Method for preparing methyl levulinate from biomass saccharide by using acidified montmorillonite as catalyst
A technology of methyl levulinate and biomass sugar, which is applied in the field of organic synthesis, can solve the problems of complicated preparation, harsh conditions, expensive raw materials, etc., and achieves the effects of simple preparation, mild reaction conditions, and easily available raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The preparation method of the hydrogen-type montmorillonite is as follows: 1g of K10-montmorillonite is added to 50ml of sulfuric acid solution (the mass concentration of the sulfuric acid solution is 20%), heated to 100°C and stirred for 0.5 to 2 hours, then stop heating and continue Stir for 0.5-1 hour. The obtained mud was filtered, washed several times with deionized water to remove sulfuric acid, and then dried at 120°C for a day and night to obtain H-MMT. The final gray powder was named 20-H-MMT.
[0024] The sulfuric acid solution concentration of 20% was replaced by 5%, 10% or 30%, and the finally obtained gray powder was named 5-H-MMT, 10-H-MMT or 30-H-MMT respectively. And all of them can be used as catalysts to catalyze the preparation of methyl levulinate from biomass sugar.
Embodiment 2
[0026] The preparation method of the sulfated montmorillonite is as follows: 1g of K10-montmorillonite is added to 50ml of sulfuric acid solution (the mass concentration of sulfuric acid solution is 20%), heated to 100°C, stirred and reacted for 0.5 to 2 hours, and the heating is stopped Stirring was continued for 0.5-1 hour. The obtained mud was filtered and then calcined at 500 °C for 5 h to obtain SO 4 2- / MMT. The final powder was named 20-SO 4 2- / MMT (wherein 20 represents that the mass concentration of the sulfuric acid solution used is 20%), can be used as a catalyst to catalyze the preparation of methyl levulinate from biomass sugar.
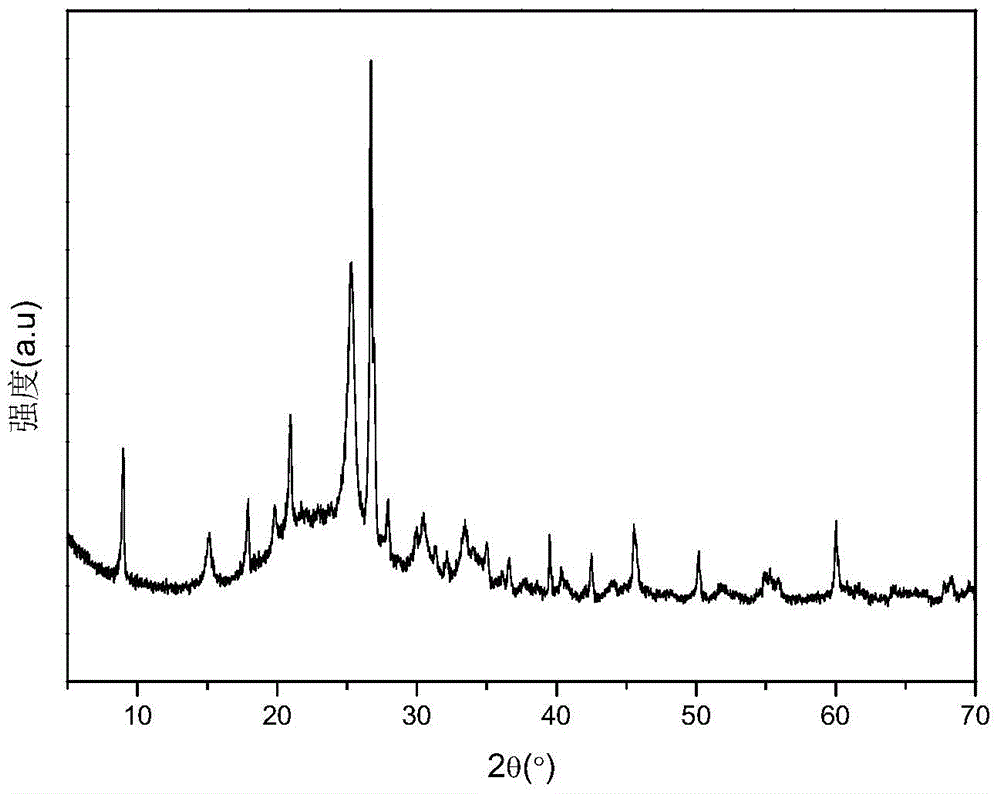
[0027] image 3 Give the 20-SO that this embodiment makes 4 2- / MMT catalyst XRD patterns.
[0028] Replace 20% of the mass concentration of sulfuric acid with 5%, 10% or 30%, and the final powders are named 5-SO 4 2- / MMT, 10-SO 4 2- / MMT or 30-SO 4 2- / MMT. And all of them can be used as catalysts to catalyze the prepar...
Embodiment 3
[0030] 0.18g (1mmol) glucose and 20-SO4 roasted at 500°C for 5h 4 2- / MMT catalyst 0.15g and anhydrous methanol 20ml were placed in a 30mL autoclave, sealed the autoclave, and reacted at 200°C for 4h, and filtered to obtain the methyl levulinate solution after the autoclave was cooled, and added the internal standard Naphthalene (16mg), to be tested.
