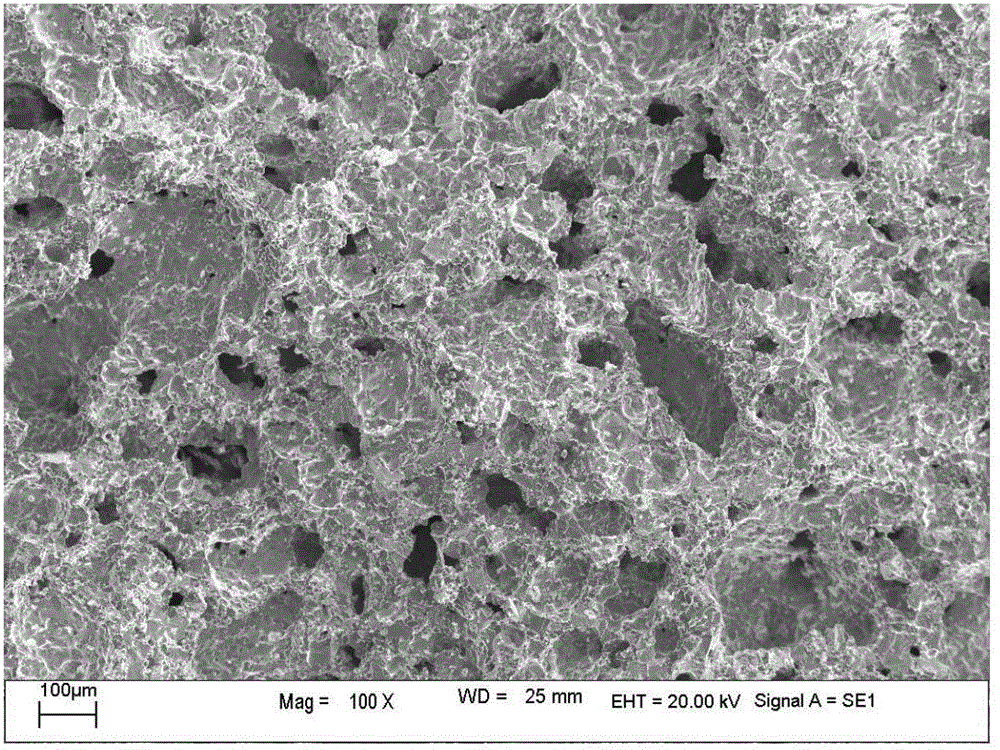
Method for preparing light Nb-Ti-Al based porous material
An nb-ti-al, porous material technology, applied in the field of powder metallurgy porous materials, can solve problems such as low strength, and achieve the effects of improving strength, simple process, flexible and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Example 1: Preparation of lightweight Nb-Ti-Al-based porous material with a porosity of 25%
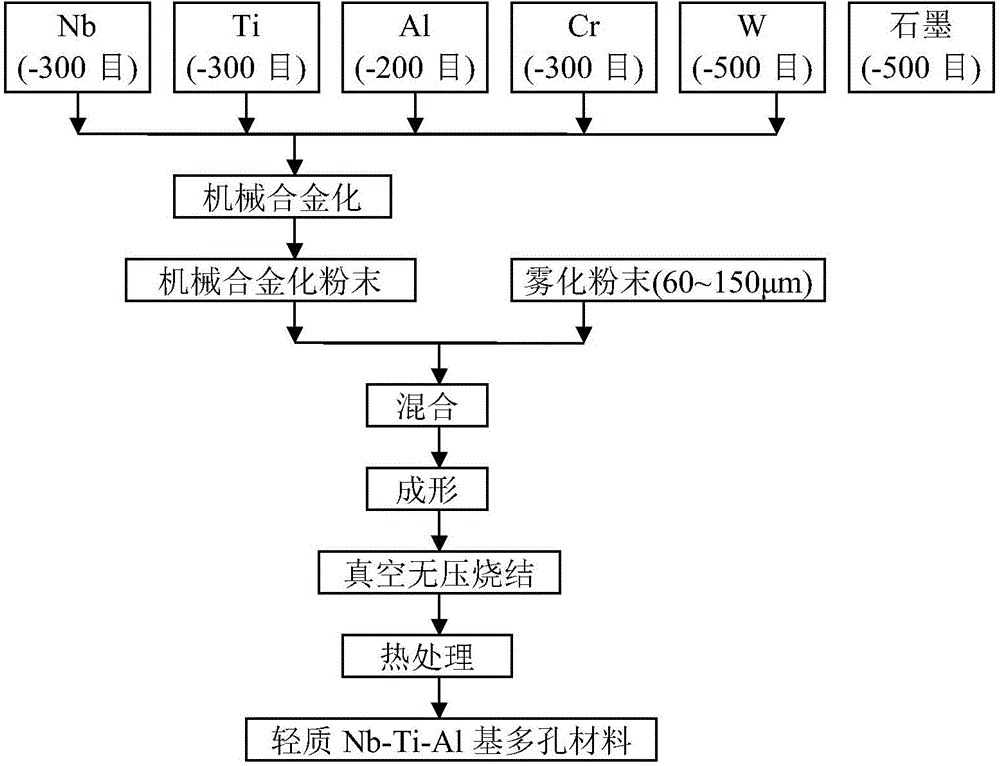
[0017] Using -300 mesh niobium powder, -300 mesh titanium powder, -200 mesh aluminum powder, -300 mesh chromium powder, -500 mesh tungsten powder, -500 mesh graphite powder as raw materials, according to the composition ratio of mechanical alloying powder quantity. The composition of the mechanical alloying powder is: 27wt.%Ti-6wt.%Al-2wt.%Cr-1wt.%W-0.02wt.%C-balance Nb. Add 0.5wt.% stearic acid to the raw material powder and pre-mix evenly, and then uniformly disperse various alloying elements in the niobium matrix by high-energy ball milling in a high-purity Ar atmosphere to form a supersaturated solid solution. The ball / material ratio was 15 / 1, the rotational speed of the ball mill was 500 rpm, and the ball milling time was 36 hours, to obtain a mechanically alloyed powder with an average particle size of 18 μm. The mechanical alloying powder and the rotating electrode ato...
Embodiment 2
[0018] Example 2: Preparation of lightweight Nb-Ti-Al-based porous material with a porosity of 29%
