Acetobacter malorum and application thereof
A technology for bacillus apple cider vinegar and fruit vinegar, which is applied to the preparation of bacteria, vinegar, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of the bitterness of fruit vinegar being difficult to be widely accepted, the negative impact of industrial production, and the like.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1: Isolation and identification of acetic acid bacteria
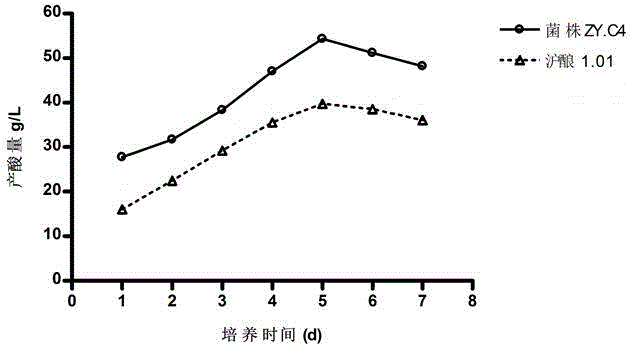
[0042] (1) Bacterial source preparation of commercially available citrus without rotten fruit, washed, beaten, and natural alcoholic fermentation first, and its sugar content was measured with a sugar meter every day. When the sugar content dropped to 5°BX and remained unchanged for a week, Start filtering. Filter with a double layer of boiled 80 mesh gauze, and store the filtrate in a stainless steel pot after filtering, that is, citrus wine. Cover the surface of the pot with gauze, and carry out natural acetic acid fermentation at 32°C to obtain naturally fermented vinegar liquid. After 5 days, the bacteria source was taken from the vinegar solution for screening and isolation.
[0043] (2) Strain isolation and screening process
[0044] Bacteria source—proliferation culture—dilution plate separation—preliminary screening—incline culture—liquid Erlenmeyer flask culture—confirmation of primary sc...
Embodiment 2
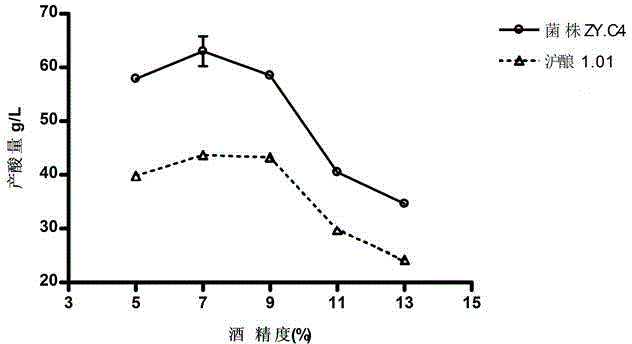
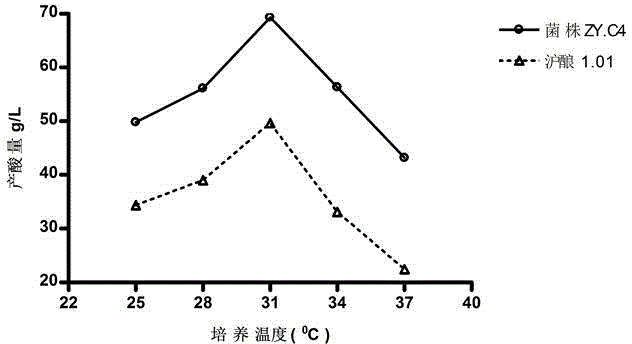
[0057] The performance measurement of embodiment 2 bacterial strains
[0058] 1. Physiological and biochemical tests:
[0059] The physiological and biochemical test results of Acetobacter malorum ZY.C4 are shown in Table 1
[0060] Table 1 Physiological and biochemical test results
[0061]
[0062] The strain ZY.C4 with high acid production was selected and sent to the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences for identification. The identification results are shown in Table 2. The ZY.C4 strain can not only oxidize ethanol, but also oxidize acetic acid, α-D-glucose, and inositol. Ability, and sensitive to troleandomycin, sodium lactate, tetrazolium blue, etc.
[0063] Table 2 Cell morphology and physicochemical experiment results of ZY.C4 strain
[0064]
[0065] 2. Toxicity test
[0066] According to GB / 4789.28-2003, the virulence test was carried out on the screened Acetobacter malorum (Acetobacter malorum) ZY.C4. They were inoculated in the enter...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Example 3 Production technology of citrus fruit vinegar
[0096] 1) preparing citrus fruit wine; including the following steps:
[0097] A: Preparation of glutinous rice saccharification solution: soak glutinous rice for 2-4 hours, drain and set aside; grind according to the ratio of water: glutinous rice = 2:1, adjust the pH to 6.2-6.4 with glacial acetic acid and sodium carbonate, add 1% (weight) Liquefaction enzyme, heated to 90-95°C to liquefy for 30 minutes, cooled to 60°C, adjusted pH to 4.5-5.0, then added 1% (weight) glucoamylase, saccharified at 60°C for 6-8 hours to obtain glutinous rice saccharification liquid;
[0098] B: Preparation of citrus juice: citrus peeled, citrus pulp mixed with 0.01% (weight) NaHSO 3 The aqueous solution was added to the beater at a ratio of 1:1, and after beating, 0.04% (weight) of pectinase was added for enzymolysis at 60°C for 60 minutes, after enzymolysis, filtered, and the filtrate was collected to obtain citrus juice;
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com