Decision Evaluation Method for Active Emissions from Nuclear Power Plant Containment
An evaluation method and containment technology, applied in the fields of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of lack of evaluation methods, failure to clearly point out the conditions for terminating discharge, and high radioactivity level of leaked gas, and achieve emergency command. Scientific and reasonable, the effect of alleviating the release of fission products and reducing radioactive pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
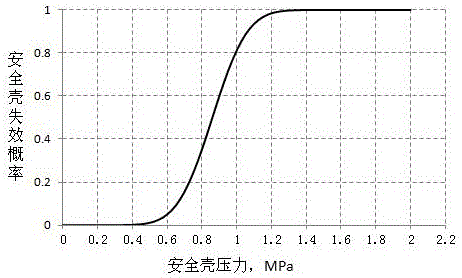
[0044] When the containment is facing the threat of overpressure after a serious accident, the decision-making evaluation method for active discharge of the containment carries out the decision-making evaluation step of overpressure threat mitigation, and the decision-making evaluation step of overpressure threat mitigation includes:
[0045] (S11) Calculate the expected value M1 of the radioactive dose consequences of the active discharge of the containment when the containment is threatened by overpressure. In this step, the radioactive dose and dose equivalent to the environment caused by the active discharge are pre-calculated, and M1 represents the total expected value of the discharged consequences , all possible probabilities and consequences should be considered comprehensively when calculating the expected value M1. For power plants with supplementary barrier equipment such as filtration, backflow, and retention, evaluate the effects of filtration, backflow, and retent...
Embodiment 2
[0054] On the basis of Embodiment 1, the decision-making evaluation method for the active discharge of nuclear power plant containment in this embodiment also includes the decision-making evaluation step of discharge termination after the threat of overpressure is eliminated, and the timing of terminating discharge is determined according to the analysis of actual monitoring results: 1) When the actual radioactive dose consequences are much greater than the expected value M1 of the active radioactive dose consequences or 2) when the actual radioactive dose consequences suddenly rise or 3) when the threat of containment overpressure is significantly alleviated, the active discharge should be stopped immediately.
[0055] Domestic power plants generally consider the need for active emissions from serious accidents in advance. The exhaust gas must eventually be discharged to the atmosphere through the chimney. The radioactive instrument in the chimney flow channel can monitor the a...
Embodiment 3
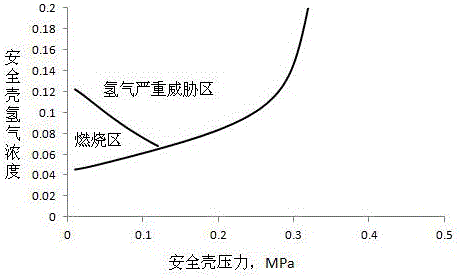
[0059] In this embodiment, on the basis of Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2, a hydrogen threat mitigation decision-making evaluation step is further added.
[0060] The consequences of a hydrogen explosion are far greater than the overpressure failure of the containment vessel, so a high-intensity hydrogen explosion must be predicted in advance. Similar to Example 1, it is first necessary to determine the critical value of the pressure at which the hydrogen explosion causes the containment to fail, and the expected value of the radioactive consequences of discharge under this critical pressure is the same as that of non-discharge, and the method includes the following steps:
[0061] (S21) Calculating the expected value M2 of radioactive dose consequences of active emissions when there is a hydrogen threat, the method is the same as step S11 in embodiment 1;
[0062](S22) To predict the pressure critical value E1 of the hydrogen explosion threat in the containment, first set M2=N2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com