Marker for diagnosing liver cancer containing anti-ATIC autoantibody, and composition for diagnosing liver cancer containing antigen thereof
An autoimmune antibody and composition technology, applied in the field of cleotide formyltransfera, can solve the problems of limited implementation, low practicability, and little diagnostic effect, and achieve effective development results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
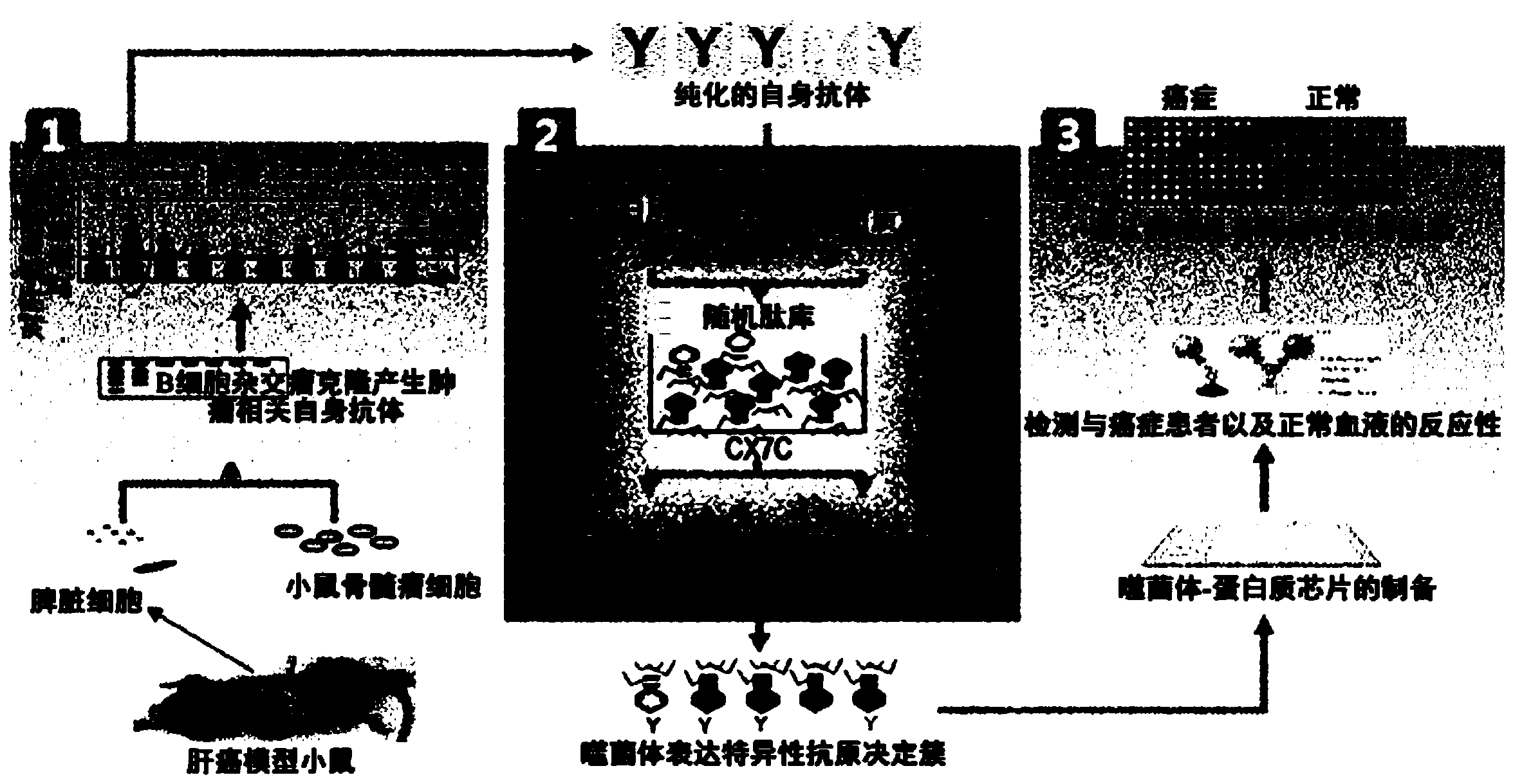
[0082] Example 1: Obtaining XC154 autoimmune antibodies derived from HBx mice
[0083] In order to obtain autoimmune antibodies produced together with cancer, HBx-transformed mice were used, and it is known that the liver cancer that develops therein has a morphology similar to that of human liver cancer. From HBx-transformed mice in breeding, the spleen (spleen) cells of individuals whose liver cancer was confirmed were taken as B cells, and cell fusion was performed with mouse myeloma cells Sp2 / 0 to prepare B-cell hybridomas cell. Cell fusion was performed according to the general method for preparing B-cell hybridoma cells. The fused cells were screened once using hypoxanthine-aminopterin-thymidine medium (HAT medium), and only cells that formed clones were cultured. In the cell culture medium, the cells that can detect the cancer cell reaction antibody are selected again, and the culture is continued.
[0084] The reactivity of autoimmune antibodies to cancer cells was ...
