Man-made rock core with multi-pore structure and preparation method of man-made rock core
An artificial core and pore structure technology, applied in the preparation of test samples, etc., can solve problems such as large differences in complex distribution, difficulty in realization, human health and environmental safety hazards, etc., to reduce the experimental cycle and cost, and improve experimental efficiency , good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0054] Preparation and screening of metal flakes and inorganic salt particles:
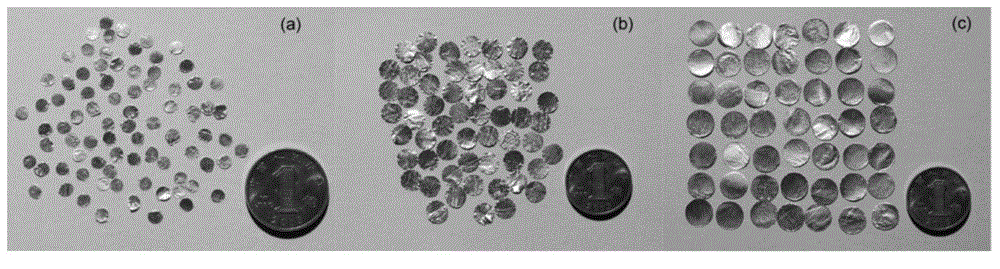
[0055] The pore aspect ratio (AR) refers to the ratio of the length of the short axis of the pore to the length of the long axis, and is an important parameter to describe the shape of the pore. Select aluminum foil paper with a thickness of 0.02mm, and use punches of different diameters to process the aluminum foil paper into discs with diameters of 3mm, 6mm, and 8mm, and the corresponding aspect ratios are 0.0067, 0.0033, and 0.0025 (such as figure 2 shown).
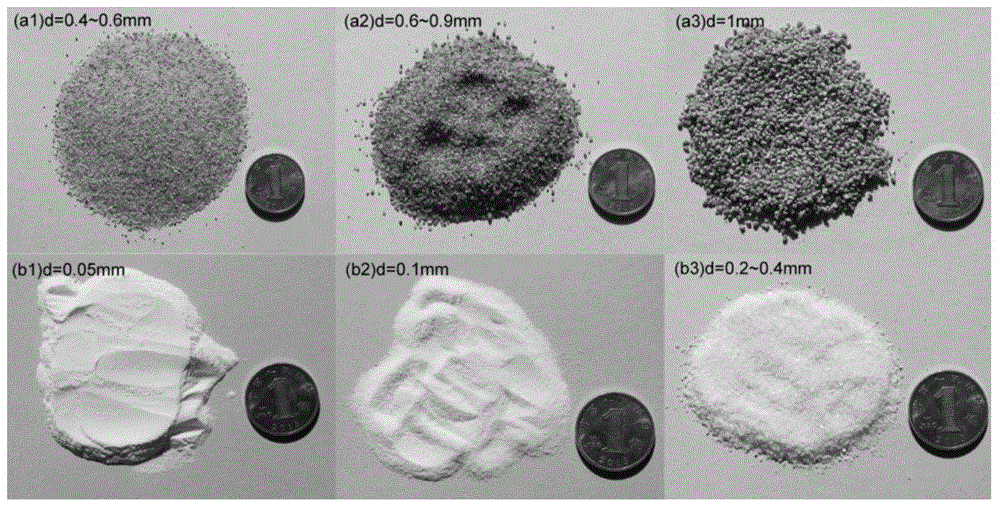
[0056] Select large pieces of sea salt, obtain sodium chloride particles through mechanical crushing and grinding, and use screens of different particle sizes to screen out sodium chloride particles with different particle size distributions. image 3 The particle size distribution of the sodium chloride particles shown is 1mm, (3~4)mm, (4~5)mm.
Embodiment 1
[0058] Take the preparation of fractured-porous sandstone artificial core as an example. The size of the designed artificial core is a standard core with a diameter of 25mm and a length of 50mm, and the volume V is 39.27cm 3 , where the microcrack size d is 3 mm, the aspect ratio AR is 0.0067, and the crack density ε is 0.0495. The number n of the circular thin iron sheets (AR=0.0067) with diameter d=3mm and thickness h=0.02mm is 45 in total, and the mass of 45 thin iron sheets is m 1 It is 0.0496g to simulate cracks. Weigh 60g of carbonate rock cuttings with a particle size of 200μm, 1.538g of epoxy resin, 0.462g of curing agent, and 0.769g of diluent. Mix sandstone cuttings with epoxy resin binder evenly. The mixture was added to the mold in 5 times on average, and during this process, thin iron sheets were picked up with tweezers and embedded randomly in the mixture one by one. After all the artificial core preparation materials are added to the mold, the mold is placed...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Take the preparation of dissolved pore-pore type double pore structure carbonate rock artificial core as an example. The design core size is 25mm in diameter, 50mm in length, standard core; the size of dissolved pores is 3mm, and the number of dissolved pores is 75. Screen 75 sodium chloride granules with a particle size of 3mm, mass m 2 It is 4.35g. Weigh 60 g of carbonate rock cuttings with a particle size of 200 μm, 0.923 g of epoxy resin, 0.277 g of curing agent, and 0.462 g of diluent. Mix the carbonate rock cuttings with the epoxy resin binder evenly, then add the screened sodium chloride particles, and mix evenly. Add the mixture to the mold and apply an axial pressure of 6MPa. At room temperature, after 12 hours, the epoxy resin binder has fully cured, and the mold is removed. Soak the formed artificial core in distilled water at 45°C and weigh it every half hour. After the quality of the core remains basically unchanged, stop soaking, and the artificial co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com