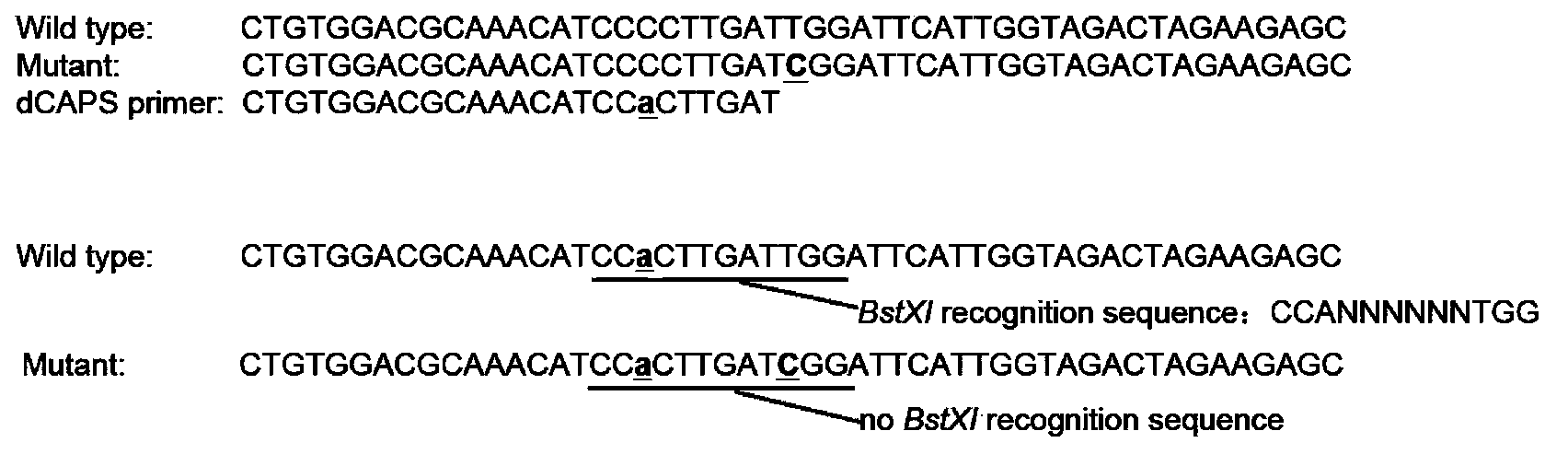SNP molecular marker used for identifying camellia nitidissima and application thereof
A molecular marker, golden camellia technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of complicated technology and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The acquisition of embodiment 1 golden camellia SNP molecular marker
[0021] Granule-bound starch synthase I (GBSSI) is a key enzyme for the synthesis of amylose in endosperm and other plant storage organs. Its function is conserved and it is a single copy in most plant families. Studies have shown that the GBSSI gene in Camellia is a single copy, and has a high sequence variation rate (the variation between different species is about 5%), which is very useful for studying the phylogeny of groups such as Camellia with many closely related species. Relationships have significant value (Yang et al., 2006).
