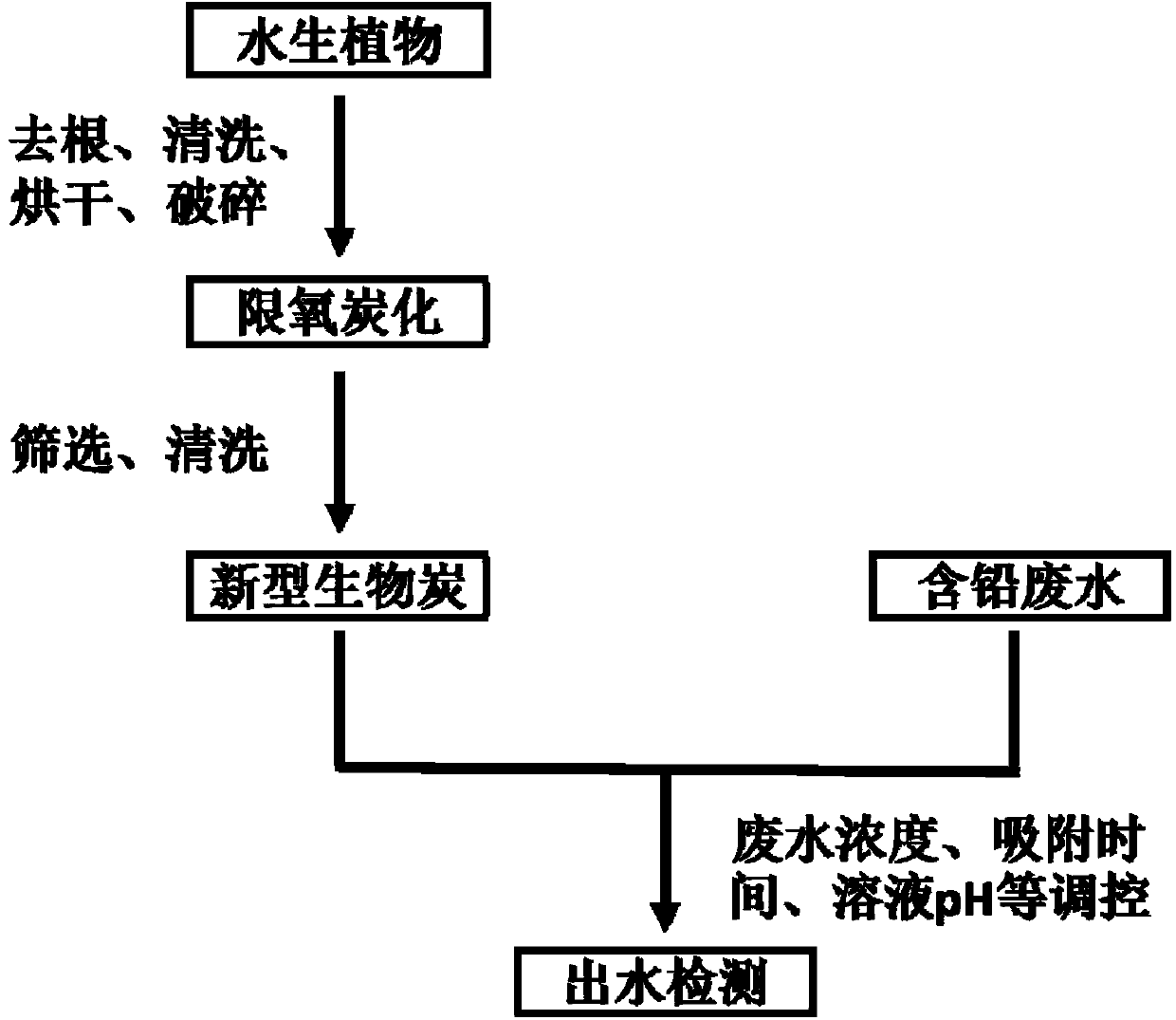
Method for removing lead in polluted water by using aquatic plant biochar
A technology of aquatic plants and biochar, which is applied in the field of environmental engineering, can solve the problems of aggravating the spread and spread of A. japonicus, re-harm, and failure to prevent and control A. japonicus, and achieve the effects of reducing damage, facilitating recycling, and realizing resource utilization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Wash the aquatic plant Alpinia chinensis, air-dry it naturally, and then cut it into small pieces of about 2 cm.
[0034] Aquatic plants were pyrolyzed in an electric furnace at 300°C for 2 h with limited oxygen, cooled naturally to room temperature, and then taken out. Pass through a 18-mesh sieve and a 35-mesh sieve to keep only biochar with a diameter between 0.5 and 1mm, wash it with ultrapure water, and dry it in an oven at 60°C to obtain biochar.
[0035] The prepared biochar can adsorb the lead solution with a pH of 5 according to the dosage of 3g / L, and the reaction time is 24 hours.
[0036] The mixed solution was passed through a 0.22 μm filter membrane, and the heavy metal content in the filtrate was determined after acid was added to the filtrate.
[0037] The yield of biochar obtained in the present embodiment was 47.1%. The adsorption capacity of lead is 223.30mg / g, and the removal rate of 700mg / L lead solution exceeds 95%.
