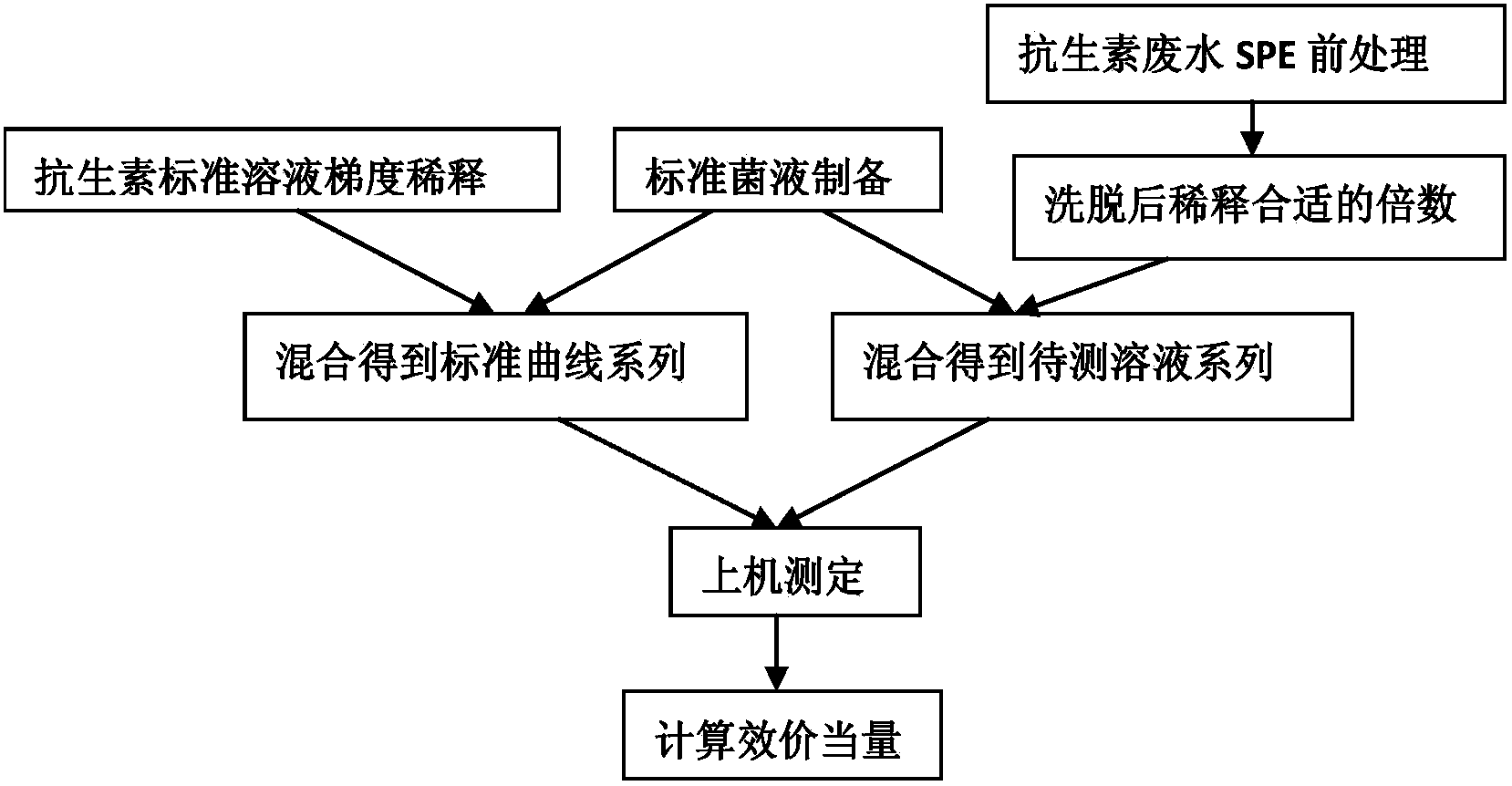
Method for evaluation of residual biopotency of antibiotics in waste water
A bio-efficacy, antibiotic technology used in the preparation of samples for testing, analysis by chemically reacting materials, and material analysis by observing the effect on chemical indicators
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Example 1 Standard Antibiotic Screening
[0090] 1. Preparation of standard bacterial solution
[0091] Take out the frozen Gram-positive bacteria Staphyloccocus aureus (Staphyloccocus aureus) and Gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) from the -80°C refrigerator, thaw in a 4°C refrigerator, shake well, and add antibiotics respectively In No. Ⅲ culture medium. Put them into a shaking incubator at 37° C. and shake them until the absorbance of the culture solution at a wavelength of 530 nm is between 0.3 and 0.7 to obtain revived Staphylococcus aureus and revived Escherichia coli respectively.
