Lithium iron phosphate anode active material preparation method and lithium iron phosphate anode active material prepared therethrough
A cathode active material, lithium iron phosphate technology, applied in battery electrodes, structural parts, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of low compaction density, unsatisfactory specific capacity and volume energy of lithium iron phosphate cathode active material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] This example illustrates the preparation of the lithium iron phosphate positive electrode active material provided by the present invention.
[0045] Weigh 30mol ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (purity 100wt%), 30mol phosphoric acid (purity 85wt%), 0.075mol cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (Tianjin Damao Chemical Reagent Factory) and 40kg deionized water to mix To obtain a mixed solution evenly, weigh 90 mol of lithium hydroxide monohydrate (purity 100wt%) and 30 kg of deionized water and mix them evenly, then add them to the above mixed solution at 120°C, and react for 30 minutes to obtain solution A.
[0046] Weigh 30mol ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (purity 100wt%), 30mol phosphoric acid (purity 85wt%), 0.075mol sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (Tianjin Kemiou Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.) and 40kg deionized water to mix Evenly, weigh 90mol of lithium hydroxide monohydrate (purity 100wt%) and 30kg of deionized water and mix evenly, then add it to the above mixed solution at 12...
Embodiment 2
[0051] This example illustrates the preparation of the lithium iron phosphate positive electrode active material provided by the present invention.
[0052] The positive electrode active material S2 was prepared by the same method as in Example 1, the different cationic surfactant was laurate quaternary ammonium salt, and the anionic surfactant was lauryl glyceryl ether carboxylate.
