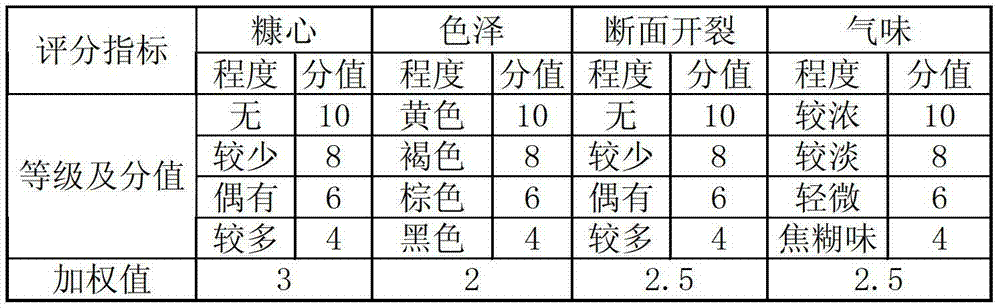
Processing method of rhubarb
A processing method and rhubarb technology, applied in the field of processing, can solve the problems of inability to provide a drying method for palm leaf rhubarb, inadequate consideration, etc., and achieve the effects of energy saving, simple method and high drying efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1 The detailed drying method of the present invention is investigated
[0034] Remove the fibrous roots of the fresh rhubarb palmate or rhubarb tangut, scrape off the rough skin, cut into sections of about 3 cm, and dry them as follows:
[0035] a. Dry in the shade String the herbs together and place them in a ventilated and cool place to dry.
[0036] b. Sun-dried The medicinal materials are dried in the sun.
[0037] c. Drying The medicinal materials are placed in an electric blast drying oven and dried at 45°C.
[0038] d. Microwave drying Use household microwave ovens to dry medicinal materials, take them out every 5 minutes, put them at room temperature, and weigh them.
[0039] e. Far-infrared drying Use a far-infrared radiation drying oven (45°C, radiation distance 25cm) to dry the medicinal materials.
[0040] f. Drying under reduced pressure Use a vacuum drying oven (vacuum degree -0.09MPa, 45°C) to dry the medicinal materials.
[0041] g. Freeze...
Embodiment 2
[0100] The comparison of the rhubarb of embodiment 2 present invention and other technology preparations
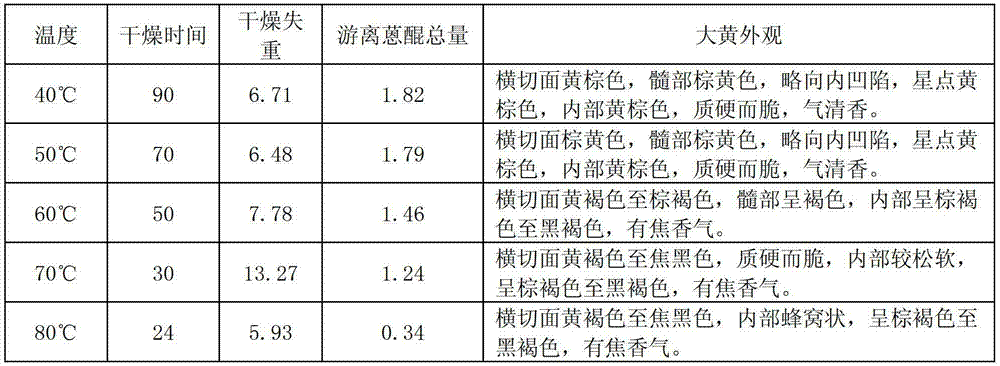
[0101] By comparing the results in Table 9, the processing method of rhubarb of the present invention, compared with the processing method of rhubarb reported at present, the processing method of rhubarb of the present invention is time-saving, energy-saving, high in drying efficiency, low in cost, simple in method, standardized and easy to implement , The medicinal properties and chemical composition content meet the pharmacopoeia standards.
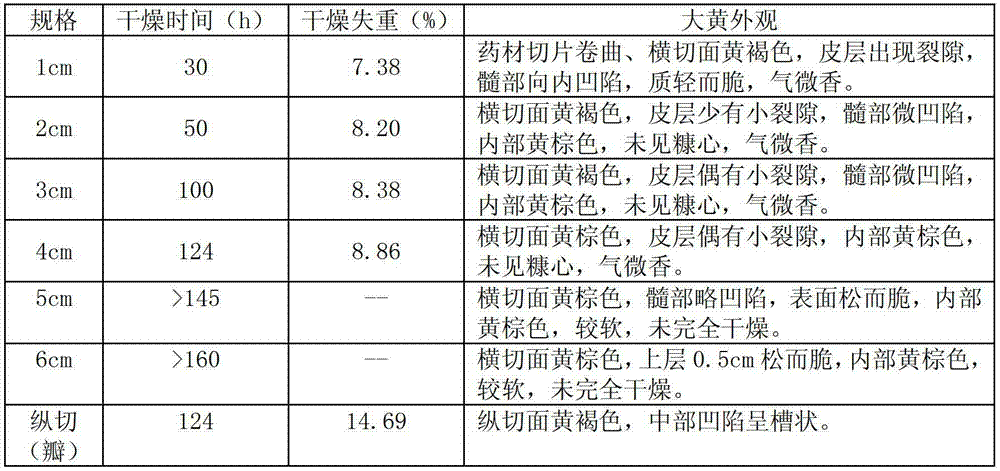
[0102] Table 2 Appearance of rhubarb after drying by different drying methods
[0103]
[0104] Table 9 The present invention and the comparison of the rhubarb prepared by other techniques
[0105]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com