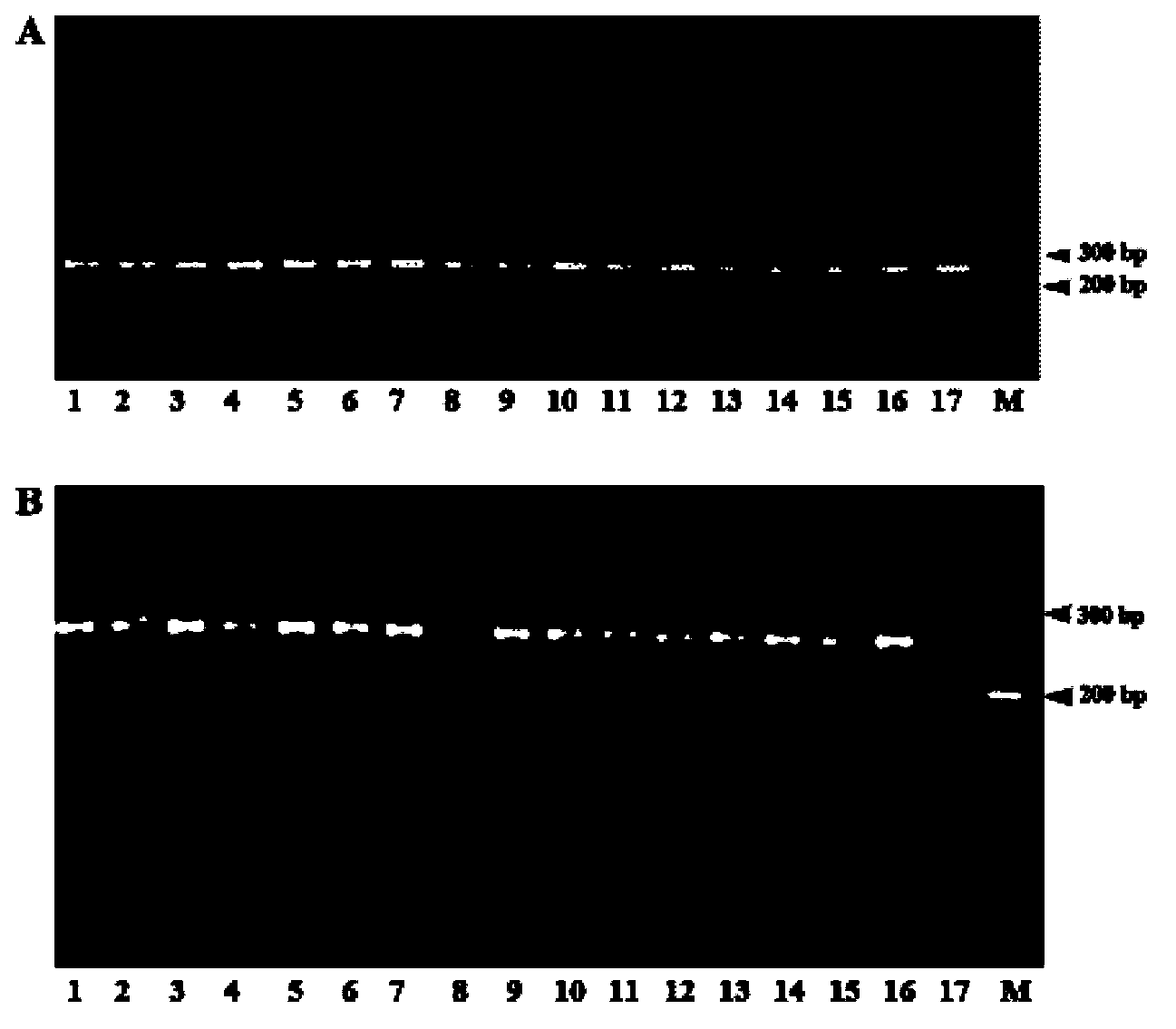
[0022] 1. According to the primers and amplification conditions of the GBSSI gene published by Yang Junbo et al. (2006), the genomic DNA of 17 Camellia species in Table 1 was used as a template for PCR amplification, and the amplified product was passed through 1.5% agar Glycogel electrophoresis detection and sequencing after qualified observation by UV gel imaging ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2 Application of Camellia SNP Molecular Markers
[0032] This example establishes the dCAPS molecular marker system based on the SNP sites of Camellia japonica, so as to quickly identify the rare and endangered species in the world-Camellia japonica.
[0033] It includes the following steps: 1) extracting the genomic DNA of the plant to be tested; 2) using the genomic DNA of the plant to be tested as a template, using the dCAPS primer (5'-CTGTGGACGCAAACATCCACTTGAT-3') and the corresponding downstream primer (5'-CCATGTATTTCTTGCCAGTGCCCT-3 '), PCR amplification of Camellia japonica GBSSI gene; 3) restriction endonuclease BstXI was used to digest the PCR amplification product (the specific method was the same as in Example 1), and the digested product was subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis, and the electrophoresis results showed 2 strips band, the plant to be tested is identified as Camellia japonica species.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com