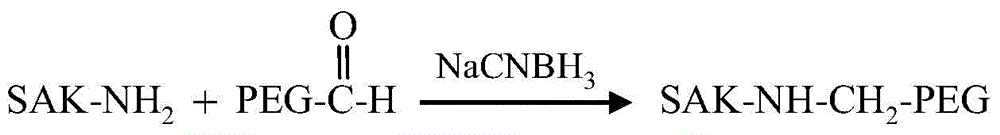Method and Application of Heat Treatment to Improve Biological Activity of Pegylated Staphylokinase
A staphylokinase biology, polyethylene glycol technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of protein biological activity reduction, loss, weakening protein and its substrate or receptor interaction, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Preparation of PEGylated SAK with site-directed single modification of N-terminus
[0026] (1) De-dimerization of SAK
[0027] Since cysteine residues are introduced into the C-terminus of SAK, it is easy to generate SAK dimers through disulfide bonds during storage, so a reducing agent is used to open the disulfide bonds before PEG modification. Recombinant staphylokinase and reducing agent tris(2-carbonylethyl)phosphate hydrochloride (TCEP) were mixed at a molar ratio of 1:5, the reaction buffer system was 20mM acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer, pH 5.0, and placed at room temperature for 3 hours, and then centrifuged to remove excess TCEP by membrane ultrafiltration with a molecular weight cut-off of 3 kDa.
[0028] (2) PEG site-directed modification of the N-terminus of SAK
[0029] The buffer system of the reaction was 20 mM acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer, pH 5.0. PEG aldehydes with molecular weights of 5kDa and 20kDa in NaCNBH 3 Reaction with SAK...
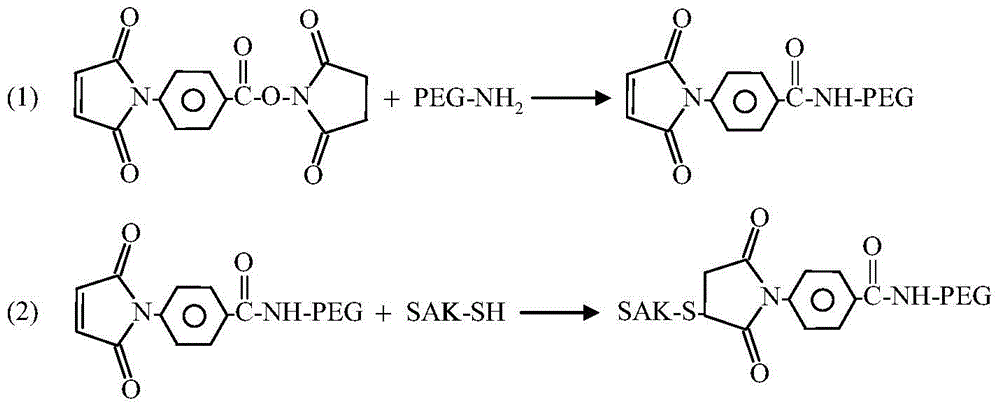
Embodiment 2
[0031] The reaction mixture was first purified by SP Sepharose HP column (1.6cm×25cm, GE Healthcare, USA). The SP Sepharose HP column was equilibrated with 20mM sodium acetate-acetic acid buffer (pH5.0). Continue to use this buffer for sufficient elution after loading the sample at a flow rate of 1.0ml / min to remove unreacted PEG aldehyde and NaCNBH 3 . Continue elution with 20 mM sodium acetate-acetic acid buffer (pH 5.0) containing 0.5 M sodium chloride at a flow rate of 1.0 ml / min, and collect the eluted peaks. The eluted peak was further purified by a Superdex200 column (2.6cm×60cm, GE Healthcare, USA). The Superdex200 column is equilibrated with 0.01M phosphate buffer (pH 7.4), and the buffer is used for elution after sample loading at a flow rate of 3.0ml / min. The PEG single-modification product (Ald5K) corresponding to the molecular weight of 5kDa and the 20kDa PEG single-modification product (Ald20K) were collected. Example 2 Preparation of PEGylated SAK whose link...
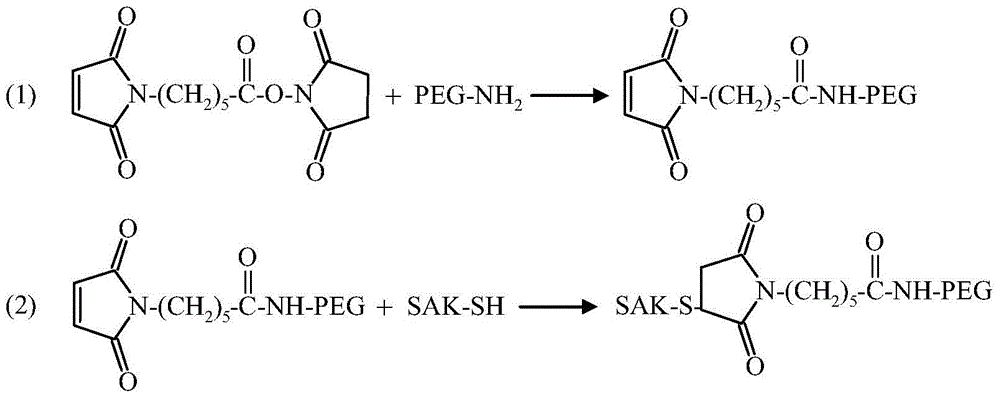
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3 Preparation of PEGylated SAK whose connecting bridge is pentyl and site-directed single modification of C-terminus
[0041] (1) De-dimerization of SAK
[0042] Since cysteine residues are introduced into the C-terminus of SAK, it is easy to generate SAK dimers through disulfide bonds during storage, so a reducing agent is used to open the disulfide bonds before PEG modification. Recombinant staphylokinase and reducing agent tris(2-carbonylethyl)phosphate hydrochloride (TCEP) were mixed at a molar ratio of 1:5, the reaction buffer system was 20mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH7.2), and reacted at room temperature for 3 hours , and then centrifuged to remove excess TCEP by membrane ultrafiltration with a molecular weight cut-off of 3 kDa.
[0043] (2) Preparation of PEG maleimide with pentyl groups
[0044] The molar ratio of PEG amines with molecular weights of 5kDa and 20kDa to EMCS is 1:2, react at room temperature for 3 hours, and dialyze through a dialysis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com