Method for producing organic acid by anaerobic fermentation of aquatic plant
An aquatic plant, anaerobic fermentation technology, applied in the direction of fermentation, can solve problems such as high energy consumption and unstable fermentation process, and achieve the effects of simple and easy method, important industrial application potential, and important ecological benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] Example 1: Preparation of fermented sludge.
[0092] The fermented sludge used in the experiment was taken from the dehydrated residual sludge of a sewage treatment plant.
[0093] Prepare acclimatization medium with the following components: glucose 15g / L, NaNO 3 3.04g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.44g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.96g / L, CaCl 2 0.72g / L, NaHCO 3 0.96g / L, MnCl 2 0.11g / L. Then put 2.5kg of dehydrated residual sludge from the sewage treatment plant into a 5L fermenter, add 4L of acclimatization medium, adjust the pH to 7.4, acclimate at 28°C for one week, and monitor and control the pH every day.
[0094] The activated sludge in the following examples were all prepared according to the above method.
Embodiment 2
[0095] Example 2: Influence of wetland plant type on fermentation effect.
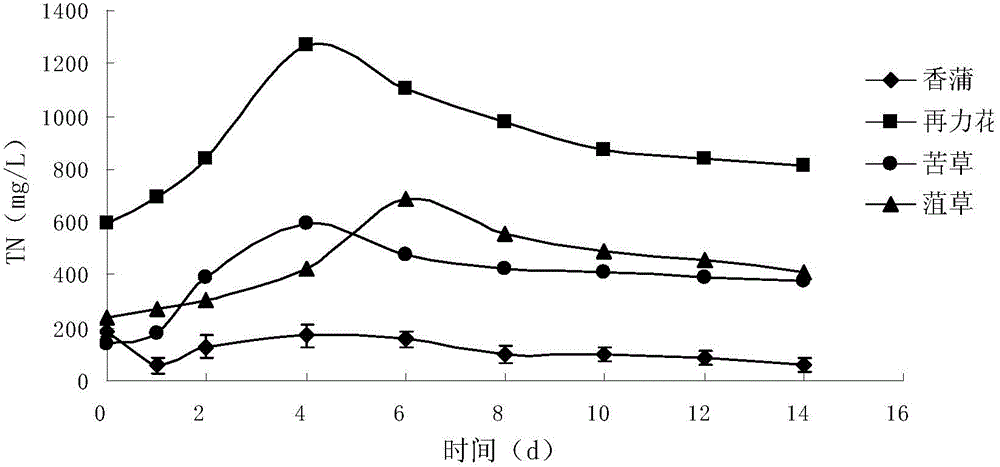
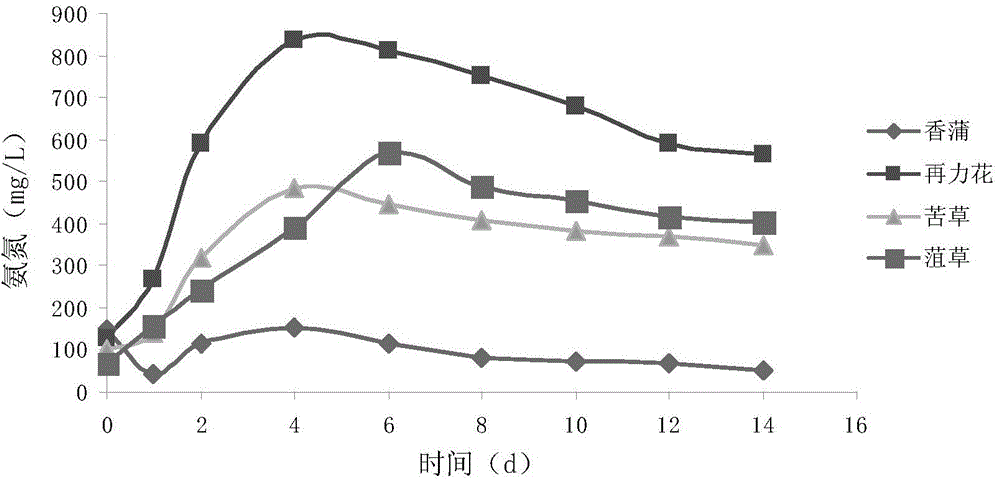
[0096] Weigh a certain amount (according to 30g dry weight) of fresh cattail stalks, Zailihua stalks, bitter grass, and weed grass, put them into a 500ml Erlenmeyer flask after crushing, add 300ml of domesticated fermented sludge (sludge concentration MLSS10000mg / L), add 200ml of water, adjust the pH value to 7-8, and place it in a thermostat at 37°C for fermentation. The test lasted for 2 weeks. On days 0, 1, 2, 4, ..., 14, take 15ml of fermentation broth, centrifuge at 12000rmp for 5 minutes, take the supernatant, and measure TN and NH in part 3 -N, TP, COD Cr , pH, and another 4ml was passed through a 0.22μm water filter membrane to measure volatile fatty acids (VFAs).
[0097] The release of nitrogen and carbon sources during the fermentation process of four constructed wetland plants, Cattail, Zailihua, Erythrophyllum, and Smilax, is as follows: Figure 1 ~ Figure 3 As shown, the maximum outpu...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Embodiment 3: the influence of temperature on the fermentation effect of Smilax chinensis.
[0106] The experimental method refers to Example 2, the difference is that, according to the results of fermentation experiments of different types of wetland plants, the submerged water plant Smilax chinensis with the best fermentation effect is selected as the object, and the effects of different temperatures (10°C, 25°C, 37°C) on fermentation are investigated. The impact of the effect.
[0107] At three fermentation temperatures of 10°C, 25°C, and 37°C, the TN, TP, and COD Cr and VFAs content changes with fermentation time as Figure 6-9 shown.
[0108] Depend on Figure 9 It can be seen that the fermentation temperature has a significant effect on the nitrogen release rate and release amount of Smilax. The order of release rate and release amount of Nitrogenin from large to small under the three fermentation temperatures was 37℃>25℃>10℃. At 37°C, the release of nitrogen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com