Method for improving color and flavor of recycled vegetable protein
A vegetable protein and color technology, applied in the field of improving the color and flavor of recovered vegetable protein, can solve the problems of limiting the application of soy protein, poor color and flavor, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
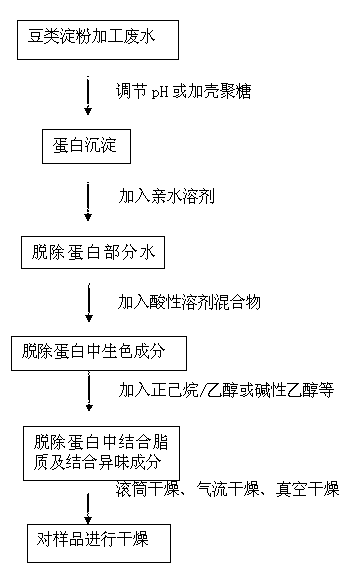
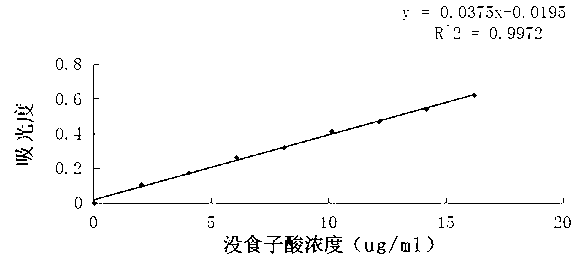
[0053] Take a certain amount of pea starch processing wastewater, adjust its pH to 5.0, centrifuge at 3000r / min for 20min, discard the supernatant, and obtain a protein precipitate. Its solid content was measured to be 31.2%, and the protein content in the solid was 66.2% (dry basis). Take a certain amount of the above-mentioned precipitated protein and add ethanol with a concentration of 95% at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:15, stir at room temperature for 1 hour, filter, and remove part of the water. The moisture content of the obtained protein powder was 14.8%, which was greatly reduced compared with the precipitated protein moisture. The protein content and lipid content in the dry matter were 68.15% and 8.97%, respectively. Take a certain amount of protein that has been partially dehydrated and add n-hexane-95% ethanol (9:1) mixed solvent at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:5, containing 1% HCl in mass concentration, extract at 45°C for 1 hour, and filter. The residual polyph...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Take a certain amount of pea starch processing wastewater, add chitosan according to 10% of the solid content in the processing wastewater, centrifuge at 3000r / min for 20min, discard the supernatant, and obtain protein precipitation. Its solid content was measured to be 12.8%, and the dry basis protein content in the solid was 55.21%. Take a certain amount of the above-mentioned precipitated protein and add n-propanol at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:15, stir at room temperature for 1 hour, filter, and remove part of the water. The moisture content of the obtained protein powder was 15.0%, the protein content was 59.35%, and the lipid content was 9.86%. Take a certain amount of protein after removing part of the water, add 80% ethanol at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:20, and add HCl with a mass concentration of 1%, extract at 50°C for 2.5h, and filter. The sample was evaporated to dryness at room temperature. The residual polyphenol content in the filter residue was mea...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Take a certain amount of pea starch processing wastewater, adjust its pH to 4.8, centrifuge at 3000 r / min for 20 minutes, discard the supernatant, and obtain protein precipitation. The solids content was measured to be 28.15%, and the protein content in the solids was 62.34% (dry basis). Take a certain amount of the above-mentioned precipitated protein and add ethanol with a concentration of 95% at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:15, stir at room temperature for 1 hour, filter, and remove part of the water. The moisture content of the obtained protein powder was 15.24%, which was greatly reduced compared with the precipitated protein moisture. The protein content and lipid content in the dry matter were 65.15% and 6.98%, respectively. Take a certain amount of protein after removing part of the water, add 80% ethanol at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:20, and add HCl with a mass concentration of 1%, extract at 50°C for 2.5h, and filter. The residual polyphenol content in the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com