Embryo quality assessment based on blastomere cleavage and morphology
一种胚胎质量、卵裂球的技术,应用在体外受精的胚胎领域
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0139] Example 1 - Retrospective Study
[0140] Materials and Methods
[0141] The research program was carried out at the Valencia Infertility Institute (Instituto Valenciano de Infertilidad, IVI), Valencia. Procedures and protocols were approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB), which prescribes and approves the database analysis and clinical IVF procedures for studies performed at IVI. The program complies with the Spanish Law (14 / 2006) governing Assisted Reproductive Technologies. A total of 2903 oocytes were included in this study, from which 2120 embryos were generated during 285 IVF treatment cycles between September 2009 and September 2010. All embryos were obtained after fertilization by intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) and were part of a clinical standard (n=188) and egg donation program (n=97). Time-lapse images of all embryos were acquired, but only those embryos that had been transferred with a known implantation outcome (i.e., 0% implantation or ...
Embodiment 2
[0185] Example 2 - Data analysis based on known implant data
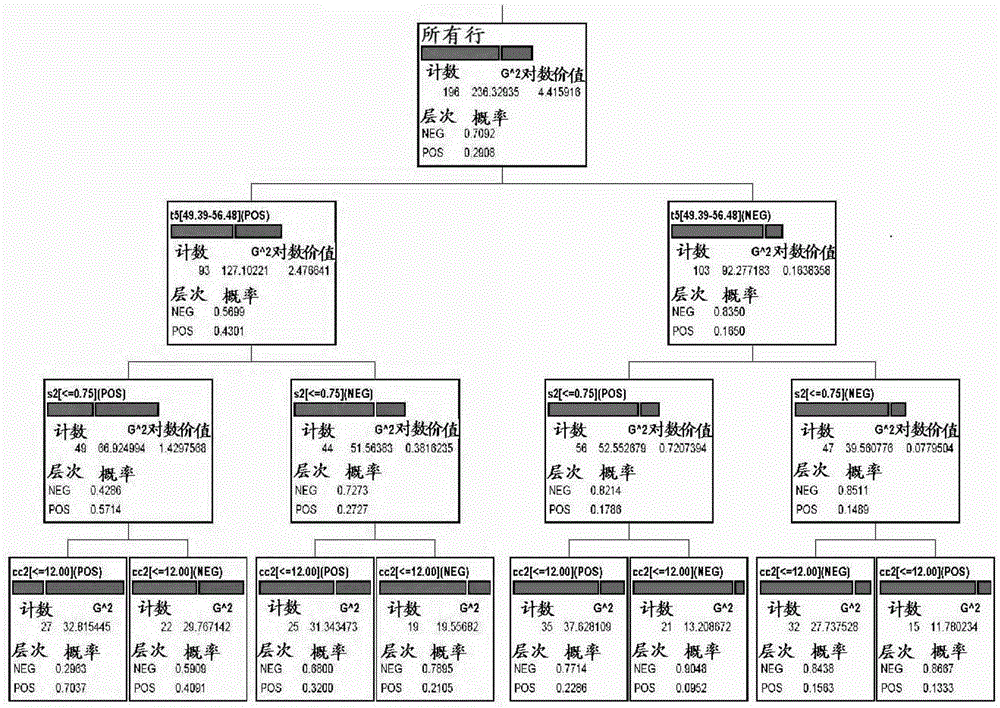
[0186] The analysis was based on known implantation data (KID) of 1598 embryos from 10 different clinics. KID embryos are embryos that have been transferred and have known implantation outcomes. In the case of multiple embryo transfers, only embryos with complete failure or complete success in implantation are used. All multiple transfers where there was implantation but fewer embryos were implanted than were transferred were discarded to be able to determine the implantation success of a particular embryo. Implantation success is assigned a value of 1 if the transferred embryo implants successfully, and a value of 0 if implantation fails. The number of embryos (N) used to calculate the expected value (probability of success) for the target and non-target groups was different for the different variables.
[0187] single variable
[0188] For a single continuous variable (eg t2), divide the data into quartiles a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com