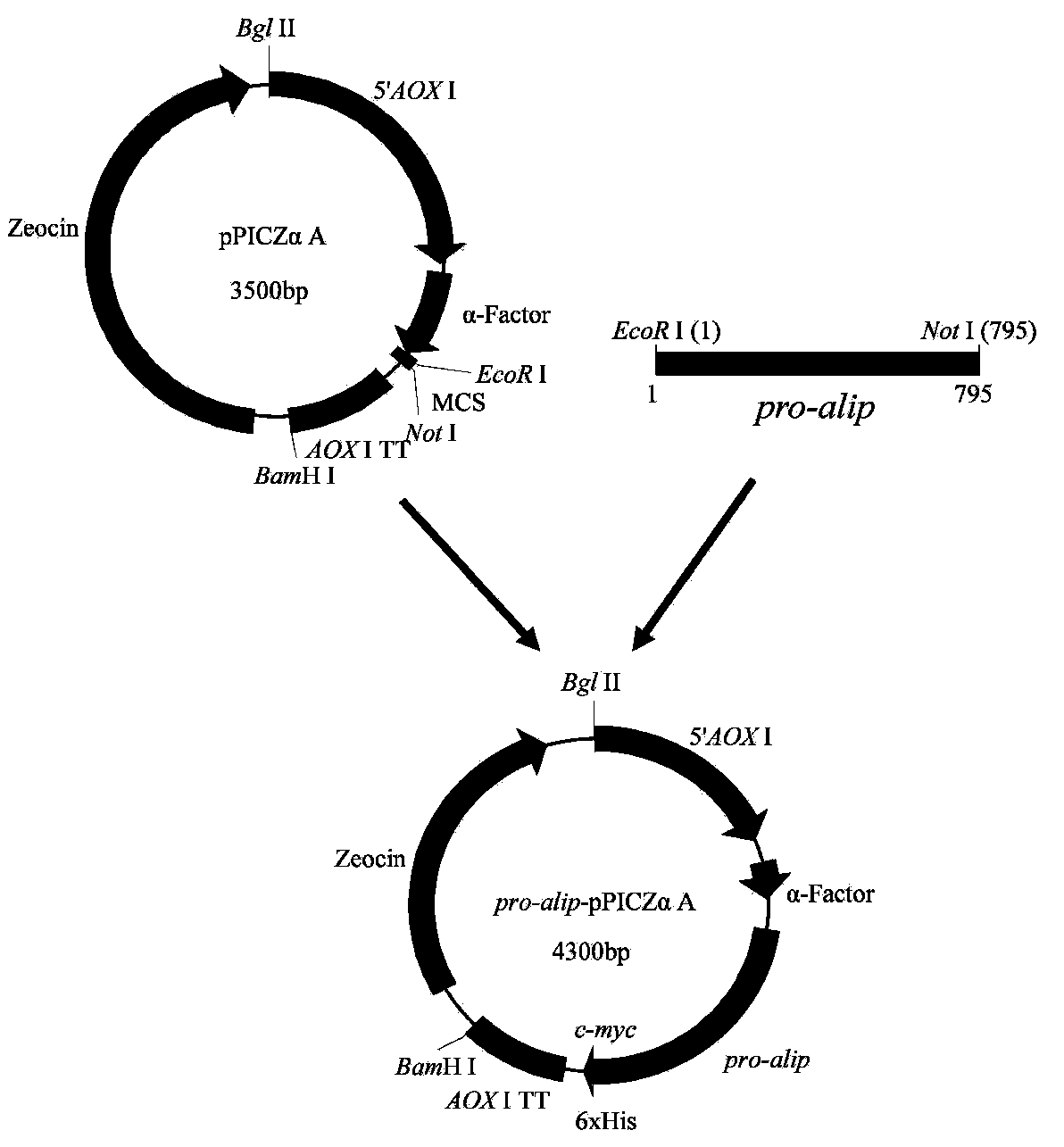
A Pichia pastoris for highly efficient heterologous expression of white Penicillium cyclopium lipase and an enzyme production medium
An arc penicillium and lipase technology, applied in the directions of enzymes, enzymes, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of expensive medium for enzyme-producing strains, limited industrial application, low enzyme activity level, etc. Catalytic reaction temperature range and the effect of improving expression efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The preparation of embodiment 1 Penicillium arcuum cDNA
[0031] 1.1 Extraction of total RNA from Penicillium albicans
[0032] (1) Take an appropriate amount of Penicillium albicans mycelia, blot dry with filter paper, grind with liquid nitrogen, add 1mL Trizol reagent (Invitrogen), oscillate for 1min, and let stand at room temperature for 5min;
[0033] (2) Add 0.2mL chloroform, shake for 15s, and let stand for 3-5min;
[0034] (3) 4°C, 12000rpm, 15min;
[0035] (4) Aspirate the supernatant, add an equal volume of isopropanol, and precipitate at -20°C for 30 minutes;
[0036] (5) 4°C, 12000rpm, 15min;
[0037] (6) Pour off the supernatant, wash the precipitate with 1mL 75% DEPC-ethanol, 12000rpm, 4°C, 5min;
[0038] (7) Repeat step (6) once;
[0039] (8) Pour off the supernatant and centrifuge at 12000rpm, 4°C for 2min. Use the tip of the pipette to absorb the residual liquid, and dry it in ice for 10 minutes; dry for 10 minutes;
[0040] (9) Add appropriate am...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2 The primer design of the Penicillium albus lipase gene pro-alip containing leader peptide
[0048] 2.1 Primer design
[0049] According to the sequence of the alip gene in GenBank (GenBank accession number is AF274320.1), the following pair of primers were designed and synthesized:
[0050] pro-alip-F (P1): 5'-CCCG GAATTC GCACCTATTTTGGAGTCGA-3'
[0051] pro-alip-R (P2): 5'-ATAAT GCGGCCGC GCTCAGATAGCCAC-3'
[0052] EcoRI and NotI restriction sites are designed at both ends of P1 and P2 respectively (see the italicized and underlined part in the above sequence)
[0053] 2.2 PCR amplification of Penicillium albus lipase pro-alip containing leader peptide
[0054] Using P1 and P2 primers, using Penicillium alba (ZhangHM, WuMC, GuoJ, et al. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Complete Gene Encodingan Alkaline Lipase from Penicilliumcyclopium. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology. 2011, 47(6): 586-593.) cDNA as a template, the PCR reaction system is:
[0055] ...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3 Secretion and expression of Penicillium albicans lipase gene pro-alip containing leader peptide in Pichia pastoris X-33
[0065] 3.1 Preparation of Pichia pastoris X-33 (purchased by Invitrogen) electroporation competent cells and their electroporation transformation
[0066] (1) Pick a fresh single colony in 5mLYPD liquid medium, and culture it at 28°C, 200rpm for 12-14h;
[0067] (2) Inoculate 0.1% inoculum into a 2L Erlenmeyer flask containing 500mL YPD medium, culture at 28°C, 200rpm for 12-14h, and make it OD 600 =1.3~1.5;
[0068] (3) Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 5 minutes at 4°C to collect cells;
[0069] (4) Wash the cells twice with 500-250 mL ice-cold sterile water;
[0070] (5) Wash the cells once with 20 mL of ice-cold 1M sorbitol solution;
[0071] (6) Resuspend the cells with 1 mL of ice-cold 1M sorbitol solution to a final volume of about 1.5 mL, and dispense 80 μL into small centrifuge tubes.
[0072] 3.2 Electric shock transformation of P...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com