Process for preparing heparin sodium through membrane separation
A technology for heparin sodium and membrane separation, applied in the field of preparation of heparin sodium, can solve the problems of large waste of resources, unstable products, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing processing costs, improving resin utilization, and reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
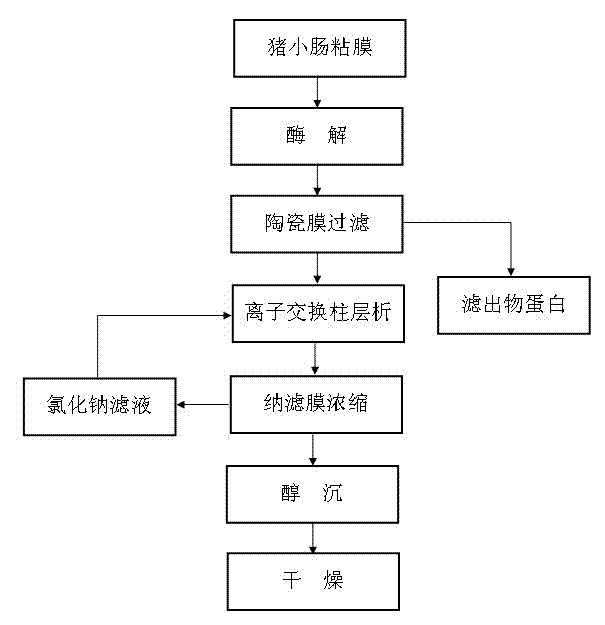
[0025] Example 1: Transfer 835 kg of intestinal mucosa scraped by 760 pig small intestines to a reaction tank, add 5310 kg of tap water, stir evenly, add 185 kg of sodium chloride to the reaction tank, and then use 20% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution After adjusting the pH of the mixed solution to 8.5, add 2190g of 2709 protease, turn on the steam to heat up and time the enzymolysis at 55°C for 5 hours to obtain the enzymolysis solution, then raise the temperature of the enzymolysis solution to 85°C and keep it warm for 17 minutes. After adjusting the pH to 7.0-9.0, cool down to 55°C, then transfer it to the storage tank, turn on the ceramic membrane equipment, adjust the pressure to 0.3MPa, and then filter through a 5nm ceramic membrane for 4 hours to obtain the filtrate. The filtrate is 10kg of protein For feed processing, the filtrate is pumped into an ion exchange column equipped with Rohm and Haas A98 resin at a temperature of 50-55°C for adsorption at a flow rate of 10L...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that 755 pig small intestines are scraped by an intestinal scraper to scrape 810 kg of intestinal mucosa and transferred to the reaction tank, then add 4050 kg of tap water, stir evenly and add 99.5 kg of sodium chloride, Then 20% sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH of the mixed solution to 9.0, then add 4320g of 2709 protease, turn on the steam to heat up and time the enzymolysis at 58°C for 3.5 hours to obtain the enzymolysis solution, then heat the enzymolysis solution to 88°C and keep it warm. After 15 minutes, adjust the pH of the enzymolysis solution to 7.0-9.0, then cool down to 57°C, and then transfer the enzymolysis solution to the storage tank. Turn on the ceramic membrane equipment, adjust the pressure to 0.28MPa, and filter through a 5nm ceramic membrane for 6 hours to obtain the filtrate. The filtrate 8.5kg protein is used as feed processing, and the filtrate is pumped into the R...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com