A method for increasing production of low-carbon olefins and aromatics by steam cracking of coker gasoline
A technology for coking gasoline and low-carbon olefins, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, hydrocarbon cracking to produce hydrocarbons, and purification/separation of hydrocarbons. Yield effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
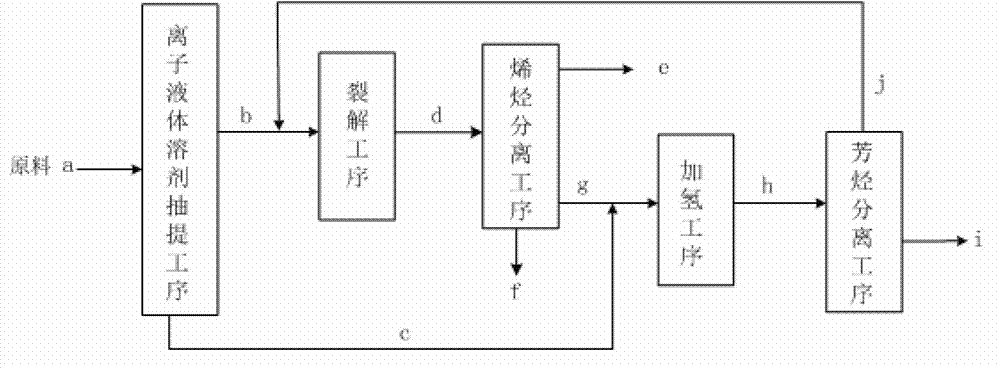
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
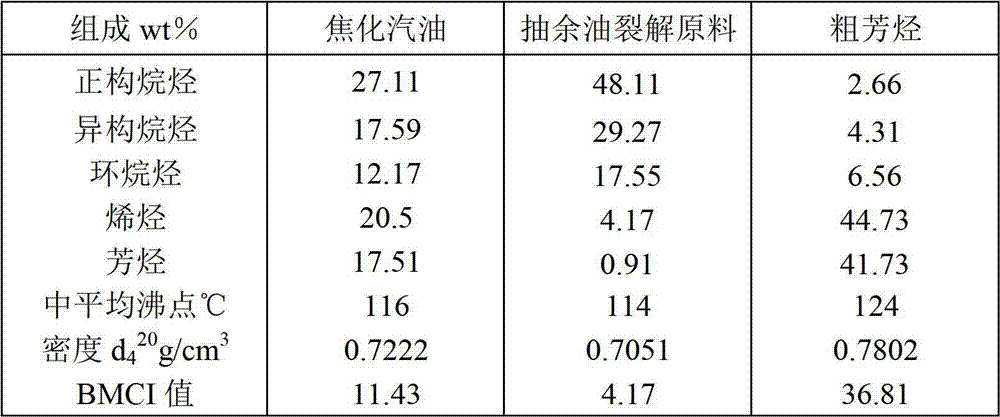
[0031] A kind of coker gasoline is used as raw material, and its raw material properties are shown in Table 1. Send to the ionic liquid solvent extraction experimental device. The extraction device is a rotating disk extraction tower with 50 actual trays and countercurrent operation. The ionic liquid solvent is 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate [BMIM][BF 4 ], and added 15mol% of AgBF 4 , the molar ratio of solvent to raw oil is 6.5, the extraction tower operates under normal pressure, and the extraction temperature is 40°C; the rich solvent flowing out from the bottom of the extraction tower is stripped by nitrogen to recover the solvent. The raffinate at the top of the tower is passed through activated carbon to absorb the solvent to obtain an aromatics-poor stream. The aromatics content of the aromatics-lean stream was 0.91 wt%, the olefins content was 4.17 wt%, the sulfur content was reduced to 634 μg / g, and the nitrogen content was reduced to 4.12 μg / g; the ...
