Pullulanase mutant with improved secretion efficiency and heat stability and preparation method of pullulanase mutant
A pullulanase and thermostability technology is applied in the field of pullulanase mutants and their preparation, and can solve the problems of low extracellular secretion efficiency and low extracellular secretion efficiency of recombinant pullulanase.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
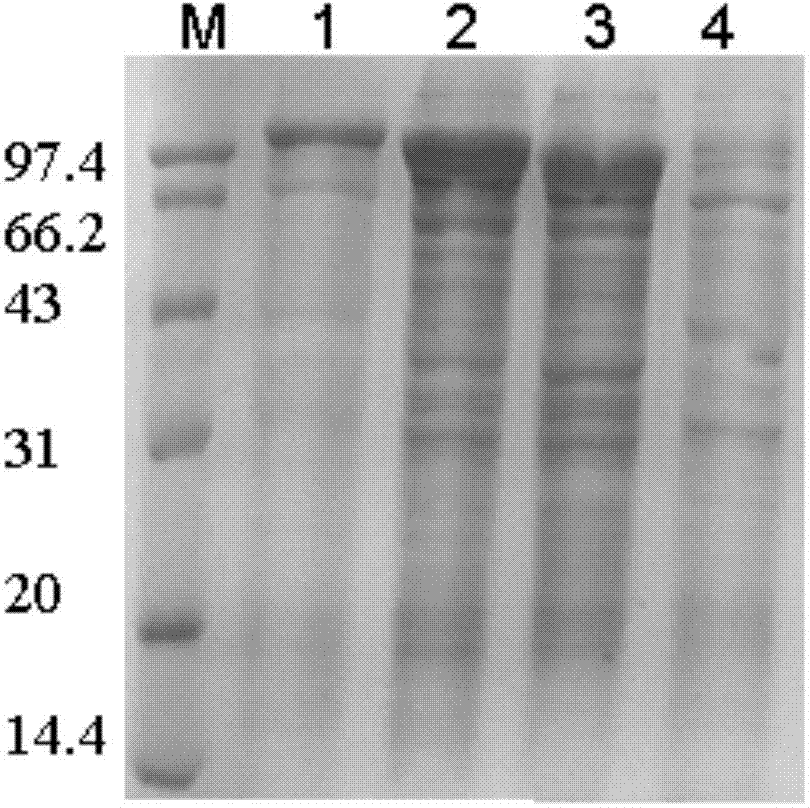
[0025] Example 1: Preparation of N-terminal truncation mutants of natural pullulanase
[0026] (1) Construction of N-terminal truncation mutants of natural pullulanase
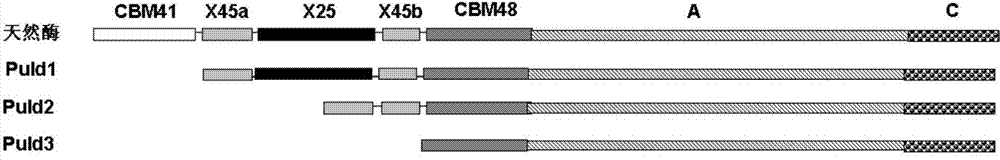
[0027] Two N-terminal domain deletion mutants Puld1 and Puld2 of pullulanase derived from B.deramificans:
[0028] Based on the comparison and analysis of pullulanase sequences from different sources, the structure of the pullulanase protein from Bacillus demycotina was simulated and analyzed, and it was found that the pullulanase from Bacillus demycotina has six structural domains: CBM41, X25, X45, CBM48, A and C. Among them, the CBM41, X25 and X45 domains at the N-terminus of the protein are connected by a flexible linker, which has strong swingability; CBM41 belongs to the carbohydrate binding domain 41 family and has the function of binding to starch substrates, while the X25 and X45 domains Function unknown. However, the three structural domains of CBM48, A and C, are connected together in a very tight...
Embodiment 2
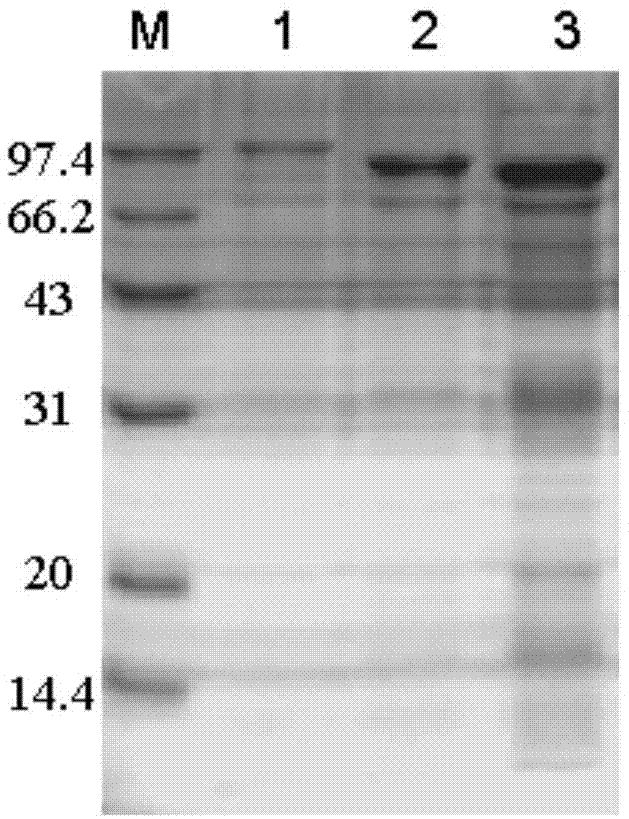
[0050] Example 2: Preparation of stacking mutants.
[0051] (1) Construction of superposition mutants
[0052] Two N-terminal domain deletion mutants D437H / D503Y / d1 and D437H / D503Y / d2 derived from the pullulanase double mutant D437H / D503Y of B.deramificans:
[0053] One domain of CBM41 at the N-terminus of the pullulanase double mutant D437H / D503Y was deleted and named as D437H / D503Y / d1; two domains of CBM41 and X25 at the N-terminus of the pullulanase double mutant D437H / D503Y were deleted and named as For D437H / D503Y / d2.
[0054] Preparation method of two N-terminal domain deletion mutants D437H / D503Y / d1 and D437H / D503Y / d2, the natural pullulanase coding gene of B.deramificans is replaced by the coding gene of pullulanase double mutant D437H / D503Y , other methods are the same as those of the N-terminal truncation mutant of natural pullulanase.
[0055] Preparation of mutants D437H / D503Y / d1 and D437H / D503Y / d2 encoding genes: Utilize rapid PCR technology, using expression v...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3: This example illustrates an enzyme activity assay.
[0071] 1) Enzyme activity assay method
[0072] The enzyme activity of pullulanase was determined by 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS method). Under certain conditions, pullulanase catalyzes the hydrolysis of pullulan sugar to generate reducing sugar, and 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid is reduced to a brownish-red amino complex after being heated together with the reducing sugar solution. The depth of its color within the range is proportional to the amount of reducing sugar, so the colorimetry can be performed at a wavelength of 540nm to calculate the enzyme activity. Definition of enzyme activity unit: Under the above conditions, the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the production of 1 μmol of glucose per minute is regarded as an activity unit.
[0073] Enzyme activity assay steps:
[0074] A. Preheating: Take 2ml of 1.5% pullulan solution (50mM pH4.5 acetic acid buffer) in a test tube, put it in a 60°C water ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com