Activated carbon immobilized ionic liquid catalyst and application thereof
A technology of ionic liquid and activated carbon, which is applied in activated carbon-supported ionic liquid catalyst and its application field, can solve the problems of weak adsorption, easy detachment of ionic liquid, and easy destruction of carrier structure, and achieve the effect of easy separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
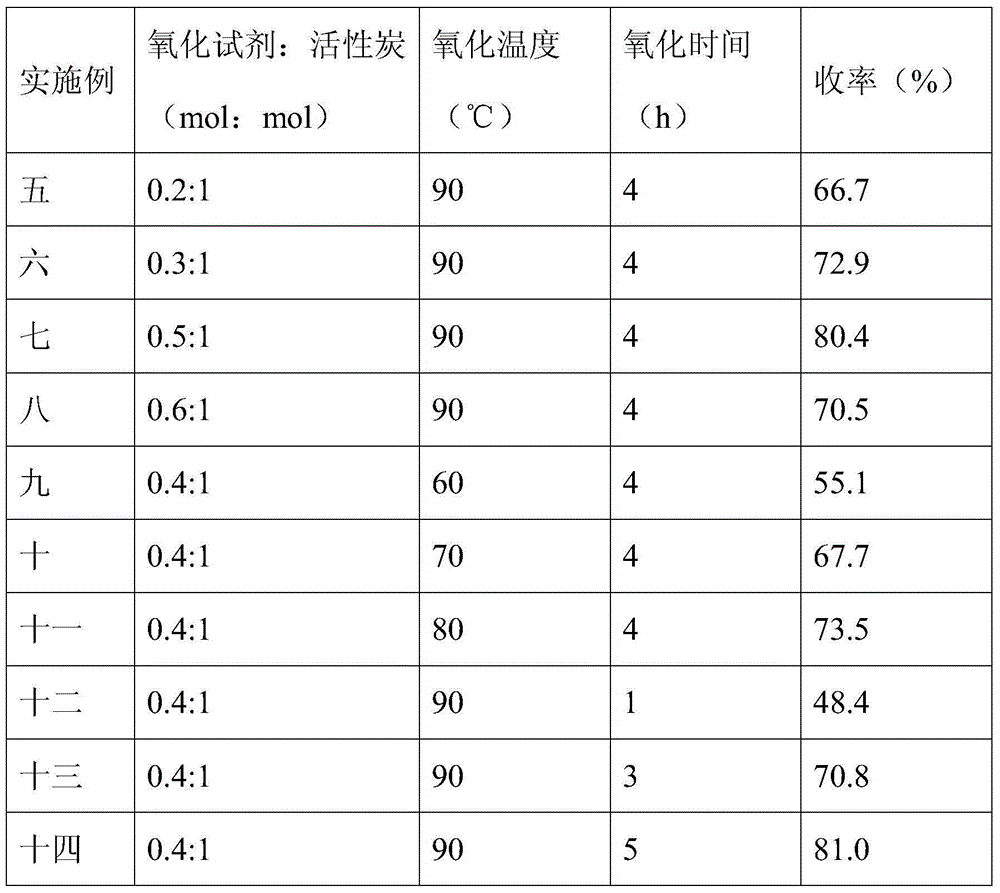
Embodiment 1 4
[0030]Examples 1 to 4 focus on the effect of the type of oxidizing agent in the oxidation treatment on the performance of the activated carbon-immobilized ionic liquid catalyst. The preparation method of the catalyst is as follows: 2 g of activated carbon and 20 mL of water are made into a slurry at a ratio of 1 g: 10 ml, and an oxidizing agent (nitric acid, hydrogen peroxide, peracetic acid, potassium permanganate, details See Table 1), heat at 90°C for 4 hours, filter, wash with deionized water until neutral and dry at 110°C to obtain activated carbon after oxidation treatment. Then 80 mL of thionyl chloride and 2 g of oxidized activated carbon were mixed at a ratio of 40 ml: 1 g, heat-treated at 60 ° C for 12 hours, and the remaining thionyl chloride was removed by distillation under reduced pressure to obtain activated carbon after oxidation and chlorination. Further, 0.5 g of oxidized and chlorinated activated carbon, 0.01 mol of 1-(2-aminoethyl hydrobromide) 3-methylimid...