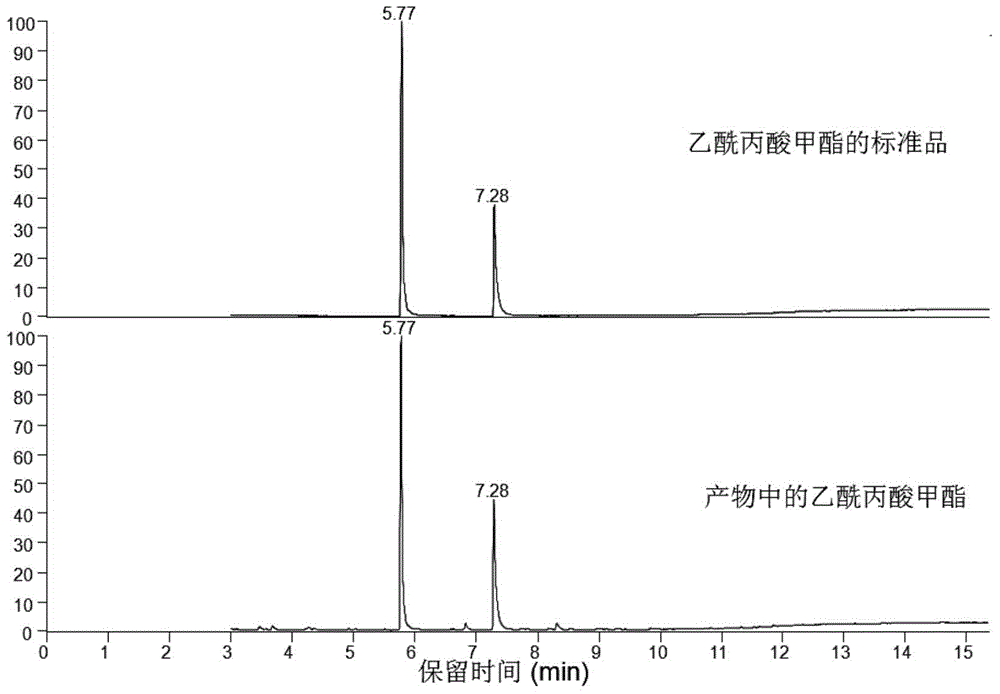
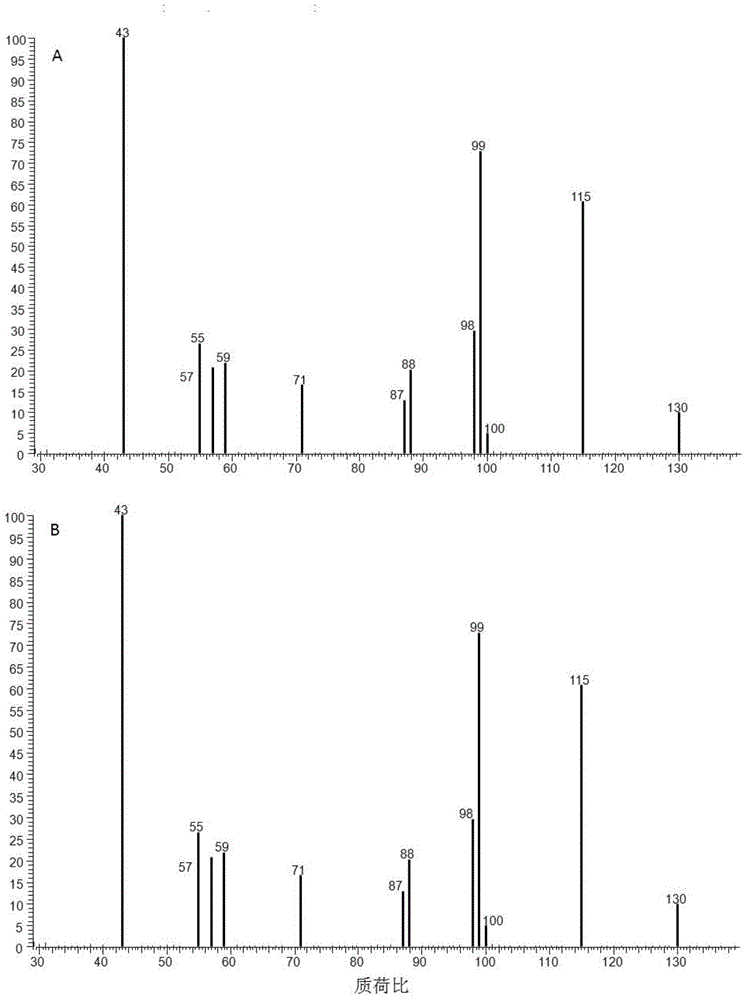
[0031] figure 1 The gas chromatogram of the product methyl levulinate is given and compared with the gas chromatogram of the methyl levulinate standard. figure 2 The mass spectrum of the product methyl levulinate is given, and compared with the mass spectrum of the methyl levulinate standard.
[0032] The obtained solution was detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS model is TRACE DSQ). According to the concentration-peak area standard curve and the product peak area, the molar yield of methyl levulinate in the product of Example 3 can be calculated to be 48%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com