Method for preparing citrate nano zero-valent iron and method of activated persulfate thereof for treating organic wastewater
A technology for activating persulfate and nano-zero valent iron, which is applied in the field of water pollution treatment, can solve the problems of complex activation conditions, reduce the utilization rate of persulfate radicals, etc., and achieve high activation efficiency, enhanced recyclability, and high reaction efficiency. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
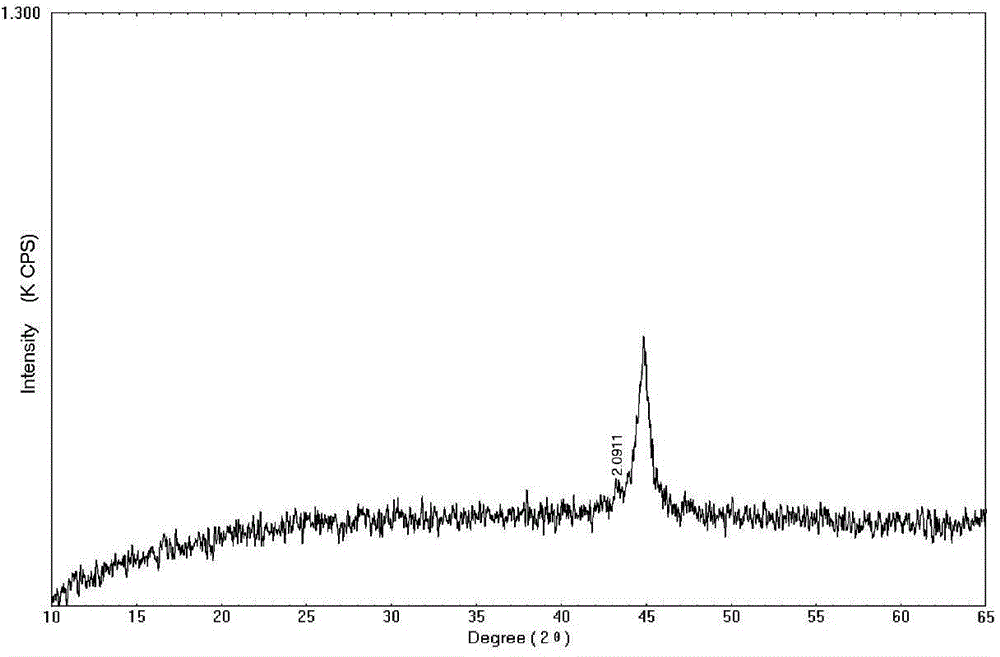
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] figure 1It is a flow chart of a method for treating organic wastewater by using citrate nanometer zero-valent iron to activate persulfate to treat organic wastewater according to a preferred embodiment of the present application. Such as figure 1 As shown, the method for using citrate nano zero-valent iron to activate persulfate to treat organic wastewater may further comprise the steps:
[0049] Step 10, adding peroxodisulfate and citrate stabilized nano zero-valent iron to the wastewater containing organic pollutants.
[0050] Wherein, the peroxodisulfate and the citrate-stabilized nanometer zero-valent iron can be added to the organic wastewater at the same time, or can be added to the organic wastewater separately, specifically according to needs. Specifically, the peroxodisulfate can be sodium peroxodisulfate, potassium peroxodisulfate or ammonium peroxodisulfate, and the molar ratio of the peroxodisulfate and organic pollutants can be determined according to the...
Embodiment 2
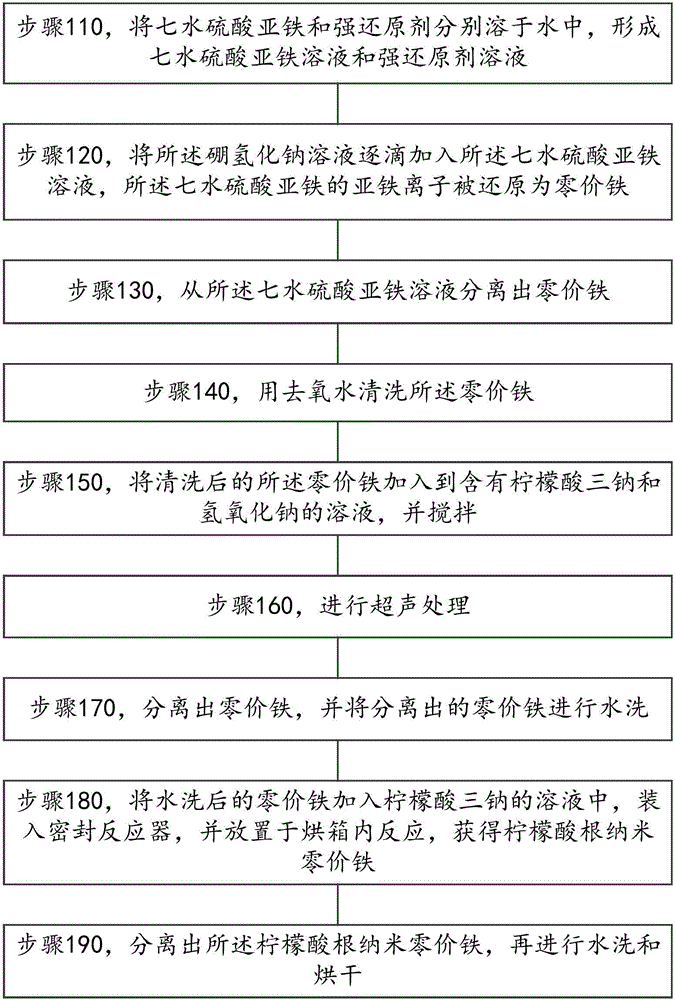
[0085] Based on the same inventive concept, the application also provides a method for preparing citrate nanometer zero-valent iron, please refer to figure 2 , the preparation method of the citrate nanometer zero-valent iron comprises the following steps:
[0086] Step 110, dissolving ferrous sulfate heptahydrate and strong reducing agent in water respectively to form ferrous sulfate heptahydrate solution and strong reducing agent solution. The strong reducing agent is specifically sodium borohydride or potassium borohydride. Specifically, when the strong reducing agent is sodium borohydride, 1.112 g of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate can be dissolved in 20 mL of water, and 0.4 g of sodium borohydride can be dissolved in 50 mL of water.
[0087] Step 120, adding the sodium borohydride solution dropwise to the ferrous sulfate heptahydrate solution, and the ferrous ions of the ferrous sulfate heptahydrate are reduced to zero-valent iron. When the ferrous ion of the ferrous sulfa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com