Embodiment 2
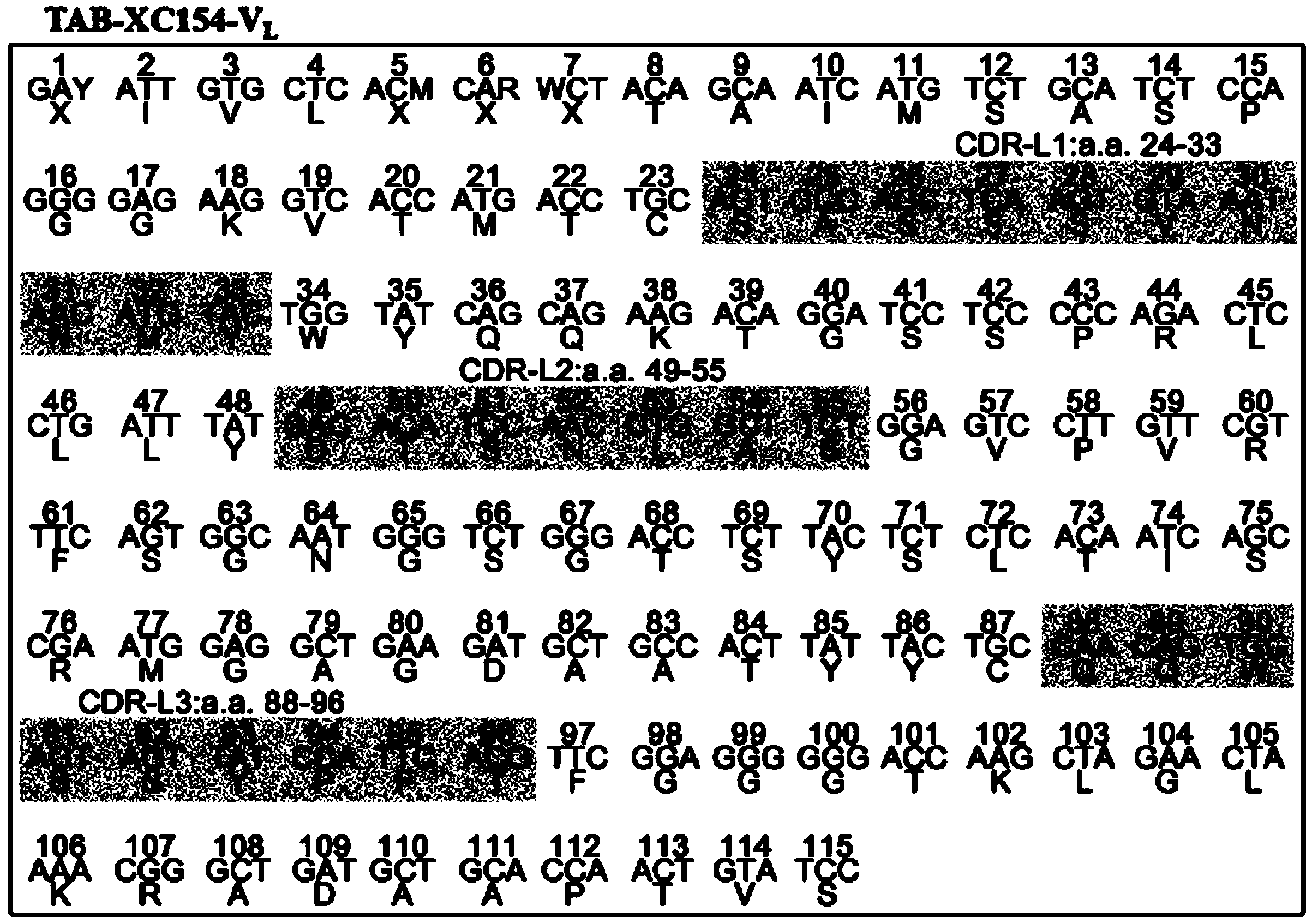
[0086] Example 2: Analysis of the Complementary Determining Region (CDR) of the XC154 antibody and purification of the antibody
[0087] After confirming that the XC154 antibody can specifically recognize the antigen expressed in cancer cells, in order to obtain information on the antigen recognition specificity of the XC154 antibody, the complementarity determining region sequences of the antibody were analyzed. The detailed method is as follows:
[0088] collect 10 6 About XC154 antibody-producing cells were used to extract total RNA using an RNA extraction kit (Qiagen). Complementary DNA synthesis (complementary DNA (cDNA) synthesis) kit (Invitrogen) was used to synthesize cDNA from 5 μg of total RNA, and the synthesized 1 μg of cDNA and mouse heavy chain constant region primers (Mouse Heavy chain constant region primer) F5'-CTT CCG GAA TTC S AR GTN MAG CTG SAG SAG TCW GG-3' (SEQ NO.21), R5'-GGA AGA TCT GAC ATT TGG GAA GGA CTG ACT CTC-3' (SEQ NO .22) and mouse light chai...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Example 3: Confirmation of the expression of XC154 antibody-specific reactive antigens in various cancer cells
[0091] In order to confirm the reactivity of the XC154 antibody to various cancer cell lines, various cancer cells were stained intracellularly by the method of Example 1 above, and analyzed by flow cytometry ( image 3 ). From the results, it was confirmed that the XC154 antibody-reactive protein was overexpressed in liver cancer cell lines such as HepG2 and SK-Hep-1, and various types of cancer cell lines such as HeLa, LNcap-LN3, and A549.
[0092] In addition, in order to confirm the expression position in the cell, intracellular staining was performed and observed with a confocal fluorescence microscope, and relatively strong staining was confirmed at the position of the cytoplasm or the position of the cell membrane ( image 3 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com