Efficient method for radiochromic film dosimetry
A radiation dose and film technology, which is applied in the field of radiation-sensitive film dosimetry, can solve the problem of reducing the spatial resolution of array devices, and achieve the effect of eliminating influence and high spatial resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0039] According to certain aspects, the present application provides methods and systems for improved radiation dosimetry. According to one aspect, the present application illustrates how a universal calibration function can be generated using any calibration function determined for radiation sensitive films on a given scanner, and more particularly EBT2 and EBT3 radiochromic films. According to one embodiment, the method comprises:
[0040] 1) Expose film from a single batch of film to a number of known doses of radiation. The number of doses is preferably 3 or more.
[0041] 2) Along with the unexposed film, scan the exposed film on a scanner to obtain a digital image. To minimize errors from post-exposure time differences, these scans should be performed at least 24 hours post-exposure.
[0042] 3) Taking measurements on the portions of the digital image corresponding to the exposed film and the unexposed film. The measured values for each film in each color channel ...
Embodiment 1
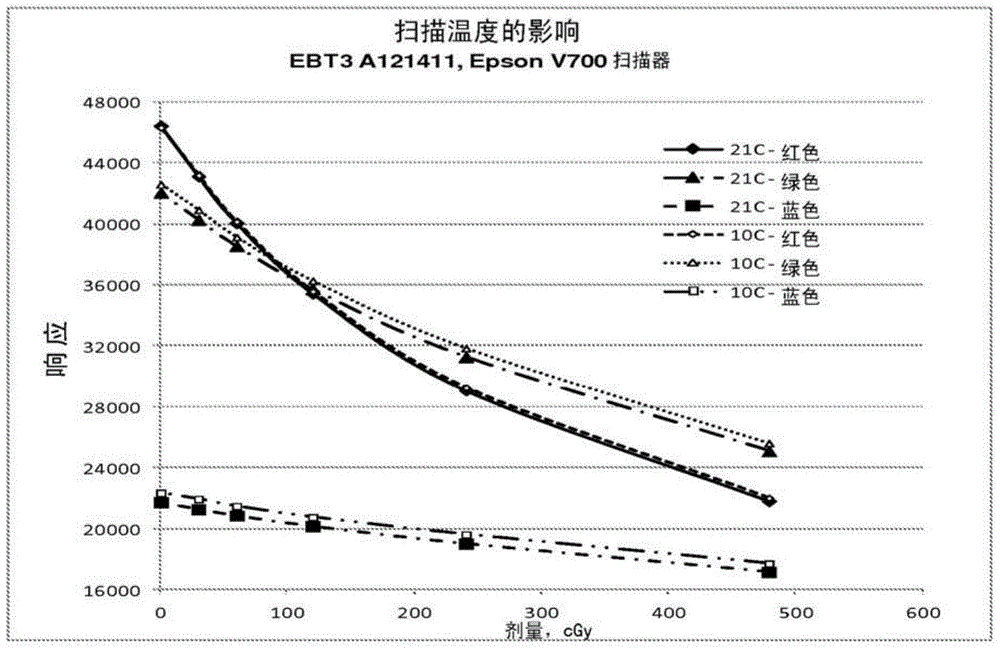
[0077] This embodiment relates to the scan-to-scan variability of an optical scanner. A piece of Gafchromic EBT3 radiochromic film was placed on the glass scanning window of an Epson 10000XL scanner. The film was scanned in transmission mode at intervals throughout the day to obtain a 48 bit rgb digital image of the radiochromic film with a spatial resolution of 72 dpi. The area corresponding to the radiochromic film in the digital image was measured using the software application FilmQA Pro. The measured values are shown in Table 1 below. Inspection of these values shows that they have a mean variability of about 0.5%.
[0078]
[0079] Table 1
[0080] Similar results were obtained from similar measurements made in the green and blue channels. Differences between scanned images are believed to occur for a number of reasons, including temperature variations over the day, instability of the scanner's light source, and variability within the scanner's individual opto...
Embodiment 2
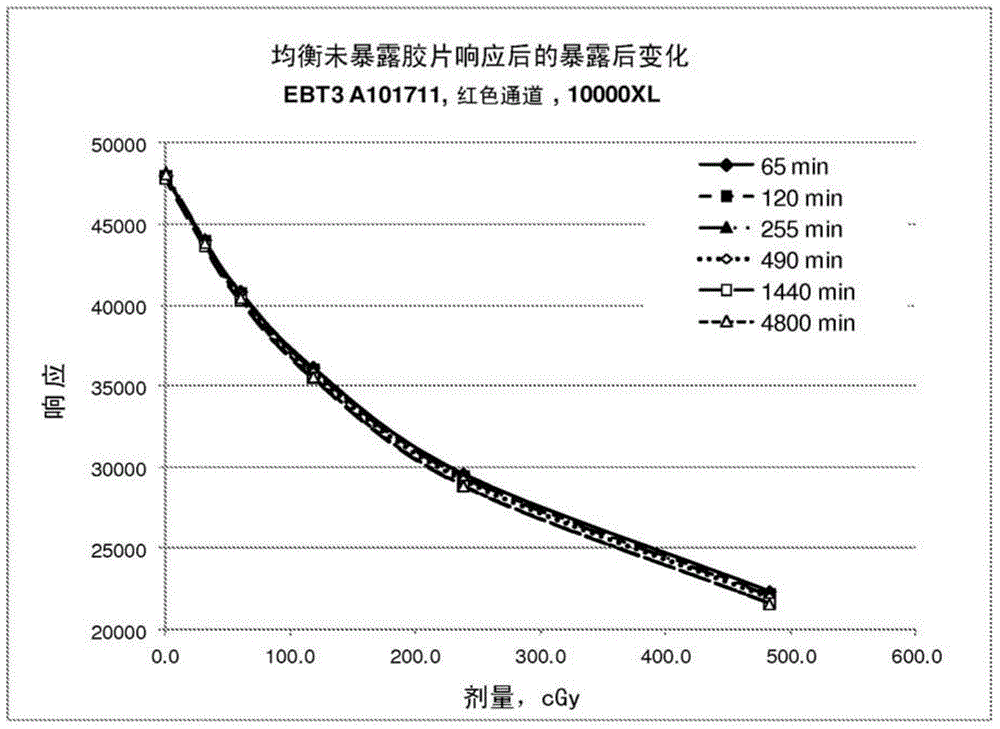
[0082]This example demonstrates the error in dose measurement due to the type of variability demonstrated in Example 1. Three pieces of Gafchromic EBT3 radiochromic film lot A101711 were exposed to calibrated X-ray radiation doses of 501.1 cGy, 253.2 cGy, and 123.7 cGy. Along with a piece of unexposed film from the same batch, and about two weeks after the film had been exposed, they were placed on an Epson V700 scanner and spaced with 72dpi was obtained from time to time throughout the day for about 16 hours 48-bit RGB digital image resolution. The purpose of waiting two weeks after film exposure is to allow the film to equalize. Gafchromic EBT3 radiochromic film is known to continue to darken after exposure, but the rate of change decreases rapidly over time. After two weeks, the rate of change was too small to be measured over the 16 hour period as used in data acquisition.
[0083] The area corresponding to the radiochromic film sample in the digital image was measured ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com