Embodiment 2
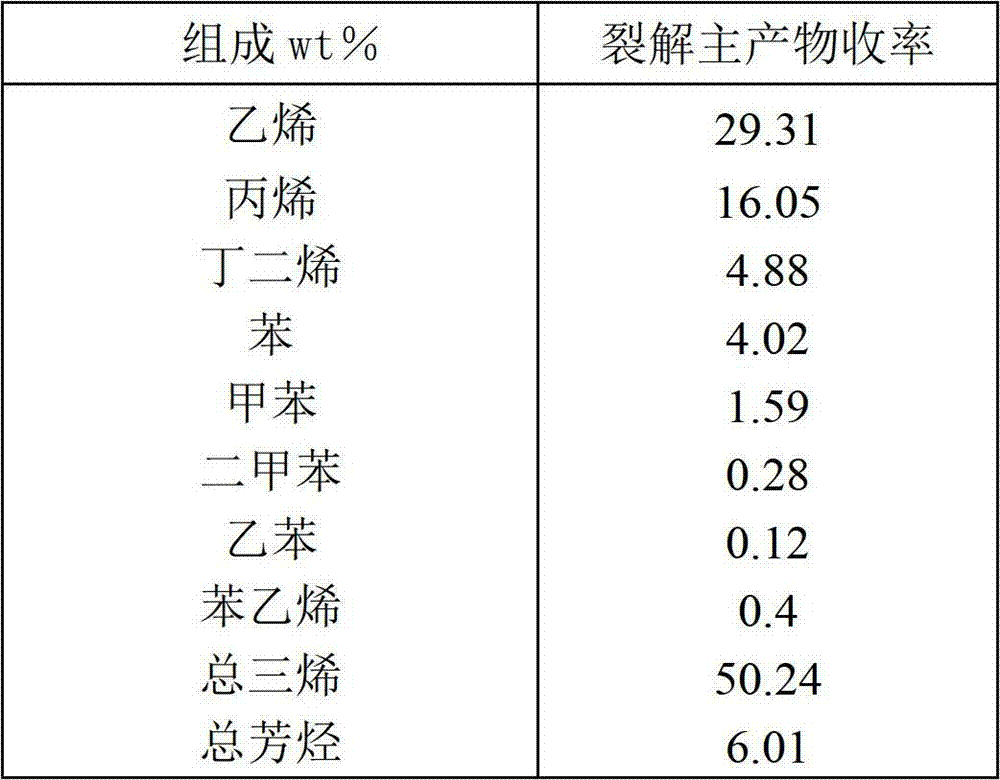
[0038] The aromatic-poor stream obtained in Example 1 is heated to 60°C and mixed with water vapor heated to 180°C at a dilution ratio of 0.5, and then introduced into the tubular furnace hydrocarbon thermal cracking reactor. The operating temperature is 835°C, and the residence time is The cleavage reaction was carried out under the condition of 0.247s to obtain rich C 2 Alkenes, C 3 Alkenes and C 4 Products of olefins, cracked fuel oils and C 6 ~C 9 The hydrocarbon mixture of aromatics, the yield of the main product of cracking is shown in Table 3.
[0039] Table 3: The cleavage yield of the main cleavage products
[0040]
Embodiment 3
[0042] The aromatic-rich stream obtained in Example 1 was subjected to hydrogenation reaction. It is carried out in two hydrogenation reactors, the first is a diene hydrogenation reactor and the second is a monoene hydrogenation reactor. In the diene hydrogenation reactor, diene is hydrogenated to generate monoolefins, the catalyst is LY-9801 (Pd-based catalyst, Pd content is 0.3wt%) the reactor inlet temperature is 60°C, the reaction pressure is 2.6Mpa, hydrogen The oil molar ratio is 0.6, the volume space velocity (fresh oil) is 3h-1, and the circulation ratio is 3.7. In the mono-olefin hydrogenation reactor, the hydrogenation catalyst is LY-9802 (Co-Mo-Ni, carrier Al2O3), the inlet temperature of the reactor is 280°C, the reaction pressure is 5.67Mpa, the molar ratio of hydrogen to oil is 4, and the volume empty The speed is 2.5h-1, and the olefins in the material are hydrogenated into alkanes. The composition of the obtained hydrogenated gasoline is shown in Table 4.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com