Embodiment 2
[0039] With other conditions unchanged, the pyrolysis temperature in Example 1 was changed to 600°C, and water hyacinth biochar was prepared in the same way for adsorption experiments.
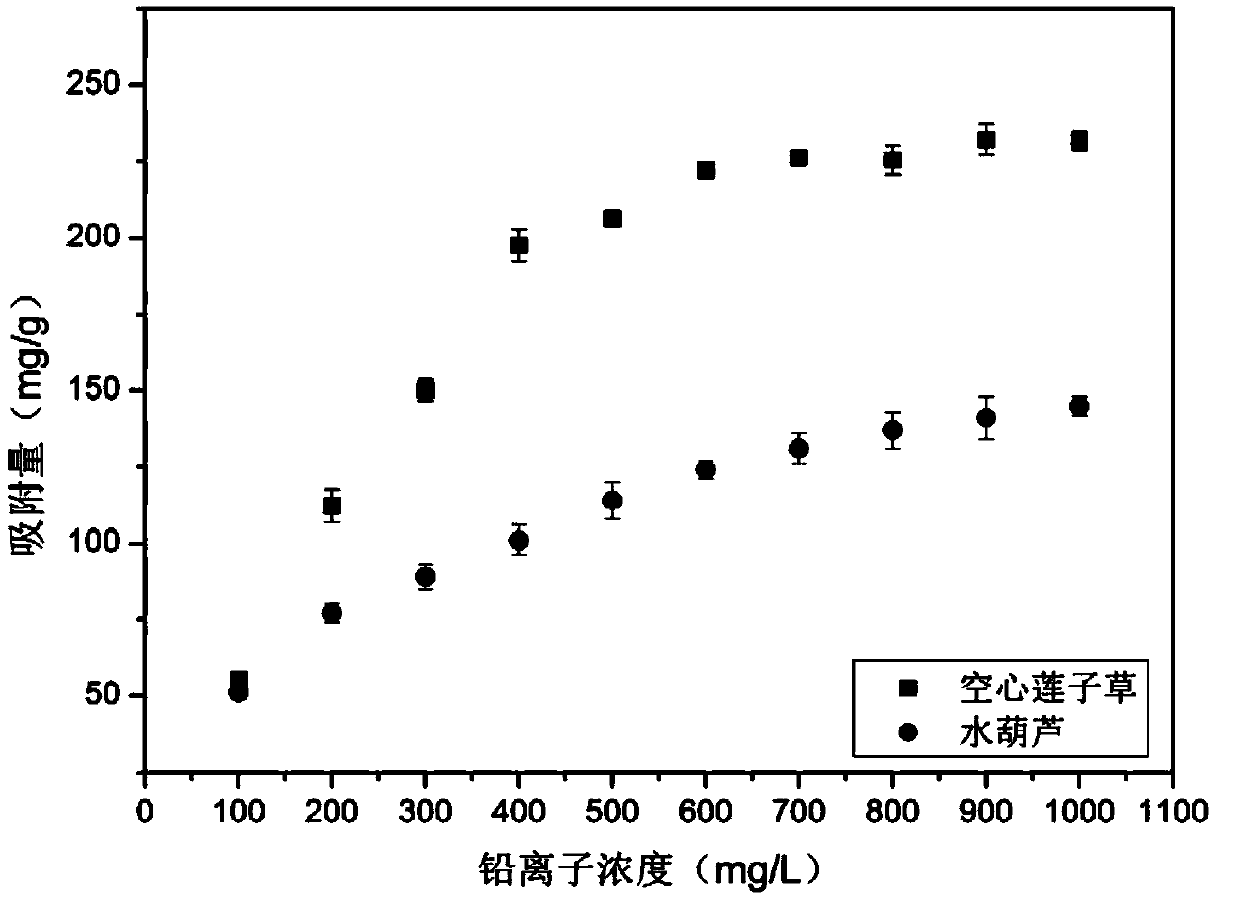
[0040] The yield of biochar of Asteroides spinosa that the present embodiment obtains is 29.8%, as image 3 As shown, when the lead concentration is 500ppm, the adsorption amount of biochar to lead is 206.19mg / g, and with the increase of lead concentration, the adsorption amount of biochar continues to increase. The removal rate of 100mg / L lead solution is 99%. The removal rate of 50mg / L lead solution is more than 99%, which is basically completely removed and meets the first-class discharge standard. The yield of water hyacinth biochar obtained in this example was 33.7%, and when the lead concentration was 500 ppm, the adsorption amount of lead by biochar was 117.35 mg / g. The removal rate of 100ppm lead solution is 99%. The removal rate of the 50mg / mL lead solution is over 99%, and the lea...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Other conditions remain unchanged, the adsorption time in Example 2 is changed to 1min-24h, and the solution concentration is 600ppm.
[0043] The result of the adsorption amount of lead at different times for the biochar of A. japonicus obtained in this example is as follows: Figure 4 It can be seen that in the initial stage, the adsorption amount of lead by biochar increased sharply with the increase of time. After 15 minutes of reaction, the adsorption amount reached 80% of the equilibrium adsorption amount, and then the upward trend tended to be gentle. All reached the adsorption equilibrium, and in the 600ppm solution, the equilibrium adsorption amount was 205.4mg / g, which was consistent with the result in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com