New mutant pathogenic gene of febrile convulsion as well as coding protein and application thereof
A gene and protein technology, applied in the field of new mutation-causing genes for febrile convulsions, can solve the problems of increased complexity, scalability, and complexity of the disease
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: Screening of FS-related pathogenic gene loci from families with dominant inheritance of FS
[0043] 1. Sample collection
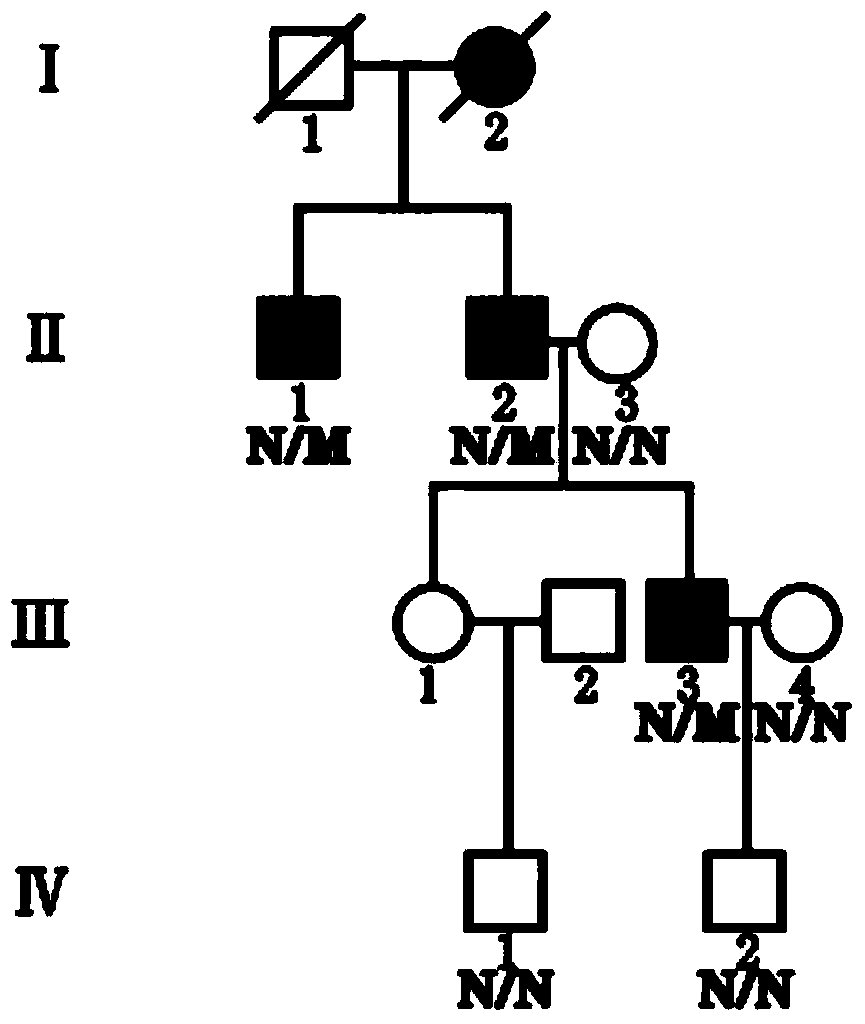
[0044] In recent years, the inventor of the present application has collected a four-generation Chinese family of FS dominant inheritance (such as figure 1 7 samples in ), including 3 patients (II-1, II-2, and Ⅲ-3) and 4 control samples (II-3, Ⅲ-4, Ⅳ-1 and Ⅳ-2). The disease diagnosis is based on fever The family history of sexual convulsions, clinical and biochemical indicators, and imaging evidence, combined with the familial cases collected by the inventor, suggest that FS is more likely. Take these 7 samples as research samples, and collect 2ml of peripheral blood samples for each sample, add EDTA for anticoagulation, and store at -80 degrees Celsius.
[0045] 2. DNA extraction
[0046] Use OMEGA Blood DNA Midi Kit whole blood DNA extraction kit to extract DNA from peripheral blood samples. The extraction steps are as follows:
[0047] (1) Tak...
