Method for producing stone-simulative microlite from slag and waste glass
A technology of waste glass and slag, applied in the field of producing imitation stone microcrystalline slag, can solve the problems of high production technology and cost, unbearable for ordinary people, monotonous colors, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
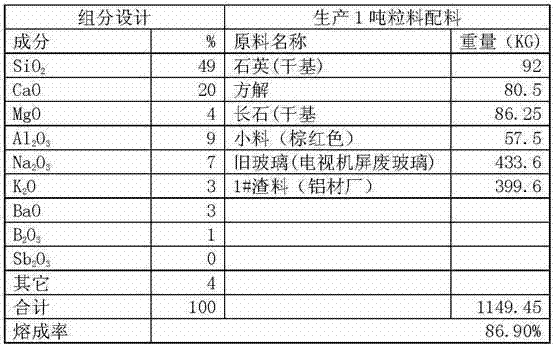
[0016] Example 1: Take the waste slag from the aluminum material factory and the TV screen glass from the waste treatment station. After testing, mix 50 tons of powder according to the following components and ingredients list, and put it into a melting furnace with an area of 5 square meters. Continuous discharge, the discharged glass is made into flakes with a tablet machine, and then the cracked glass block base material is obtained after direct rapid air cooling or water cooling, and then the 150KG glass block base material is placed on an effective specification of 1240×2480 Spread the shed flat, then enter the crystallization kiln to heat up according to a certain heating system, keep warm at 1150°C for 30 minutes, then slowly cool and anneal according to the corresponding temperature system, and leave the kiln. 18 brown-red microcrystalline jue stone plate with clear stone grain.
[0017]
example 2
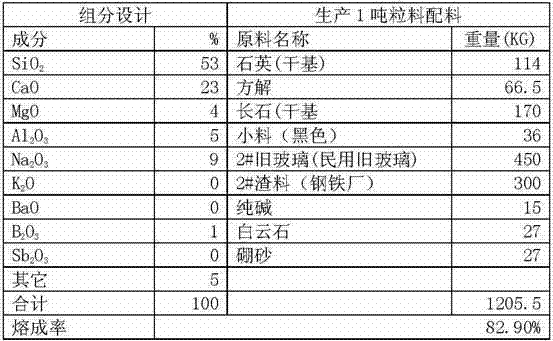
[0018] Example 2: Take the waste slag from the iron and steel plant and the old civil glass recovered from the waste treatment station. After testing, mix 50 tons of powder according to the following components and ingredients list, and put it into a 5-square-meter melting furnace for continuous feeding. After 24 hours at 1500 ° C, it will be discharged continuously. Material, the discharged glass is made into flakes with a tablet machine, and then the cracked glass block substrate is obtained after rapid air cooling or water cooling, and then the 150KG glass block substrate is placed on a shelf with an effective specification of 1240×2480 Lay flat on the top, then enter the crystallization kiln to heat up according to a certain heating system, hold at 1150°C for 30 minutes, then slowly cool and anneal according to the corresponding temperature system, and leave the kiln. Pure black microcrystalline stone slab.
[0019]
example 3
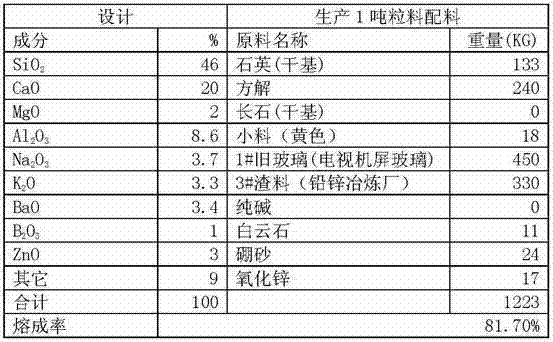
[0020] Example 3: Take lead-zinc smelter waste residue and TV screen glass, after testing, mix 50 tons of powder according to the following components and ingredients list, put it into a melting furnace with an area of 5 square meters and continuously feed it, and then discharge it continuously after 24 hours at 1500°C , the discharged glass is made into flakes with a tablet machine, and then the cracked glass block substrate is obtained after direct rapid air cooling or water cooling, and then the 150KG glass block substrate is placed on a shelf with an effective specification of 1240×2480 Pave it flat, then enter the crystallization kiln to heat up according to a certain heating system, keep warm at 1150°C for 30 minutes, then slowly cool and anneal according to the corresponding temperature system, and leave the kiln. Yellow microcrystalline stone plate with clear stone pattern and highly simulated stone.
[0021]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com