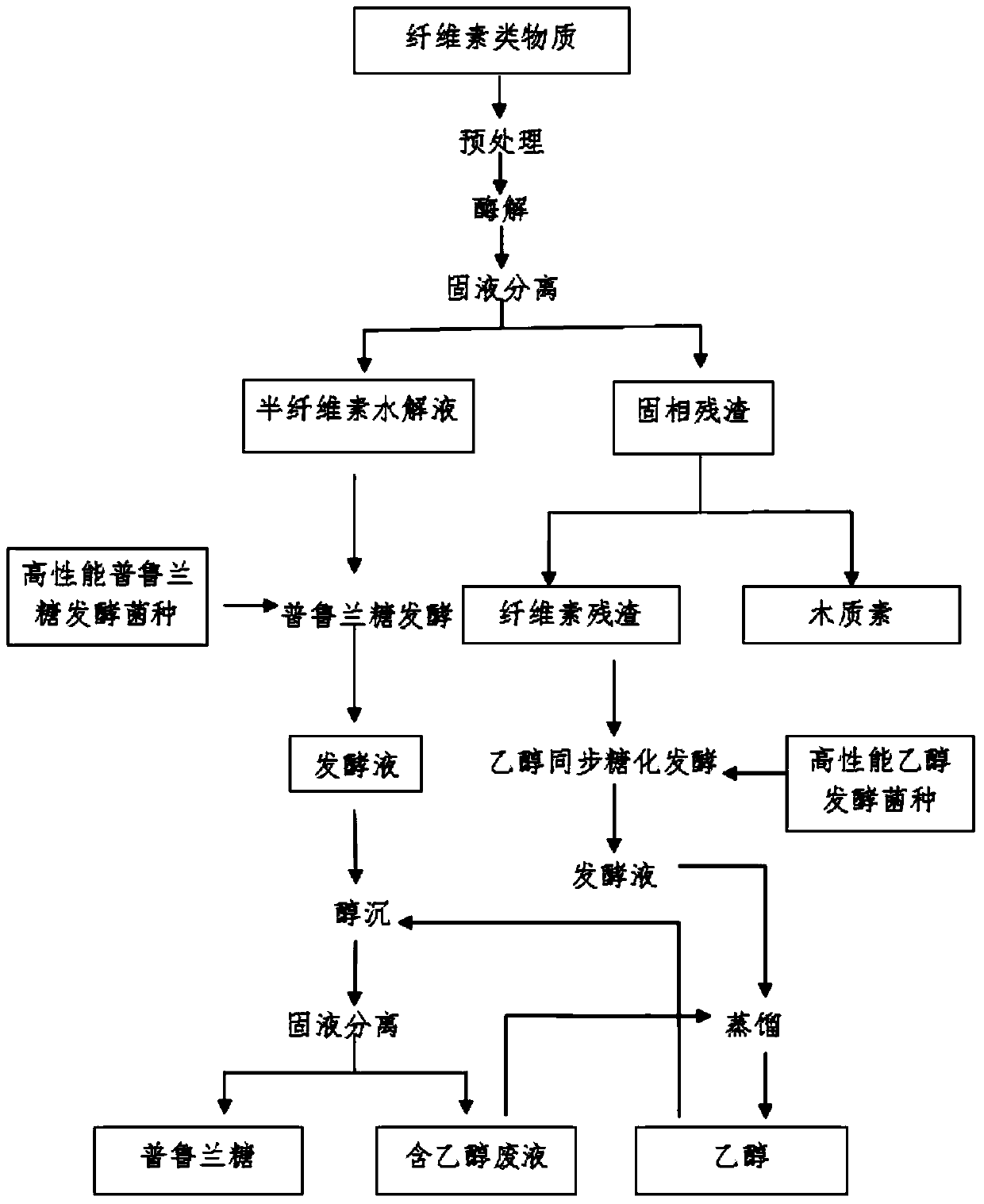
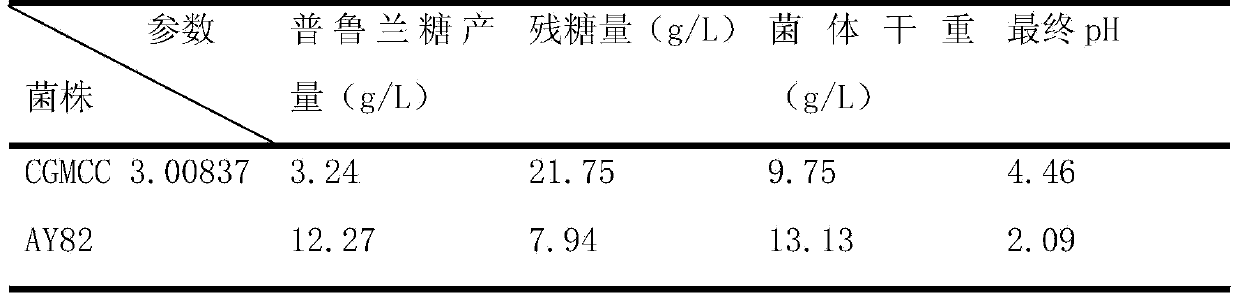
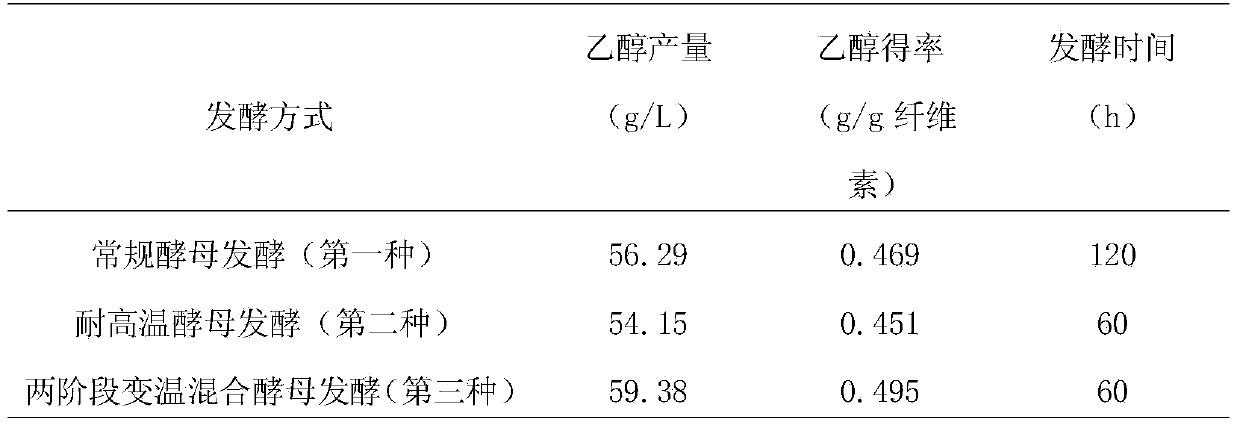
Method for combined production of bioethanol and pullulan from lignocellulose substances
A technology of lignocellulosic and pullulan sugar, which is applied in the field of biotransformation of fibrous substances, can solve the problems of ineffective utilization of xylose and high production cost of pullulan sugar, and achieve resource saving, production cost reduction, and high-efficiency biotransformation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0033] The preparation method of the corn flour hydrolyzate is as follows: add 1500 g of corn flour to 4500 mL of 65-70° C. tap water, and place for 20 minutes to make the corn flour particles fully absorb water and expand. Add 0.9mL of liquefaction enzyme (a-amylase), and liquefy at 85~90℃ for 1.5h. After the liquefaction is completed, the temperature is lowered to 60°C, and 3 mL of glucoamylase is added. Saccharification at 55-60°C for 20h. Filter the saccharification liquid with a filter cloth to obtain a clear filtrate, which is the corn hydrolysate, and boil it for 10 minutes to cool for later use.
[0034] (2) Genome rearrangement
[0035] All cell populations of the mutant strain library were inoculated into YPD liquid medium, cultured to logarithmic phase at 30°C and 180 rpm, and the cells were collected by centrifugation. Wash the bacteria with sterile water, then put the sludge into the pre-spore culture medium (10g / LKAc, 10g / L yeast powder, 20g / L peptone), culture at ...
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1: Preparation of bagasse hemicellulose hydrolysate
