Ecological enzymes that can rapidly increase the density and degradation efficiency of beneficial bacteria in the reaction environment
A degradation efficiency, ecological enzyme technology, applied in sustainable biological treatment, biological water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in greatly improving the degradation rate of pollutants and long domestication time, etc. Achieve the effect of inhibiting the production of miscellaneous bacteria, increasing the density of beneficial bacteria and increasing the density of bacteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] For the aerobic section of municipal and industrial sewage treatment, the ecological enzymes that can rapidly improve the degradation efficiency of municipal and industrial sewage treatment processes include multi-layer fiber filament structures and biological enzyme preparations; the raw materials of the biological enzyme preparations include strong bacterial flora and biological enzyme.
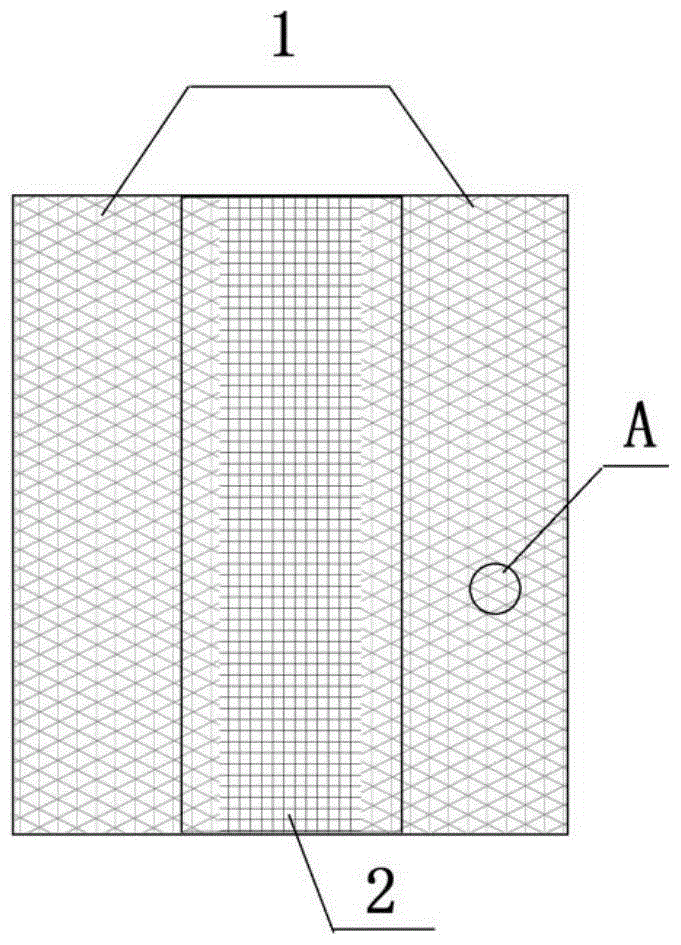
[0034] Among them, the multi-layer fiber filament structure such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the multi-layer fiber silk structure is composed of a loose layer, a dense layer and a nutrient base layer, the dense layer is sandwiched between two loose layers, the nutrient base layer is wrapped on the surface of the loose layer and the dense layer, and the nutrient base layer The thickness of the layer is 0.15mm, the thickness of the loose layer is 4.28mm, and the thickness of the dense layer is 2.57mm.
[0035] The loose layer is composed of fiber filaments, the dense layer is a...
Embodiment 2
[0038] This embodiment is the preparation method of the strong flora of embodiment 1, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0039] (1) Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Sphingomonas, denitrifying bacteria, saccharomyces, nitrifying bacteria, Pseudomonas stutzeri, and lactic acid bacteria were respectively cultivated to a saturated state in their respective culture media;
[0040] (2) Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Sphingomonas, denitrifying bacteria, saccharomyces, nitrifying bacteria, Pseudomonas stutzeri and lactic acid bacteria obtained by step (1) are by 10.3 with the number of effective viable bacteria: The ratio of 11.1: 16.4: 18.9: 15.8: 12.6: 14.9 is used for mixed culture, and fructooligosaccharides are added to the mixed flora according to the weight ratio of (8-10): 1 during the mixed culture process. Cultivate until the total number of effective viable bacteria is no less than 32 billion cfu / g.
Embodiment 3
[0042] This embodiment is the preparation method of the multi-layer fiber filament structure described in embodiment 1, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0043] (1) The fiber filaments are assembled into sheets to obtain a loose layer;
[0044] (2) the dense layer is sandwiched between two loose layers, and then 27% of the fiber filaments are pressed into the porous honeycomb structure of the dense layer, so that the loose layer and the dense layer are connected;
[0045] (3) Immerse the product obtained in step (2) in the nutrient base solution, wrap the nutrient base layer on its surface, and dry it at 110° C. for 30 minutes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com