Embodiment 2
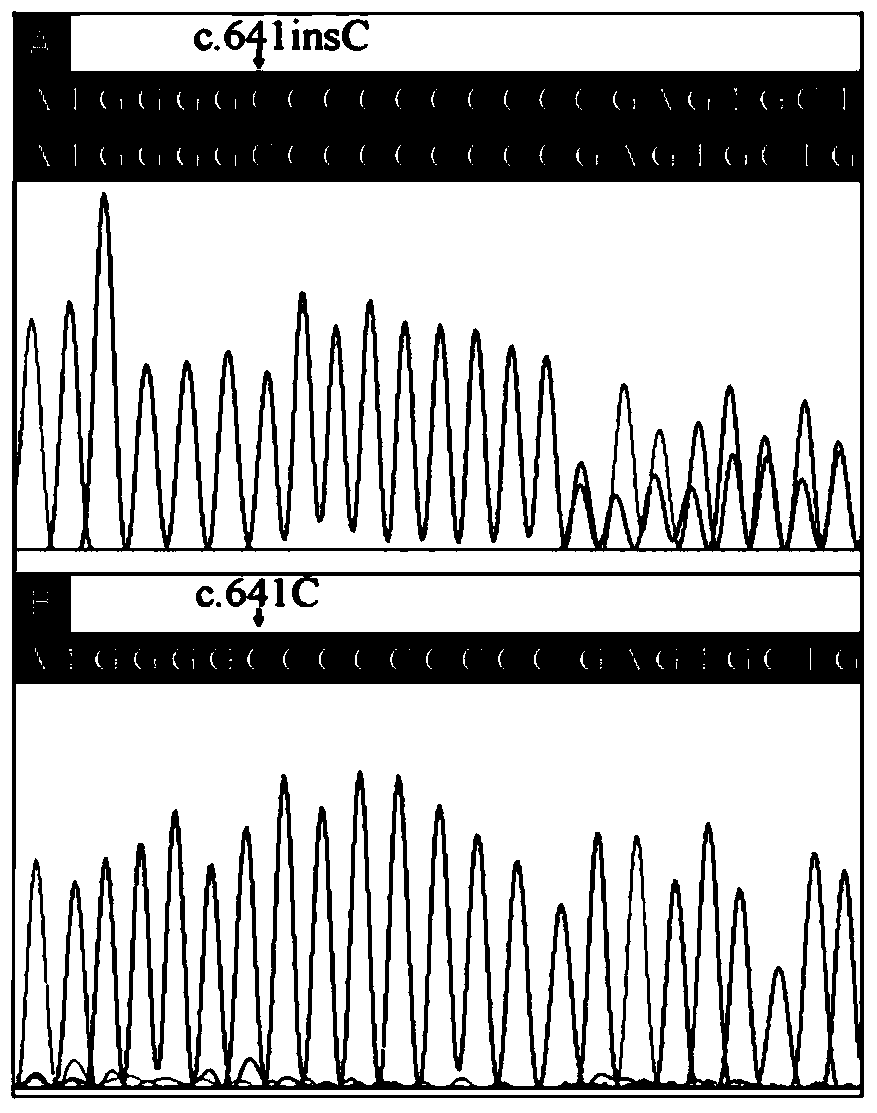
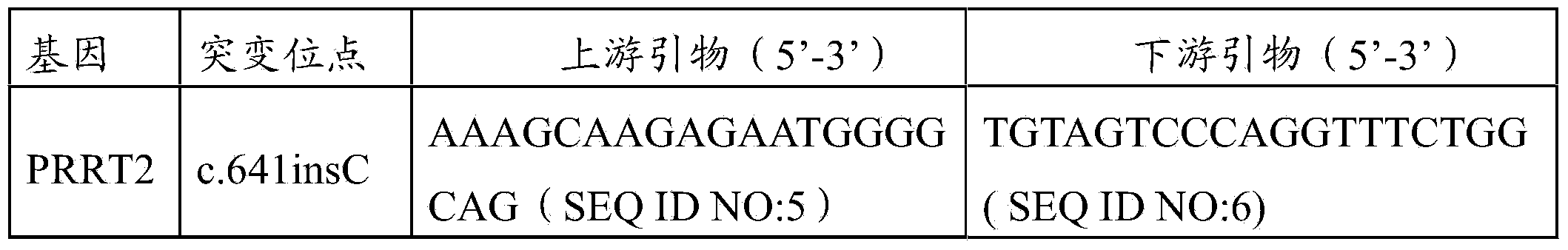
[0075] Example 2: Sanger method sequencing verification
[0076] Sanger sequencing was used to verify the mutations detected by whole-exome sequencing on the PRRT2 gene in Example 1, and to verify the correlation between this mutant gene and FS disease. The PCR primers used to amplify the region of the mutation were Primer3 (http: / / frodo. wi.mit.edu / primer3 / ) design. The amplified fragments were sequenced using ABI3100 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) genetic analyzer and ABI BigDye Terminator cycle sequencing kit v3.1 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). The specific method steps are as follows:
[0077] ① DNA extraction
[0078] Take the peripheral venous blood of these 7 samples to extract genomic DNA according to the method in Example 1, and measure the DNA content spectrophotometrically.
[0079] ②Primer design and PCR reaction
[0080] First, refer to the human genome sequence database GRCh37.1 / hg19, and use Primer3.0 to design the exon-specific primers of PRRT2 gene res...
Embodiment 3
[0100] Example 3: In vitro detection of PRRT2 gene kit for FS patients
[0101] In order to detect pathogenic mutations in FS patients, all exons in the coding region of PRRT2 gene and primer sequences at the junction of exons and introns can be designed. In this example, the kit primers and amplification and sequencing conditions are as in Example 2.
[0102] 1. The composition of the kit:
[0103] Primer: as shown in Example 2;
[0104] Taq enzyme
[0105] Buffer
[0106] dNTP
[0107] Extract and purify genetic material (DNA samples) from biological samples to be tested
[0108] 2. How to use:
[0109] (1) Genomic DNA extraction: Use Wizard Genomic DNA extraction kit from Promega of the United States to extract genomic DNA from peripheral blood samples.
[0110] (2) First use the above PCR primers, Taq enzyme, sample genomic DNA, buffer, dNTP, etc. to perform PCR amplification reaction;
[0111] (3) Purify PCR amplification products;
[0112] (4) Perform BigDye reaction on the purified PCR...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com