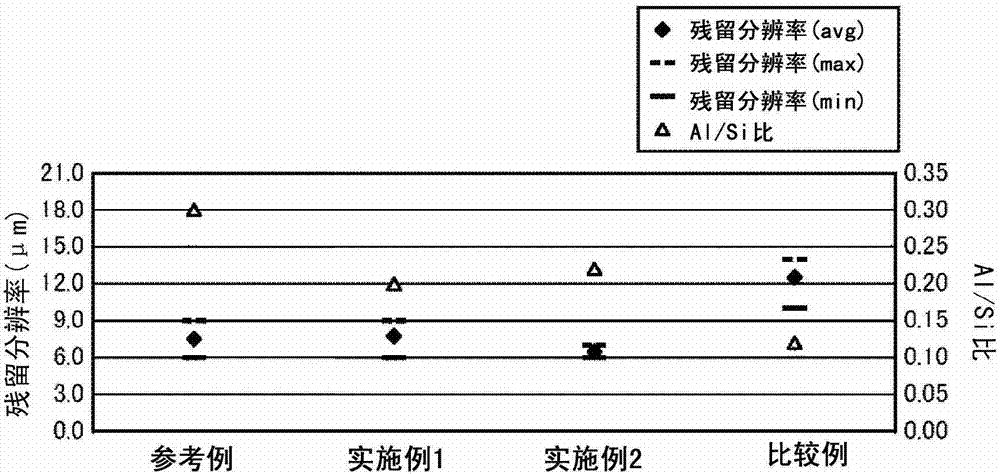
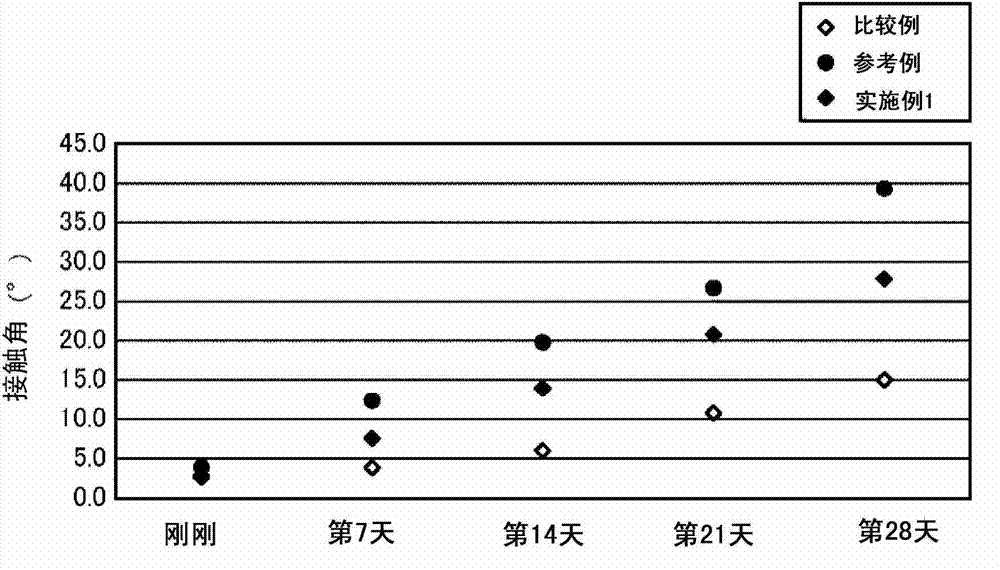
Glass substrate cleaning method
A glass substrate and cleaning liquid technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, detergent compositions, detergent compounding agents, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient cleaning performance, inability to fully remove abrasive residues, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing peeling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] In Examples 1 and 2, when the composition is recorded as 100 parts, an acidic compound containing 9.0 parts of organic phosphonic acid, 1.0 part of polycarboxylic acid salt, 10.0 parts of aromatic sulfonic acid and 1.0 part of amine-alkylene oxide, and the rest is water. Cleaning agent stock solution (manufactured by Parker Co., Ltd., trade name; PK-LCG491A) was diluted with water so that the concentration of the stock solution (including water) became 0.5%, and the obtained acidic cleaning solution (pH 2.3 to 2.8) was The surface of the polished glass substrate was sprayed at a flow rate of 25 L (hereinafter referred to as cleaning liquid flow rate) within 1 minute, while scrubbing with a rotating PVA brush, followed by acid cleaning and alkali cleaning. Alkaline cleaning was carried out by diluting the stock solution of alkaline cleaning agent (manufactured by Parker, trade name; PK-LCG211) with water so that the concentration of the stock solution (including water) be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com