Method for producing ADC (azodicarbonamide) foaming agent by chlorine dioxide biurea
A technology of ADC foaming agent and biuret is applied in the field of producing ADC foaming agent by oxidizing biuret with chlorine gas, which can solve the problems of high reaction control requirements, wide product particle size distribution, low gas generation, etc., so as to reduce peroxide Effects of side reactions, reduction of particle size distribution width, and reduction of COD content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Weigh 150 g of biurea, beat it into a biurea slurry with a solid content of 30% with industrial water, then add 1.5 g of sodium bromide therein, and stir to dissolve it. Pour the slurry into a 1L covered glass reactor with a built-in coil. Coolant is passed through the coil to control the temperature of the reaction system at 35°C. The exhaust port on the top of the cover is connected to the exhaust fan to maintain a slight negative pressure in the reactor. Chlorine gas is fed into the bottom of the reactor after being vaporized by the liquid chlorine cylinder, and the speed of chlorine gas feeding is based on maintaining a slight negative pressure in the reactor. Until the reaction is finished, the slurry is filtered, washed, and dried to analyze the gas generation and particle size.
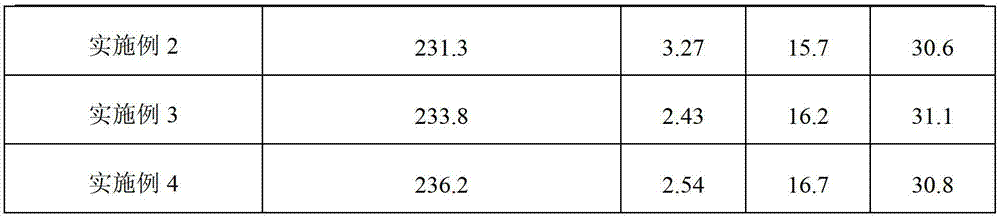
Embodiment 2
[0019] The filtered mother liquor of Example 1 is mixed with a certain amount of industrial water to form a dilute hydrochloric acid solution with an HCl content of 5%. Weigh 150 g of the same batch of biurea, and then beat the biurea slurry with 5% dilute hydrochloric acid solution, then add 1 g of sodium bromide and 0.5 g of ferric chloride, and stir to dissolve it. Pour the slurry into a 1L covered glass reactor with a built-in coil. Coolant is passed through the coil to control the temperature of the reaction system at 35°C. The exhaust port on the top of the cover is connected to the exhaust fan to maintain a slight negative pressure in the reactor. Chlorine gas is fed into the bottom of the reactor after being vaporized by the liquid chlorine cylinder, and the speed of chlorine gas feeding is based on maintaining a slight negative pressure in the reactor. Until the reaction is finished, the slurry is filtered, washed, and dried to analyze the gas generation and particle...
Embodiment 3
[0021] The filtered mother liquor of Example 1 is mixed with a certain amount of industrial water to form a dilute hydrochloric acid solution with an HCl content of 5%. Weigh 150g of the same batch of biurea, and then use 5% dilute hydrochloric acid solution to form a biurea slurry, then add 0.5g of sodium bromide and 1g of ferric chloride, and stir to dissolve it. Pour the slurry into a glass reactor with a cover and a coil with a volume of 1 L, and a refrigerant is passed through the coil to control the temperature of the reaction system at 40°C. The exhaust port on the top of the cover is connected to the exhaust fan to maintain a slight negative pressure in the reactor. Chlorine gas is fed into the bottom of the reactor after being vaporized by the liquid chlorine cylinder, and the speed of chlorine gas feeding is based on maintaining a slight negative pressure in the reactor. Until the reaction is finished, the slurry is filtered, washed, and dried to analyze the gas gen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com