Polyester composite material with polyvinylidene fluoride fiber as nucleating agent and preparation method thereof
A polyester composite material, polyvinylidene fluoride technology, applied in the field of polymer material preparation, can solve the problems of crystallization nucleating agent reunion and uneven dispersion, poor dimensional stability, slow crystallization rate, etc., to overcome low production efficiency, Excellent stability and improved crystallization speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] 1) Dry the polyethylene adipate under vacuum at 40°C for 3 hours, and dry the polyvinylidene fluoride fiber under vacuum at 100°C for 3 hours;
[0024] 2) Mechanically blend 60% polyester and 40% polyvinylidene fluoride fibers, and put the mixed powder into a mold of a flat vulcanizer for molding;
[0025] 3) Pre-molding the preformed blank, raising the temperature to 90°C and keeping it for 60 minutes to form the molding material, and applying 10 5 Pa pressure applies shear stress to the melt, and then the temperature is lowered to 45°C by furnace cooling, and then the pressure is removed, so that polyethylene adipate is crystallized into a film, and the molded composite material together with the mold Take out together;
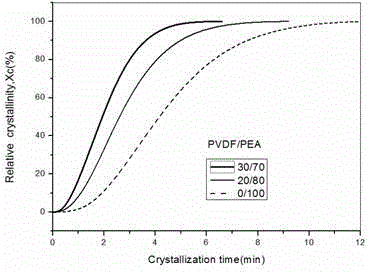
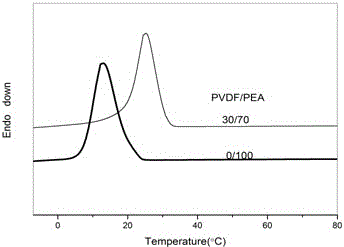
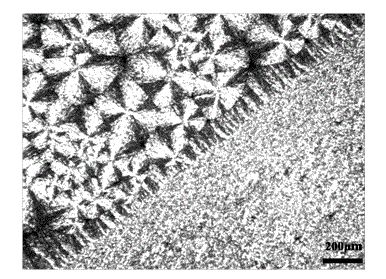
[0026] The tensile strength was tested on a tensile machine; the thermodynamic stability and crystallization speed were tested by a differential scanning calorimeter; the morphology and structure of the interface region of the sample was observed by...
Embodiment 2
[0028] 1) Dry polyethylene adipate under vacuum at 25°C for 8 hours, and dry polyvinylidene fluoride fibers under vacuum at 60°C for 8 hours;
[0029] 2) Mechanically blend 80% polyester and 20% polyvinylidene fluoride fibers, and put the mixed powder into a mold of a flat vulcanizer for molding;
[0030] 3) Pre-molding the pre-formed blank, raising the temperature to 85°C and keeping it for 30 minutes to form the molding material, and applying 10 5 Pa pressure applies shear stress to the melt, and then the temperature is lowered to 45°C by furnace cooling, and then the pressure is removed, so that polyethylene adipate is crystallized into a film, and the molded composite material together with the mold Take out together;
[0031] The composite material was spin-coated, and its tensile strength was tested on a tensile machine; its thermodynamic stability and crystallization speed were tested by a differential scanning calorimeter; the tensile strength of the polyester composi...
Embodiment 3
[0033] 1) Dry polyethylene adipate under vacuum at 32°C for 5 hours, and dry polyvinylidene fluoride fibers under vacuum at 80°C for 5 hours;
[0034] 2) Mechanically blend 70% polyester and 30% polyvinylidene fluoride fibers, and put the mixed powder into the mold of a flat vulcanizing machine for molding;
[0035] 3) Pre-molding the preformed blank, raising the temperature to 115°C and keeping it for 45 minutes to form the molding material, and applying 10 5 Pa pressure applies shear stress to the melt, and then the temperature is lowered to 45°C by furnace cooling, and then the pressure is removed, so that polyethylene adipate is crystallized into a film, and the molded composite material together with the mold Take out together;
[0036] The composite material is spin-coated, and its tensile strength is tested on a tensile machine; its thermodynamic stability and crystallization speed are tested by a differential scanning calorimeter; the tensile strength of the polyester...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com