[0092] In the present invention, the resurrection culture temperature of Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria is 35-37°C, which is suitable for the present invention; the culture time is 4-5h.
[0093] After sterilizing the inoculation loop, dip in the revived Staphylococcus aureus standard bacteria solution and the revived Escherichia coli stand...
Embodiment 2
[0144] Example 2 Determination of comprehensive biological efficacy of spiramycin production wastewater residues
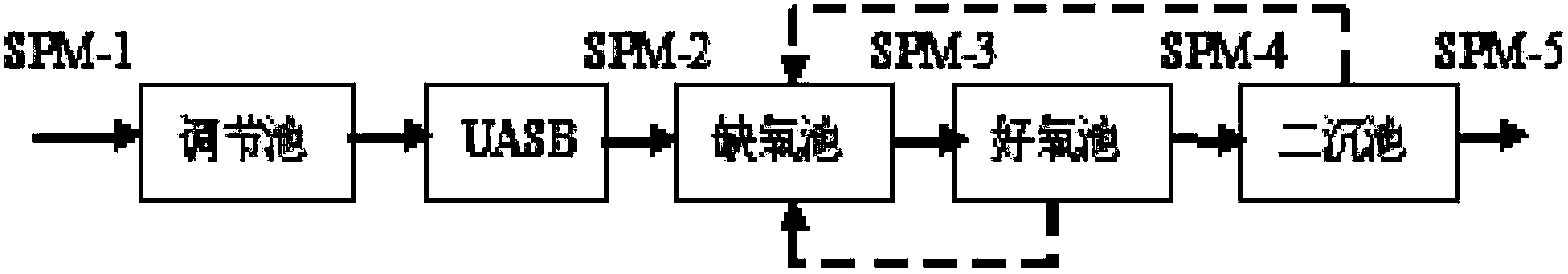
[0145] The embodiment of the present invention takes spiramycin production wastewater as an example to describe in detail, and the treatment process of spiramycin production wastewater is as follows figure 1 As shown, the wastewater from spiramycin production passes through the regulating tank, the up-flow anaerobic sludge bed (UASB, Up-flow Anaerobic Sludge Bed / Blanket), the anoxic tank, the aerobic tank, and the secondary sedimentation tank in sequence, and reaches the level of "fermentation type". Discharge Standard for Water Pollutants in the Pharmaceutical Industry GB21903-2008", direct discharge, in which: SPM-1 is the influent water before entering the regulating tank; SPM-2 is the anaerobic effluent after anaerobic sludge bed treatment; SPM-3 is the The effluent treated by the anoxic tank; SPM-4 is the effluent treated by the aerobic tank; SPM-5 is the eff...
Embodiment 3-6
[0174] Example 3-6 Determination of comprehensive biological efficacy of spiramycin production wastewater residues
[0175] In addition to collecting wastewater water samples (SPM-2) from the effluent of the wastewater treatment workshop of the spiramycin production plant (SPM-2), anaerobic biological treatment from the wastewater treatment workshop of the spiramycin production plant Waste water samples (SPM-3) were collected from the effluent of the anoxic pool after the spiramycin production plant, wastewater samples (SPM-4) were collected from the effluent of the aerobic pool after aerobic biological treatment in the wastewater treatment workshop of the spiramycin production plant, and The wastewater sample (SPM-5) was collected from the outlet of the secondary sedimentation tank after the secondary biological treatment in the wastewater treatment workshop of the spiramycin production plant. The dilution factor of the wastewater sample (SPM-2) in Example 3 was 50 times. 200...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com