Method for preparing nano-pore ferric phosphate, nano-pore ferric phosphate and application
A technology of iron phosphate and nanopores, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as difficult recovery of surfactants, complex process flow, strict reaction conditions, etc., and achieve excellent electrochemical performance, process Simple, material-reactive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
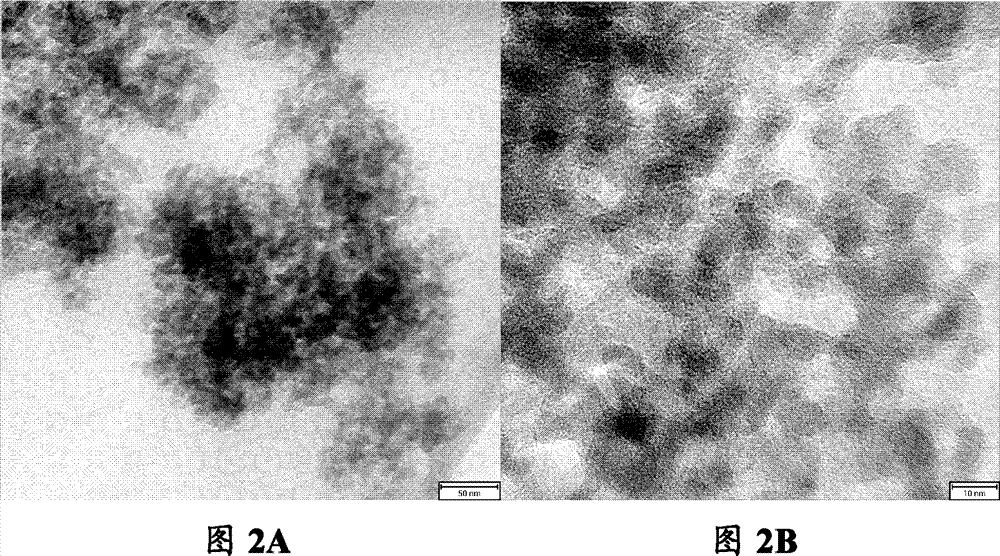
[0042] This example is used to illustrate the method for preparing nanoporous iron phosphate of the present invention.
[0043] 1) Preparation of iron source solution: weigh 1g Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O was dissolved in 8 mL of ethanol to obtain an iron source solution, in which the concentration of iron was 0.29 mol / L.
[0044] 2) Preparation of extractant: 5g of N1923 (purchased from Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences) was weighed and mixed with 50mL of n-heptane to prepare extractant, wherein N1923 accounted for 10wt% of the extractant.
[0045] 3) Preparation of phosphorus source solution: mix the extractant with 3.1mol / L phosphoric acid aqueous solution to extraction equilibrium, and then separate the organic phase containing phosphoric acid after standing still, which is the phosphorus source solution, wherein the concentration of phosphorus element is 0.3mol / L L.
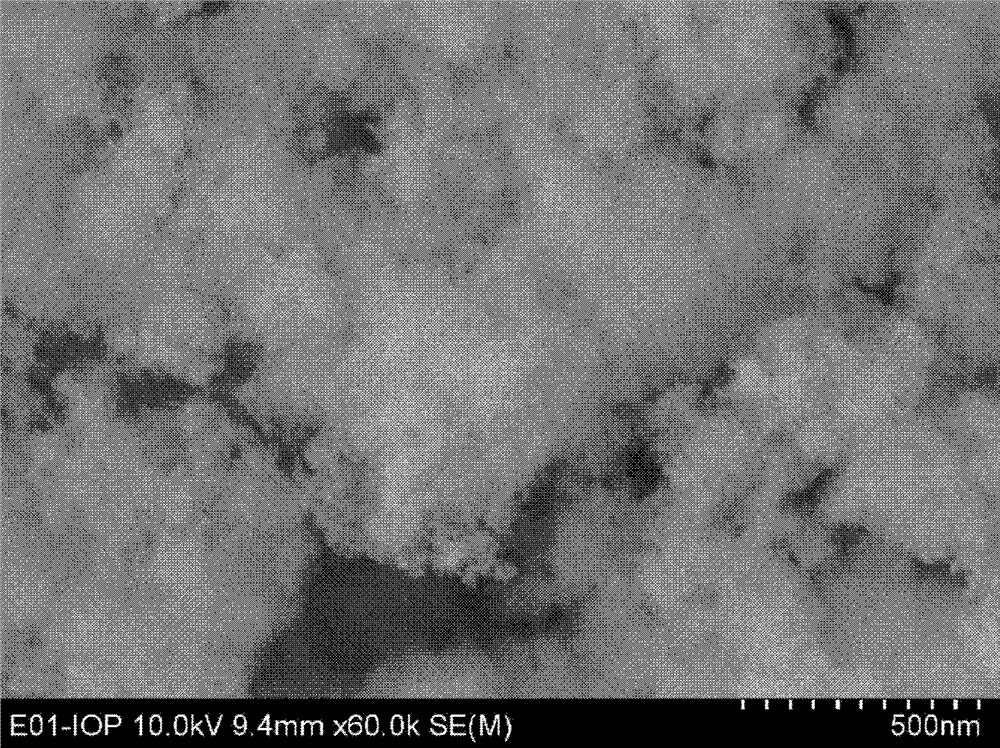
[0046] 4) Preparation of nanoporous iron phosphate: according to the molar ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] This example is used to illustrate the method for preparing nanoporous iron phosphate of the present invention.