[0052] Remove the impurities in the bagasse and pulverize to 20-30 mesh, add 0.7% NaOH solution according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:12 (g / mL), and pretreat it in the reactor for 1.5h at 40℃ . At this time, the retention rate of each component of bagasse is: 96.37% of cellulose, 81.02% of hemicellulose, 80.62% of lignin, and the yield of xylose is 62.93%. Wash the pretreated bagasse to neutrality, put the raw materials into the pH 4.5-5.5 enzymatic buffer aqueous solution according to the solid-liquid ratio of 1:18 (g / mL), and add the commercially available xylan according to the 150IU / g raw material Enzymes, while adding surfactant RH (rhamnolipid) 0.005%, Tween-800.25%, PEG60000.25%, Triton X-100 (Triton X-100) 0.15%, and enzymatically digest at 40℃ 48h. The yield of hemicellulose enzymatic hydrolysis was 98.52%%, which was 26.38% higher than that of enzymatic hydrolysis without surfactant. In the o...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2: Extraction of lignin from bagasse and preparation of cellulose residue
[0054] After orthogonal optimization of the lignin extraction conditions, the optimal lignin extraction process is obtained: adding the solid residue obtained in Example 1 to the lignin extraction mixture, the solid-liquid ratio is 1:15 (g / mL), formic acid :Ethanol is 9:1 (v / v), the temperature is 90℃, and the reaction time is 2.5h. At this time, the extraction rate of lignin was 68.44%, and the yield of lignin was 49.61%. The cellulose content in the residue after lignin extraction is 68.16%, and the others are 22.22%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com