Novel surface roughening method for GaN-based light emitting diode
A technology of light-emitting diodes and surface roughening, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the complexity of existing processes, the difficulty of obtaining mask materials, and the lack of commercialization, etc., and achieves low cost and easy Clean, easily repeatable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
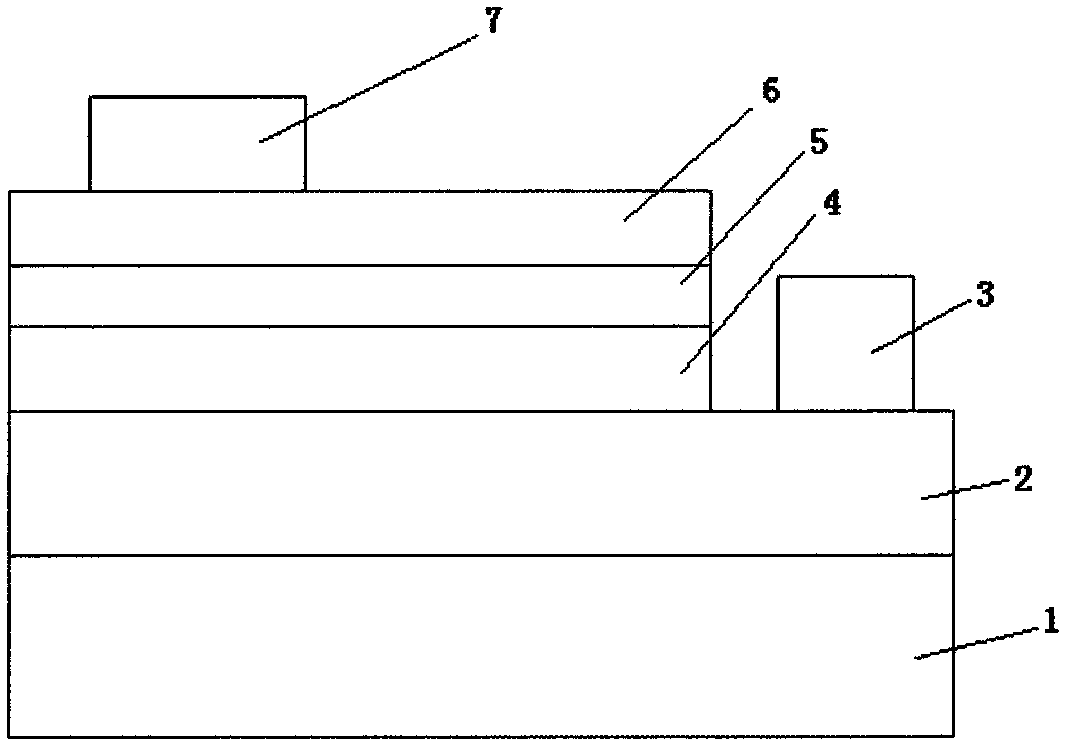
[0029] Embodiment 1, at first, on sapphire substrate 1, grow n-type semiconductor layer sequentially by MOCVD method
[0030] 2. The light emitting layer 4 and the p-type semiconductor layer 5 that control the light emitting wavelength. GaN epitaxial wafers were obtained after annealing. The above methods for forming GaN-based epitaxial wafers are well known to those skilled in the art to which the present invention belongs, and thus will not be described in detail.
[0031] A current spreading layer (transparent electrode layer ITO) 6 is vacuum evaporated on the epitaxial wafer with a thickness of 1000-6000A and an evaporation temperature of 100-700°C. Uniformly disperse a layer of SiO with a diameter of 300nm on the transparent electrode by spin coating 2 nanosphere solution. The solution is dried at a temperature of 50-500° C., followed by ICP dry etching, and the etching time is 10-500 seconds. Finally, the SiO was washed off with hydrofluoric acid solution 2 Nanosphe...
Embodiment 2
[0033] In Embodiment 2, first, an n-type semiconductor layer 2 , a light-emitting layer 4 for controlling the light-emitting wavelength, and a p-type semiconductor layer 5 are sequentially grown on a silicon substrate 1 by MOCVD method. GaN epitaxial wafers were obtained after annealing. The above methods for forming GaN-based epitaxial wafers are well known to those skilled in the art to which the present invention belongs, and thus will not be described in detail.
[0034] A current spreading layer (transparent electrode layer) 6 is vacuum evaporated on the epitaxial wafer with a thickness of 1000-6000A and an evaporation temperature of 100-700°C. Uniformly disperse a layer of SiO with a diameter of 300nm on the transparent electrode by spin coating 2 nanosphere solution. The solution is dried at a temperature of 50-500° C., followed by ICP dry etching, and the etching time is 10-500 seconds. Finally, the SiO was washed off with hydrofluoric acid solution 2 Nanospheres f...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3, at first, on sapphire substrate 1 by MOCVD method, grow n-type semiconductor layer sequentially
[0037] 2. The light emitting layer 4 and the p-type semiconductor layer 5 that control the light emitting wavelength. GaN epitaxial wafers were obtained after annealing. The above methods for forming GaN-based epitaxial wafers are well known to those skilled in the art to which the present invention belongs, and thus will not be described in detail.
[0038] A current spreading layer (transparent electrode layer) 6 is vacuum evaporated on the epitaxial wafer with a thickness of 1000-6000A and an evaporation temperature of 100-700°C. Uniformly disperse a layer of SiO with a diameter of 600 nm on the transparent electrode by spin coating 2 nanosphere solution. The solution is dried at a temperature of 50-500° C., followed by ICP dry etching, and the etching time is 10-500 seconds. Finally, the SiO was washed off with hydrofluoric acid solution 2 Nanospheres...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com