Inverter parallel control method based on controllable virtual impedance
A technology of virtual impedance and control method, applied in output power conversion devices, single-grid parallel feeding arrangements, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of increasing voltage waveform distortion, affecting the quality of output voltage and power, and reducing circulating current. , easy expansion, good reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
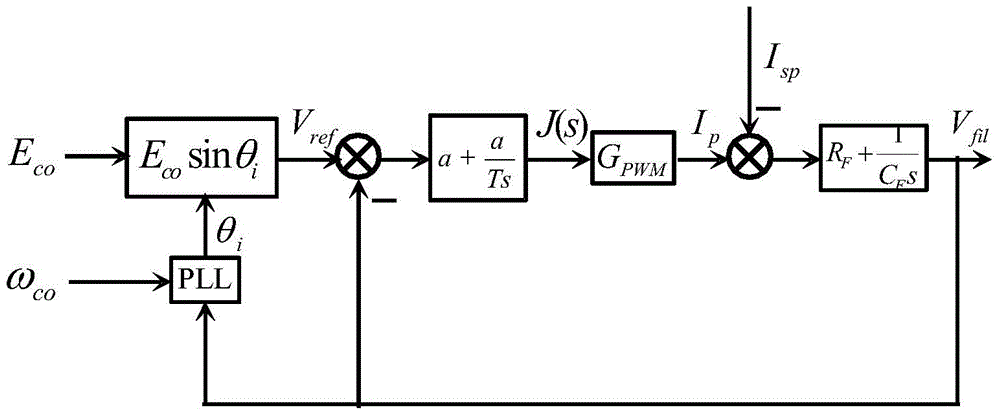
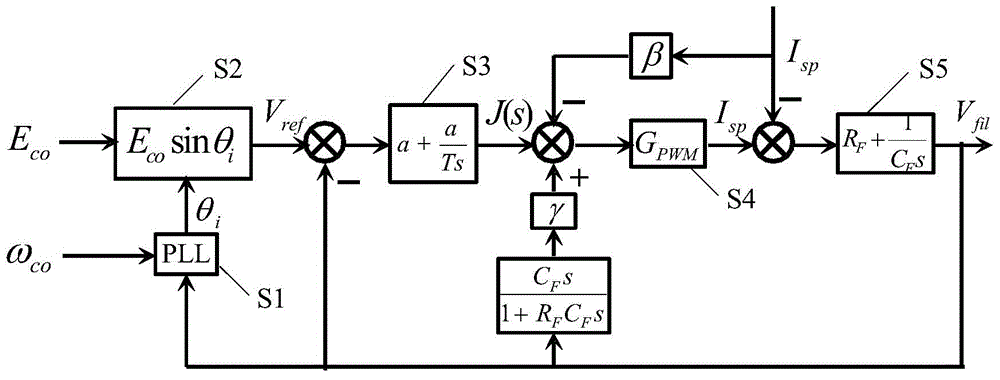
[0039] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. This embodiment is carried out on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation and specific operation process are given, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments.
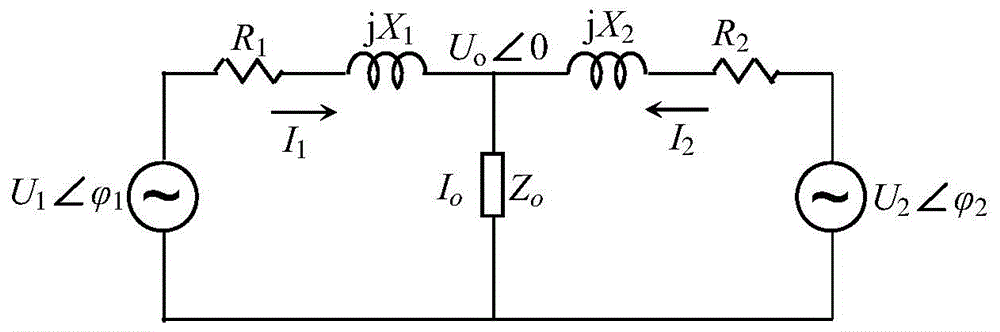
[0040] Such as figure 1 As shown, taking two inverters connected in parallel as an example, the parallel inverter model is used for system power analysis, and the inverter is equivalent to a voltage source with internal resistance, U 1 , U 2 is the output line voltage of the inverter, U 0 is the AC parallel bus voltage, R n +jX n = Z n ∠θ n is the sum of the output impedance of the inverter and the connection impedance, is the inverter output voltage phase, θ n For the equivalent output impedance phase, the relationship between the circulating current and the output impedance...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com