Method for clearing wild algae contamination in live history micro-phase of large economic algae
A technology of economical algae and life history, which is applied in the field of removing miscellaneous algae pollution in the microscopic stage of the life history of large economical algae. It can solve the problems of preservation pollution, death, and inhibition of target algae damage, and achieves a wide range of seaweed materials, easy separation and acquisition, and high versatility. sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: Isolation and culture of Daphnia and morphological and molecular identification
[0033] 1. Isolation and culture of flea species
[0034] The lower benthic Daphnia were collected from the intertidal zone of Qingdao sea area, rinsed with sterilized seawater and separated from two paired individuals, and maintained and multiplied by feeding benthic diatoms.
[0035] 2. Morphological observation
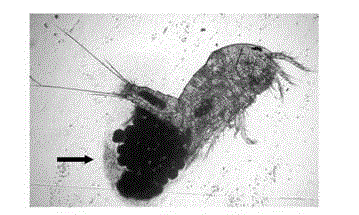
[0036] Pick a typical intact individual, use scanning electron microscope and optical microscope to observe the morphological characteristics and image, the electron microscope shows that the mouthparts diameter of Daphnia is about 10 μm, which is larger than the diameter of common filamentous cyanobacteria, unicellular cyanobacteria and diatoms, and smaller than common large cyanobacteria. Cell dimensions of the microscopic stages of economical seaweed. Light microscopy shows that female individuals form oocysts, which contain a large number of eggs and have a high...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2: The filamentous cyanobacteria that pollutes Enteromorpha seedlings are removed by daphnia
[0045] Enteromorpha seedlings can be used to preserve germplasm. Filamentous cyanobacteria are common polluting organisms, which are very prone to serious entanglement with seedlings and eventually complete encapsulation. Due to complete inhibition of photosynthesis and competition for nutrients, the preserved seedling germplasm dies.
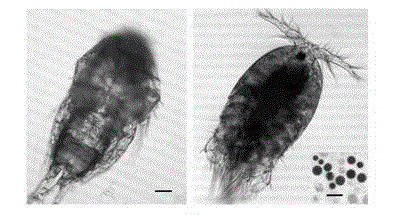
[0046] Take seedlings that are in a long-term dormant state and have seriously polluted filamentous cyanobacteria at the rhizomes, and mix them with an appropriate amount of Daphnia (about 20) in a petri dish, and treat for about half an hour. During the whole process, microscopic examination and photographs were taken every 10 minutes (see Figure 5 ). It can be seen in the figure that the filamentous cyanobacteria are seriously entangled with the rhizoids, but the removal of the cyanobacteria by Daphnia is very thorough and effici...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3: Diatoms that pollute Ulva seedlings are removed by Daphnia
[0048] Ulva seedlings can be used to preserve germplasm. Diatoms are common polluting organisms, which are very easy to adhere to the seedlings. In severe cases, they will be completely encapsulated, and the germplasm of preserved seedlings will die due to complete inhibition of photosynthesis and competition for nutrients.
[0049] Take the Ulva seedlings that are in a long-term dormant state and are seriously polluted with diatoms, and mix them with an appropriate amount of Daphnia (about 20) in a petri dish, and treat them for about half an hour. During the whole process, microscopic examination and photographs were taken every 10 minutes (see Figure 6 ). It can be seen from the figure that the unicellular diatoms are seriously adhered to the seedling algae, but the diatoms are completely and efficiently removed by Daphnia.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com