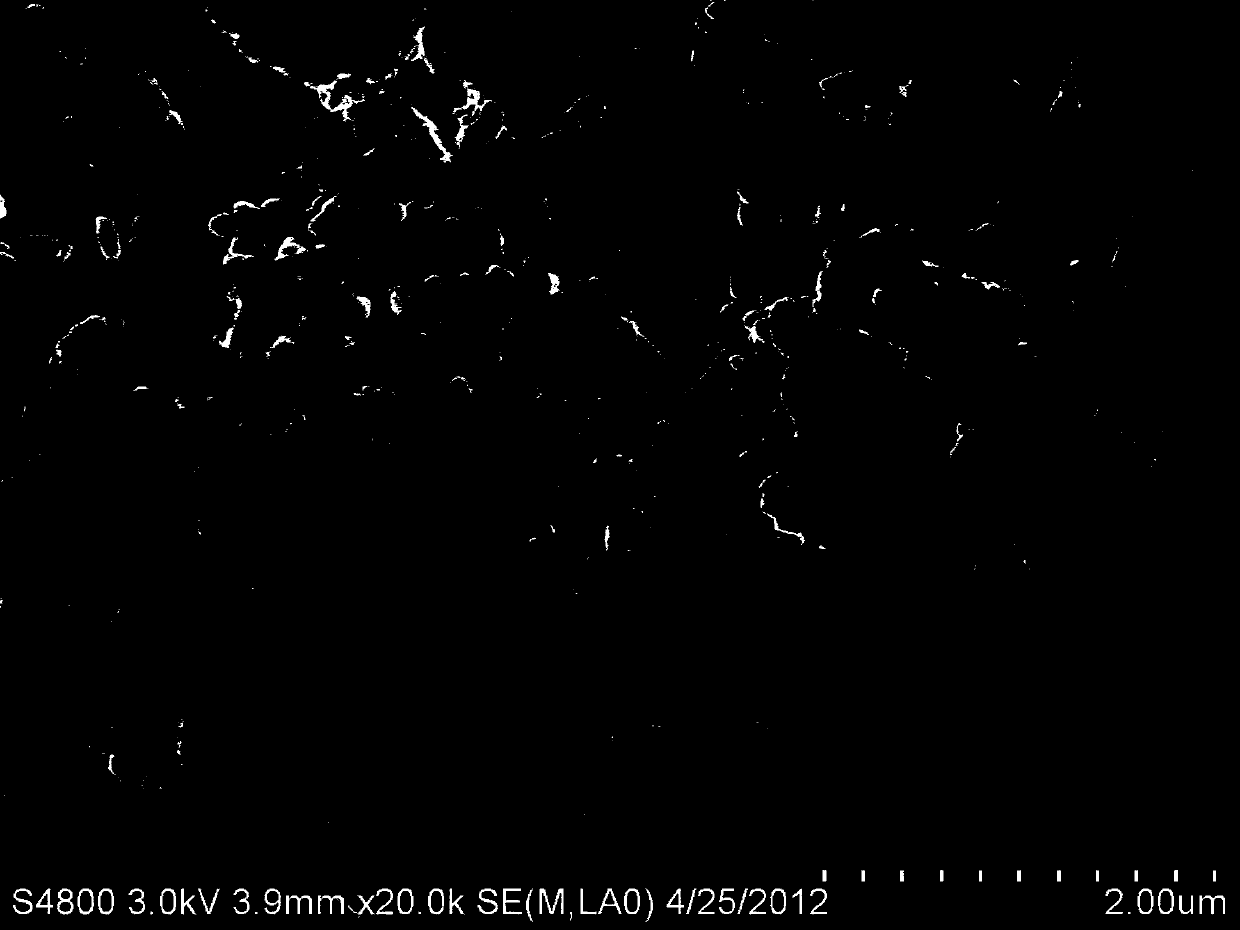
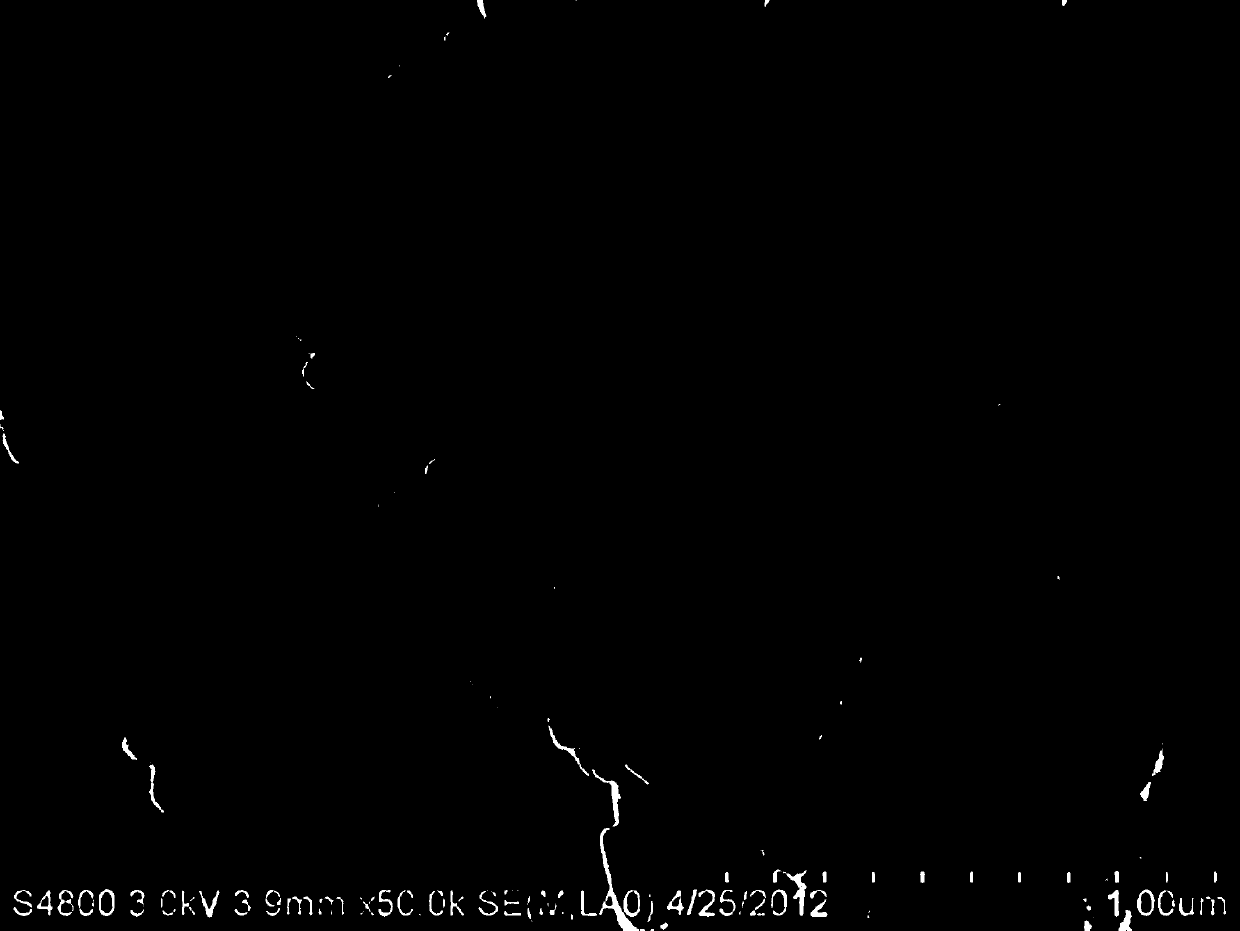
[0053] The SEM photos (magnified 2000 times and 50000 times) of the above-mentioned lithium iron phosphate composite material sample S2 obtained by using the SSX-550 scanning electron microscope produced by Shimadzu, Japan are as follows: image 3 with Figure 4 shown. from image 3 with Figure 4 It can be seen from the SEM photo that there is obvious agglomeration phenomenon between the particles, and the secondary particles are obvious. Due to the obvious reason for the agglomeration, and the close contact between the particles, the gap between the primary particles becomes smaller and less...
Embodiment 3
[0055] This example illustrates the preparation of the lithium iron phosphate positive electrode active material provided by the present invention.
[0056] Weigh 30mol ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (purity 100wt%), 30mol phosphoric acid (purity 85wt%), 0.075mol cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (Tianjin Damao Chemical Reagent Factory) and 40kg deionized water to mix To obtain a mixed solution evenly, weigh 90 mol of lithium hydroxide monohydrate (purity 100wt%) and 30 kg of deionized water and mix them uniformly, then add them to the above mixed solution at 50°C, and react for 30 minutes to obtain solution A.
[0057] Weigh 30mol ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (purity 100wt%), 30mol phosphoric acid (purity 85wt%), 0.075mol sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (Tianjin Kemiou Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.) and 40kg deionized water to mix Evenly, weigh 90mol of lithium hydroxide monohydrate (purity 100wt%) and 30kg of deionized water and mix evenly, then add it to the above mixed solution at ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com