[0019] Using -300 mesh niobium powder, -300 mesh titanium powder, -200 mesh aluminum powder, -300 mesh chromium powder, -500 mesh tungsten powder, -500 mesh graphite powder as raw materials, according to the composition ratio of mechanical alloying powder quantity. The composition of the mechanical alloying powder is: 28wt.%Ti-8wt.%Al-4wt.%Cr-5wt.%)W-0.03wt.%C-balance Nb. Add 1wt.% stearic acid to the raw material powder and pre-mix evenly, and then uniformly disperse various alloying elements in the niobium matrix by high-energy ball milling in a high-purity Ar atmosphere to form a supersaturated solid solution. The ball / material ratio was 17 / 1, the rotational speed of the ball mill was 400 rpm, and the ball milling time was 24 hours, to obtain a mechanically alloyed powder with an average particle size of 32 μm. The mechanical alloying powder and the rotating electrode atom...
Embodiment 3
[0020] Example 3: Preparation of lightweight Nb-Ti-Al-based porous material with a porosity of 32%
[0021]Using -300 mesh niobium powder, -300 mesh titanium powder, -200 mesh aluminum powder, -300 mesh chromium powder, -500 mesh tungsten powder, -500 mesh graphite powder as raw materials, according to the composition ratio of mechanical alloying powder quantity. The composition of the mechanical alloying powder is: 30wt.%Ti-8wt.%Al-6wt.%Cr-3wt.%)W-0.05wt.%C-balance Nb. Add 1.5wt.% stearic acid to the raw material powder and pre-mix evenly, and then uniformly disperse various alloying elements in the niobium matrix by high-energy ball milling in a high-purity Ar atmosphere to form a supersaturated solid solution. The ball / material ratio was 19 / 1, the rotational speed of the ball mill was 450 rpm, and the ball milling time was 48 hours to obtain a mechanically alloyed powder with an average particle size of 27 μm. The mechanical alloying powder and the rotating electrode atom...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com