[0053] The steps of preparing nanoporous iron phosphate in this embodiment are basically the same as in Example 1, the only difference being:
[0054] In step 1), weigh 0.4g Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O was dissolved in 10 mL of ethanol, and the concentration of iron element in the obtained iron source solution was 0.1 mol / L. In step 3), the concentration of phosphoric acid solution is 1.7mol / L; the concentration of phosphorus element in the obtained phosphorus source solution is 0.28mol / L. In step 4), the iron source solution and the phosphorus source solution are respectively measured according to the molar ratio of the iron element and the phosphorus element being 1:1; the obtained precipitate is washed with ethanol.
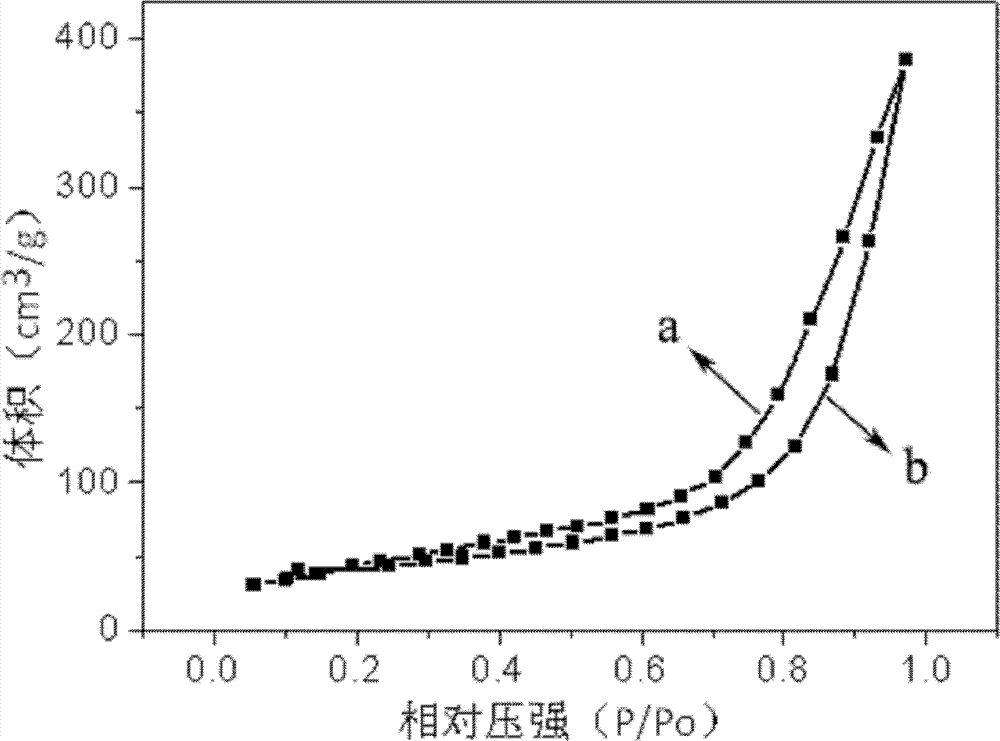
[0055] Measured using the same assay method as in Example 1, the average pore diameter of the nanoporous iron phosphate of the present embodimen...
Embodiment 3
[0058] This example is used to illustrate the method for preparing nanoporous iron phosphate of the present invention.
[0059] The steps of preparing nanoporous iron phosphate in this embodiment are basically the same as in Example 1, the only difference being:
[0060] In step 1), weigh 1g FeCl 3 9H 2 O was dissolved in 10 mL of ethanol, and the iron element concentration in the obtained iron source solution was 0.37 mol / L. In step 2), 1.25g of N235 (purchased from sigma company) was weighed and mixed with 25mL of benzene to prepare an extractant, and N235 accounted for 5wt% of the extractant. In step 3), the concentration of phosphoric acid solution is 1.5mol / L; the concentration of phosphorus element in the obtained phosphorus source solution is 0.18mol / L. In step 4), the iron source solution and the phosphorus source solution are respectively measured according to the molar ratio of the iron element and the phosphorus element being 1:1; the obtained precipitate is wash...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com