Detoxification and fermentation method of large red algae biomass degradation liquid
A fermentation method and technology for degrading liquid, applied in fermentation, biofuel and other directions, can solve the problems of single type of inhibitor, increased extra cost, low removal efficiency, etc., and achieve the effects of low cost, short time consumption and fast start-up speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
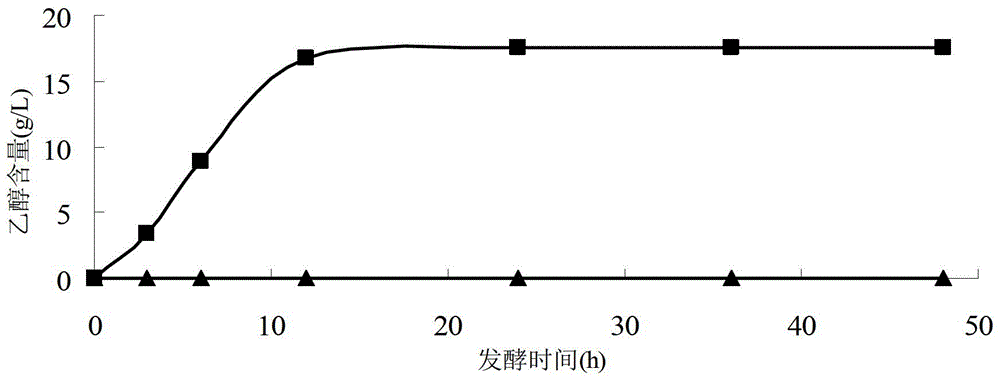
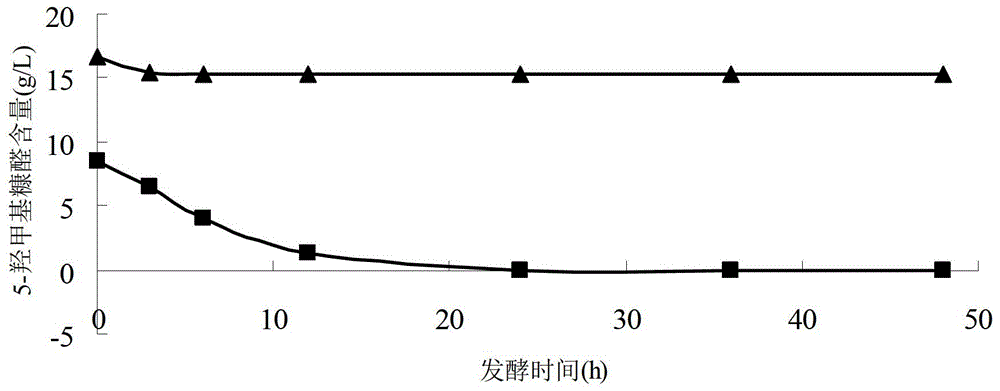
[0025] In this embodiment, the algae biomass is Gelidiales, and the liquid acid hydrolyzate of the algae biomass is anaerobically fermented to obtain ethanol. The detoxification agents are activated carbon and bentonite. The specific process is as follows.
[0026] (1) Take 200 grams of dry rock cauliflower, crush it, add 1 liter of 2% sulfuric acid solution, and mix well. Under the environment of 125 degrees centigrade, acid hydrolyze for 2 hours, and press filter to obtain the degradation liquid of Geliflower. Sodium hydroxide was added to the degradation solution to adjust the pH to 6.0.
[0027] (2) Measure 50 ml of degradation solution, add 1 g of activated carbon, and detoxify in a shaker for 30 minutes at a speed of 150 rpm. After detoxification, remove the activated carbon by suction filtration. Then, take 1 gram of calcium-based bentonite, add it into the detoxified degradation liquid through activated carbon, and carry out double detoxification. bentonite, and th...
Embodiment 2
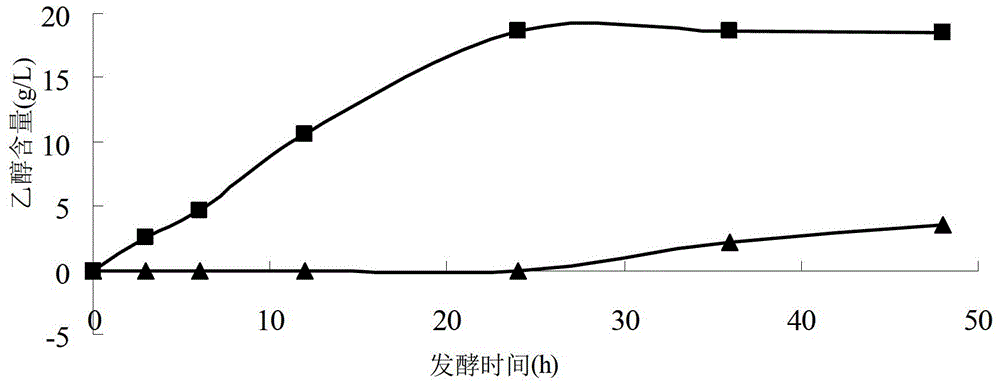
[0041] In this embodiment, the algae biomass is Grateloupia, and the enzymatic hydrolysis product of the algae biomass is subjected to anaerobic fermentation to obtain ethanol. The detoxification agent is β-molecular sieve and diatomaceous earth.
[0042] (1) Weigh 300 grams of centipede algae powder, add 1 liter of 4% phosphoric acid aqueous solution and mix well. Degrade at 100°C for 1 hour to make up for the evaporated water. Use sodium hydroxide powder to adjust the pH of the acid degradation solution to 6.5, add 200 U / g of liquefying enzyme, and degrade at 60°C for 72 hours. After the liquefaction enzyme degradation process was completed, the pH of the degradation solution was adjusted to 5.0 with hydrochloric acid, and then 100 U / g of glucoamylase was added to continue the enzymatic hydrolysis at 60°C for 72 hours, and then squeezed and filtered to obtain the degradation solution.
[0043] (2) Measure 50 ml of the degradation solution, adjust the pH to 6.0 with sodium ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] In this embodiment, the algae biomass is Porphyra, and the acid gas explosion hydrolyzate of the algae biomass is anaerobically fermented to obtain butanol. The detoxification agent is active carbon, ZSM-5 molecular sieve and NaY molecular sieve.
[0058] (1) Weigh 300 grams of laver powder, add 0.5 liter of 4% nitric acid aqueous solution, mix well, and soak at room temperature for 2 hours. Put it into a steam explosion machine, process it at 180 degrees Celsius and 1.2Mpa for 3 minutes, quickly release the pressure, add 0.5 liters of water to the obtained product, stir well, squeeze and filter to obtain a degradation solution, and use calcium hydroxide powder to adjust the pH of the degradation solution to 7.0.
[0059] (2) Measure 50 ml of degradation solution, add 0.25 g of activated carbon, stir continuously at 50 degrees Celsius for 10 minutes for detoxification, and remove the activated carbon by suction filtration after detoxification. Then add 0.25 g of ZSM-5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com