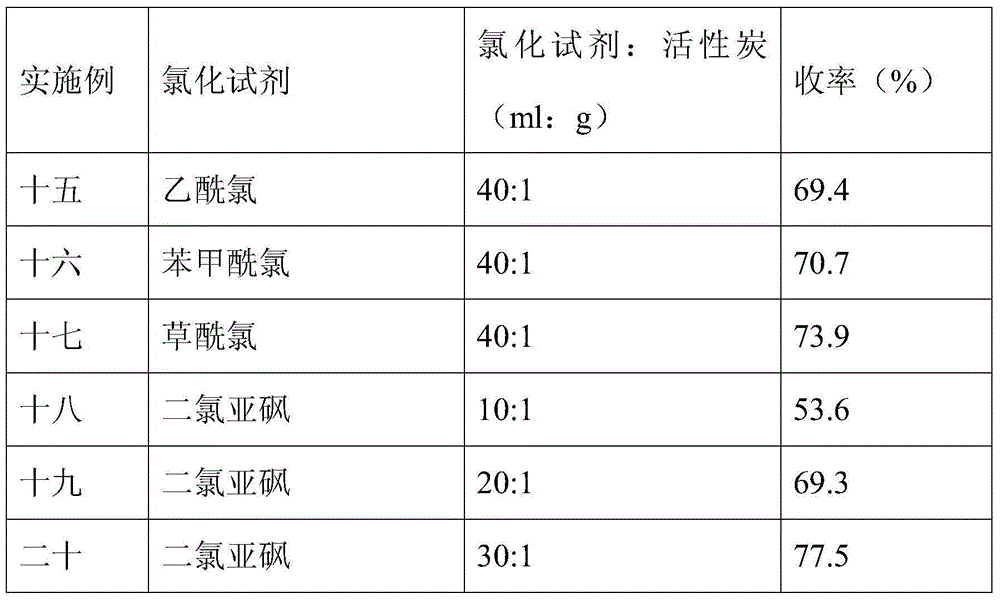
Embodiment 15 20
[0040] Examples 15 to 20 focus on the effects of the type and ratio of chlorination reagents in chlorination treatment on the performance of activated carbon-immobilized ionic liquid catalysts. The catalyst preparation method is as follows: make activated carbon and water into a slurry at a ratio of 1 g: 10 ml, add nitric acid with a molar ratio of 0.4: 1 to activated carbon, heat treatment at 90 ° C for 4 h, filter, wash with deionized water until neutral and place in Dry at 110°C to obtain activated carbon after oxidation treatment. Then different chlorination reagents (thionyl chloride, acetyl chloride, benzoyl chloride, oxalyl chloride, see Table 3 for details) and activated carbon after oxidation treatment were mixed in different proportions (see Table 3 for details), and heated at 60°C After 12 hours of treatment, the residual chlorination reagent was removed by distillation under reduced pressure to obtain activated carbon after oxidation and chlorination treatment. Fu...
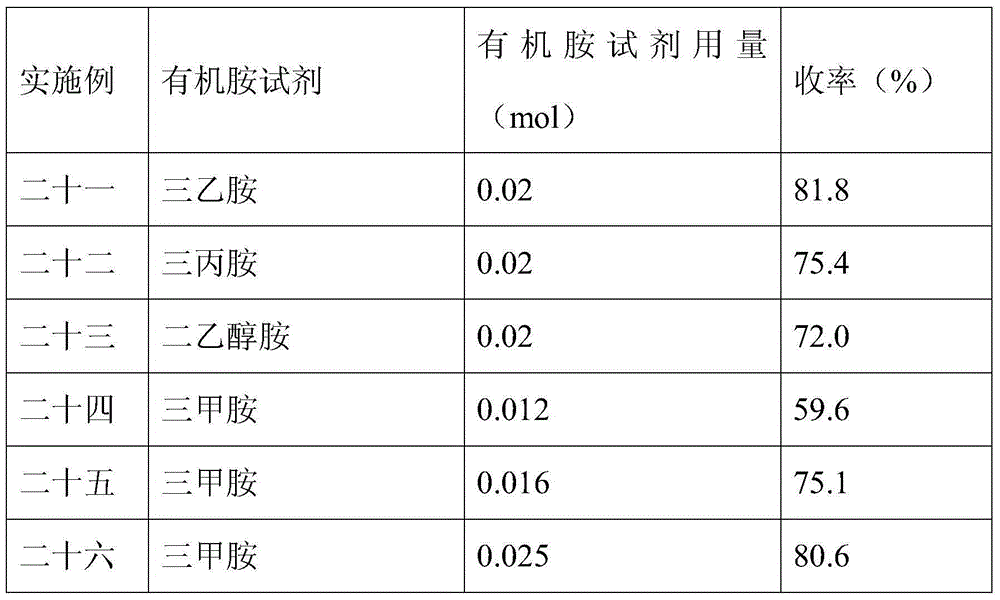
Embodiment 21
[0044] Embodiments 21 to 26
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com